
Benzaldehyde gives a positive test with which of the following?
a.) Tollen's reagent
b.) Fehling solution
c.) Benedict's solution
d.) All of these
Answer
522.5k+ views
Hint: Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen bonded to the carbonyl carbon. And the other attachment may be to a carbon or a hydrogen. In all of the cases, the carbon(s) which are attached to the carbonyl group may be aliphatic i.e. not part of an aromatic ring or aromatic i.e. part of an aromatic ring.
Complete step by step solution:
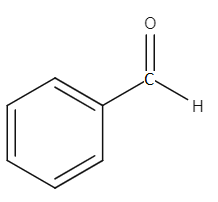
Benzaldehyde is an aromatic aldehyde and the carbonyl group is an electron withdrawing group. Therefore, the carbonyl group pulls the electron from the electron-rich benzene ring. Due to this reason, the polarity of the C−H bond in the carbonyl group is reduced as the C−H bond now has a higher electron density. Thus, the C−H bond becomes stronger as polarity of a bond becomes less, the bond becomes stronger. The structure of benzaldehyde is given below.
Now, let’s see our options.
Tollens reagent (\[{{(Ag(N{{H}_{3}}))}^{+2}}\]) is also a mild oxidizing agent. The carbonyl group present in benzaldehyde is oxidized in the reaction and the \[A{{g}^{+}}\] is reduced. The resultant of the reaction is an oxidized aldehyde, which is now a radical cation. This reacts with hydroxide to form a tetrahedral intermediate. A gem-diol like intermediate is formed via a hydrogen shift, which then goes on to form the final carboxylate anion. Hence, it tests positive for Tollens reagent.
Fehling's reagent uses a \[C{{u}^{2+}}\] ion which is complexed with two tartrate ions. Aldehydes such as benzaldehyde, lack alpha hydrogens and cannot form an enolate and thus do not give a positive test with Fehling’s solution which is comparatively a weaker oxidizing agent than Tollen's reagent, under usual conditions. Therefore, it tests negative.
Benedict’s is also a comparatively weaker oxidizing agent than Tollen's reagent. It is similar to the Tollen’s test but it uses cupric salts (\[C{{u}^{2+}}\]) as the oxidizing reagent. These get reduced to copper I salts (\[C{{u}^{+}}\]) as the aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid. But aliphatic aldehydes and reducing sugars only will give positive tests and benzaldehyde is aromatic. Therefore, it tests negative.
So, the correct option is (a).
Note: Generally, aldehydes are more reactive because primary carbocation formed in the polarizing as a result the resonance structure of an aldehyde becomes less stable and therefore more reactive.
Complete step by step solution:
Benzaldehyde is an aromatic aldehyde and the carbonyl group is an electron withdrawing group. Therefore, the carbonyl group pulls the electron from the electron-rich benzene ring. Due to this reason, the polarity of the C−H bond in the carbonyl group is reduced as the C−H bond now has a higher electron density. Thus, the C−H bond becomes stronger as polarity of a bond becomes less, the bond becomes stronger. The structure of benzaldehyde is given below.
Now, let’s see our options.
Tollens reagent (\[{{(Ag(N{{H}_{3}}))}^{+2}}\]) is also a mild oxidizing agent. The carbonyl group present in benzaldehyde is oxidized in the reaction and the \[A{{g}^{+}}\] is reduced. The resultant of the reaction is an oxidized aldehyde, which is now a radical cation. This reacts with hydroxide to form a tetrahedral intermediate. A gem-diol like intermediate is formed via a hydrogen shift, which then goes on to form the final carboxylate anion. Hence, it tests positive for Tollens reagent.
Fehling's reagent uses a \[C{{u}^{2+}}\] ion which is complexed with two tartrate ions. Aldehydes such as benzaldehyde, lack alpha hydrogens and cannot form an enolate and thus do not give a positive test with Fehling’s solution which is comparatively a weaker oxidizing agent than Tollen's reagent, under usual conditions. Therefore, it tests negative.

Benedict’s is also a comparatively weaker oxidizing agent than Tollen's reagent. It is similar to the Tollen’s test but it uses cupric salts (\[C{{u}^{2+}}\]) as the oxidizing reagent. These get reduced to copper I salts (\[C{{u}^{+}}\]) as the aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid. But aliphatic aldehydes and reducing sugars only will give positive tests and benzaldehyde is aromatic. Therefore, it tests negative.
So, the correct option is (a).
Note: Generally, aldehydes are more reactive because primary carbocation formed in the polarizing as a result the resonance structure of an aldehyde becomes less stable and therefore more reactive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




