
Astral rays arise from
(a) Centrosomes
(b) Cytoplasm
(c) Chromatid
(d) None of the above
Answer
603.3k+ views
Hint: Astral rays arise from a non-membranous organelle found in animal cells which helps in cell division. It contains two cylindrical structures called ‘centrioles.’ Both the centrioles are arranged perpendicular to each other within the cell and each one has an organisation like a cartwheel.
Complete answer:
Astral rays arise from centrosomes. Let’s look into the cell division in detail to understand better.
- Cell division is considered a very important process in all living organisms.
- The ‘cell cycle’ is the sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, then forms the other constituents of the cell and ultimately divides into two daughter cells.
The cell cycle is divided into two phases:
M phase (Mitosis phase): represents the phase when the actual cell division or mitosis occurs.
Interphase:
- It represents the phase between two consecutive M phases.
- One of the important events that occur in this phase is the duplication of the centrosome.
M Phase:
- The mitotic phase is also called the equational division.
- For convenience, mitosis has been divided into four stages of nuclear division or karyokinesis. They are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
Let's learn briefly about the events characteristic of prophase.
- The centrosome which had duplicated in the interphase begins to move towards the opposite poles of the cell.
- Long microtubules subsequently radiate out of each centrosome. These radiating tubules are called ‘asters.’
- The two asters at the opposite poles along with the spindle fibers together form mitotic apparatus.
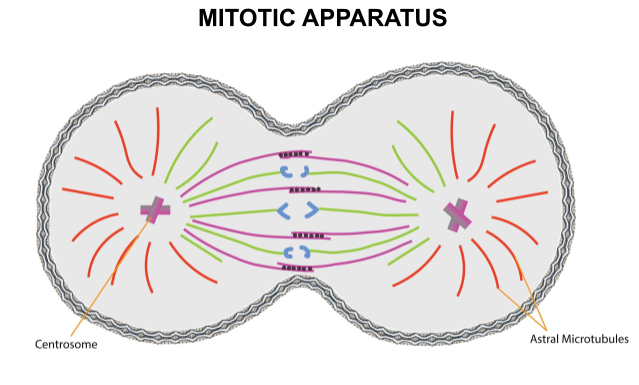
So, the correct answer is ‘Centrosomes.’
Note: The division of cytoplasm usually occurs at the end of the M phase. This phenomenon is known as ‘cytokinesis.’ Duplication of centrioles occurs within the cytoplasm.
- During prophase, two chromatids attached at the centromere together form a chromosome.
-In anaphase, two daughter chromatids are formed by the splitting of each chromosome. These daughter chromatids are now referred to as daughter chromosomes for the future nucleus.
Complete answer:
Astral rays arise from centrosomes. Let’s look into the cell division in detail to understand better.
- Cell division is considered a very important process in all living organisms.
- The ‘cell cycle’ is the sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome, then forms the other constituents of the cell and ultimately divides into two daughter cells.
The cell cycle is divided into two phases:
M phase (Mitosis phase): represents the phase when the actual cell division or mitosis occurs.
Interphase:
- It represents the phase between two consecutive M phases.
- One of the important events that occur in this phase is the duplication of the centrosome.
M Phase:
- The mitotic phase is also called the equational division.
- For convenience, mitosis has been divided into four stages of nuclear division or karyokinesis. They are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase.
Let's learn briefly about the events characteristic of prophase.
- The centrosome which had duplicated in the interphase begins to move towards the opposite poles of the cell.
- Long microtubules subsequently radiate out of each centrosome. These radiating tubules are called ‘asters.’
- The two asters at the opposite poles along with the spindle fibers together form mitotic apparatus.

So, the correct answer is ‘Centrosomes.’
Note: The division of cytoplasm usually occurs at the end of the M phase. This phenomenon is known as ‘cytokinesis.’ Duplication of centrioles occurs within the cytoplasm.
- During prophase, two chromatids attached at the centromere together form a chromosome.
-In anaphase, two daughter chromatids are formed by the splitting of each chromosome. These daughter chromatids are now referred to as daughter chromosomes for the future nucleus.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




