
Complete the following reaction.
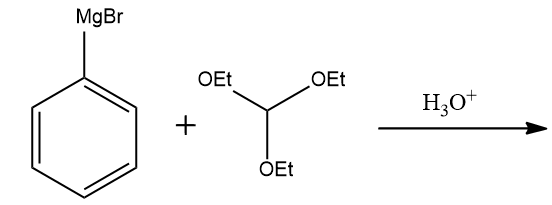

Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint :This is a Grignard reaction. The Grignard Reaction is the addition of an organomagnesium halide (Grignard reagent) to a ketone or aldehyde, to form a tertiary or secondary alcohol, respectively. The reaction with formaldehyde leads to a primary alcohol.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The Grignard reaction is an organometallic synthetic reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (Grignard reagent) is added to a carbonyl gathering in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is significant for the development of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction of a natural halide with magnesium isn't a Grignard reaction, however gives a Grignard reagent.
Additional Information:
Grignard reagents are made through the expansion of magnesium metal to alkyl or alkenyl halides. The halide can be $ Cl, $ $ Br $ , $ I, $ (not $ F $ ) . It's marginally simpler to make Grignards from the iodides and bromides, nonetheless. Note what's going on here – the magnesium is "embeddings" itself between the carbon and the halide. This halide the " $ X $ " alluded to when we allude to Grignard reagents as " $ RMgX $ ".They're very acceptable nucleophiles, responding with electrophiles like carbonyl mixtures (aldehydes, ketones, esters, carbon dioxide, and so on) and epoxides. They're additionally solid bases and will respond with acidic hydrogens (like alcohols, water, and carboxylic acids).
Note :
Grignard reagents are utilized artificially to frame new carbon–carbon bonds. A Grignard reagent has a polar carbon–magnesium bond in which the carbon molecule has an incomplete negative charge and the metal a fractional positive charge.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The Grignard reaction is an organometallic synthetic reaction in which alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (Grignard reagent) is added to a carbonyl gathering in an aldehyde or ketone. This reaction is significant for the development of carbon–carbon bonds. The reaction of a natural halide with magnesium isn't a Grignard reaction, however gives a Grignard reagent.

Additional Information:
Grignard reagents are made through the expansion of magnesium metal to alkyl or alkenyl halides. The halide can be $ Cl, $ $ Br $ , $ I, $ (not $ F $ ) . It's marginally simpler to make Grignards from the iodides and bromides, nonetheless. Note what's going on here – the magnesium is "embeddings" itself between the carbon and the halide. This halide the " $ X $ " alluded to when we allude to Grignard reagents as " $ RMgX $ ".They're very acceptable nucleophiles, responding with electrophiles like carbonyl mixtures (aldehydes, ketones, esters, carbon dioxide, and so on) and epoxides. They're additionally solid bases and will respond with acidic hydrogens (like alcohols, water, and carboxylic acids).
Note :
Grignard reagents are utilized artificially to frame new carbon–carbon bonds. A Grignard reagent has a polar carbon–magnesium bond in which the carbon molecule has an incomplete negative charge and the metal a fractional positive charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




