
Bacteria which convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen compounds are called
(a) Nitrogen-fixing bacteria
(b) Nitrifying bacteria
(c) Putrefying bacteria
(d) Denitrifying bacteria
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Only prokaryotic organisms can reduce atmospheric ${ N }_{ 2 }$ to ammonia because they have an enzyme known as nitrogenase which is found exclusively in them. There are many bacteria that reduce nitrogen found in soil as free forms or as symbionts.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The process of conversion of nitrogen ${ N }_{ 2 }$ present in the air to ammonia is known as nitrogen fixation. The bacteria which convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen compounds are known as nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Dead plants and animals can be converted into ammonia by the process of decomposition then it will be known as ammonification.
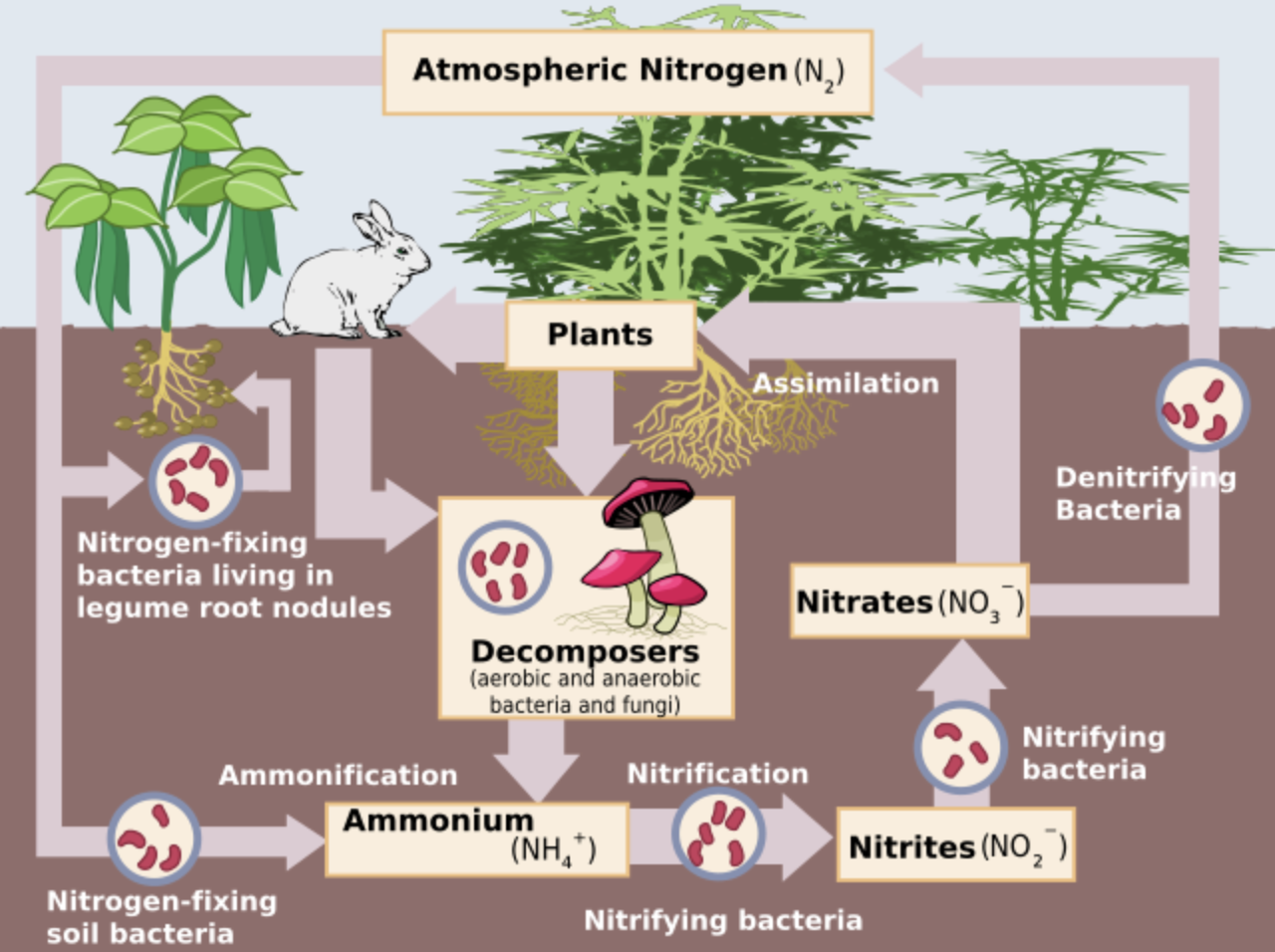
So, the correct option is ‘Nitrogen- fixing bacteria’.
Additional information:
Let us learn more about the type and examples of biological nitrogen fixers.
- Free-living nitrogen fixers: These are free-living and fix nitrogen in the soil because they are chemoautotrophs which means they derive energy by breaking or oxidizing chemical compounds.
- Aerobic bacteria: Azotobacter, Beijerinckia, Anabaena, Nostoc
- Anaerobic bacteria: Rhodospirillum
- Symbiotic nitrogen fixers: The best example of symbiotic nitrogen fixation is the legume- bacteria relationship. Rod-shaped Rhizobium lives in a symbiotic relationship with many leguminous plants such as alfalfa, sweet clover, sweet pea, lentils, etc. This association is found in the form of nodules which are small outgrowths.
Frankia performs nitrogen fixation by having a symbiotic relationship with non- leguminous plants such as Alnus.
Note:
- Both Rhizobium and Frankia are seen as free- living in soil but when found as symbionts they fix nitrogen in exchange for food and nutrients.
- The process of oxidation of ammonia to nitrite and then nitration is known as nitrification and is done by bacteria such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter respectively.
- Some bacteria also convert the ammonia in the soil back to atmospheric nitrogen and this process is called denitrification and is carried out by Pseudomonas and Thiobacillus.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The process of conversion of nitrogen ${ N }_{ 2 }$ present in the air to ammonia is known as nitrogen fixation. The bacteria which convert atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen compounds are known as nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Dead plants and animals can be converted into ammonia by the process of decomposition then it will be known as ammonification.

So, the correct option is ‘Nitrogen- fixing bacteria’.
Additional information:
Let us learn more about the type and examples of biological nitrogen fixers.
- Free-living nitrogen fixers: These are free-living and fix nitrogen in the soil because they are chemoautotrophs which means they derive energy by breaking or oxidizing chemical compounds.
- Aerobic bacteria: Azotobacter, Beijerinckia, Anabaena, Nostoc
- Anaerobic bacteria: Rhodospirillum
- Symbiotic nitrogen fixers: The best example of symbiotic nitrogen fixation is the legume- bacteria relationship. Rod-shaped Rhizobium lives in a symbiotic relationship with many leguminous plants such as alfalfa, sweet clover, sweet pea, lentils, etc. This association is found in the form of nodules which are small outgrowths.
Frankia performs nitrogen fixation by having a symbiotic relationship with non- leguminous plants such as Alnus.
Note:
- Both Rhizobium and Frankia are seen as free- living in soil but when found as symbionts they fix nitrogen in exchange for food and nutrients.
- The process of oxidation of ammonia to nitrite and then nitration is known as nitrification and is done by bacteria such as Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter respectively.
- Some bacteria also convert the ammonia in the soil back to atmospheric nitrogen and this process is called denitrification and is carried out by Pseudomonas and Thiobacillus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




