
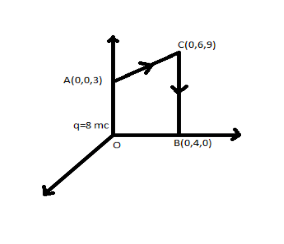
Calculate the work done in taking a charge $ - 2 \times {10^{ - 9}}C$ from A and B via C (in diagram).
A. 0.2 J
B. 1.2 J
C. 2.2 J
D. Zero

Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint:To calculate the work done in moving the charge from point A to point B firstly, calculate the potential at the point A and B respectively. Then, calculate the potential difference between the point A and B created due to charge present at the origin. At last multiply the calculated potential difference with the charge moving from point A and B.
Formula used: $W = {q_1}\left( {{V_B} - {V_A}} \right)$
Here, $q_1$ is the charge which moves. ${V_B}$ is the potential at B due to q and ${V_A}$ is the potential at A due to q.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we want to find out the work done in bringing a charge $ - 2 \times {10^{ - 9}}C$ from A to B via C. But as we know that moving a charge in electric field is independent of path chosen to move the charge in electric field and depends only on electric potential difference between them.
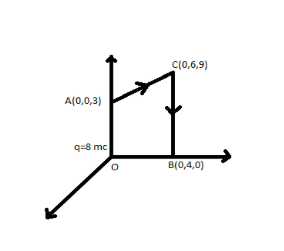
If charge directly moves from A to B then the result will be the same.
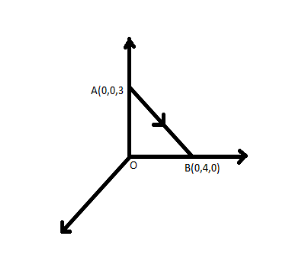
The only thing we need to do is to find the potential at A due to charge \[q = 8mc\] at the origin i.e., .
${r_{OA}} = $ Distance between origin and the point \[A = 3cm\].
Similarly, potential at B due to charge, \[q = 8mc\]at the origin
${r_{OB}} = $ Distance between origin and the point \[B = 4cm\].
$\therefore work\;done = {q_1}\left( {{V_B} - {V_A}} \right)$
Now, by substituting the values we get,
Now, putting all the values,
${q_1} = - 2 \times {10^{ - 9}}C$
$q = 8mc = 8 \times {10^{ - 3}}C$
${r_{OB}} = 4cm$
${r_{OA}} = 3cm$
$W = - 2 \times {10^{ - 9}} \times 8 \times {10^{ - 3}} \times 9 \times {10^9}\left( {\dfrac{1}{4} - \dfrac{1}{3}} \right)$
\[\;\therefore W = 1.27{\text{ }}J\;\] (Answer)
Note:Charge which is moving from one point to another is always multiplied to potential difference between the points, whatever the path of charge will be.
Formula used: $W = {q_1}\left( {{V_B} - {V_A}} \right)$
Here, $q_1$ is the charge which moves. ${V_B}$ is the potential at B due to q and ${V_A}$ is the potential at A due to q.
Complete step by step answer:
In this question, we want to find out the work done in bringing a charge $ - 2 \times {10^{ - 9}}C$ from A to B via C. But as we know that moving a charge in electric field is independent of path chosen to move the charge in electric field and depends only on electric potential difference between them.

If charge directly moves from A to B then the result will be the same.

The only thing we need to do is to find the potential at A due to charge \[q = 8mc\] at the origin i.e., .
${r_{OA}} = $ Distance between origin and the point \[A = 3cm\].
Similarly, potential at B due to charge, \[q = 8mc\]at the origin
${r_{OB}} = $ Distance between origin and the point \[B = 4cm\].
$\therefore work\;done = {q_1}\left( {{V_B} - {V_A}} \right)$
Now, by substituting the values we get,
Now, putting all the values,
${q_1} = - 2 \times {10^{ - 9}}C$
$q = 8mc = 8 \times {10^{ - 3}}C$
${r_{OB}} = 4cm$
${r_{OA}} = 3cm$
$W = - 2 \times {10^{ - 9}} \times 8 \times {10^{ - 3}} \times 9 \times {10^9}\left( {\dfrac{1}{4} - \dfrac{1}{3}} \right)$
\[\;\therefore W = 1.27{\text{ }}J\;\] (Answer)
Note:Charge which is moving from one point to another is always multiplied to potential difference between the points, whatever the path of charge will be.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




