
Assertion: Among isomeric alkanes, branching increases the boiling points.
Reason: branching lowers the intermolecular van der waals force of attraction.
A. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
B. Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
C. Assertion is correct and Reason is incorrect.
D. Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Answer
541.5k+ views
Hint :With increase in branching, the surface of the molecule will decrease. Surface area of the molecule affects the intermolecular van der waals attraction forces. As distance between the atom increases the bond energy also decreases.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Surface area of the molecule affects the intermolecular attraction forces, if the surface of a molecule is more then more surfaces are in contact with other molecules and stronger intermolecular attraction forces.
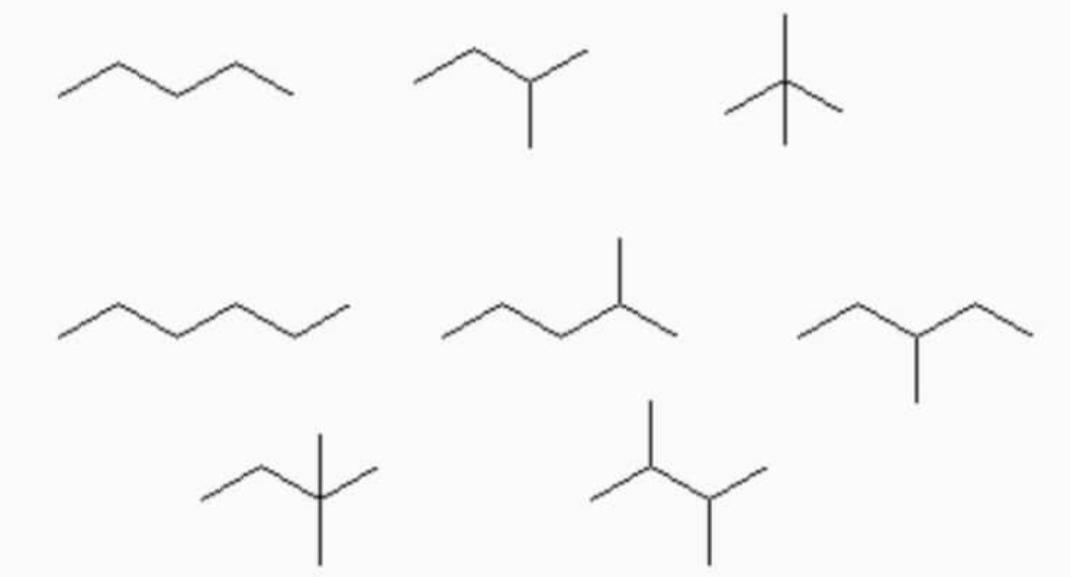
Branched carbon chains
Intermolecular van der waals attraction force is directly proportional to the surface area of the molecule. As branching increases in isomeric alkanes, molecular shape becomes spherical and surface area of the molecule will decrease and cause decrease in intermolecular attraction forces. Boiling point is directly proportional to intermolecular attraction force and with increase in branching, boiling point of the molecules will decrease.
For example: boiling point of n-Hexane is more than that of neo-Hexane because in neo-hexane due to branching, surface area is lesser than that of n-Hexane and results in less intermolecular van der waals force of attraction between the molecules of neo-hexane as compared to n-Hexane.
Amount of heat required to boil the compound depends upon the intermolecular force of attraction and boiling enthalpy is inversely proportional to the intermolecular force of attraction. Hence, for isomeric alkanes branching decreases the boiling point, because branching lowers the intermolecular van der waals force of attraction.
Therefore, Correct answer is (D) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Note :
Branching affects the surface area and surface area affects intermolecular force of attraction. If intermolecular force of attraction is weaker, then it needs less temperature or heat to boil the compound.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Surface area of the molecule affects the intermolecular attraction forces, if the surface of a molecule is more then more surfaces are in contact with other molecules and stronger intermolecular attraction forces.

Branched carbon chains
Intermolecular van der waals attraction force is directly proportional to the surface area of the molecule. As branching increases in isomeric alkanes, molecular shape becomes spherical and surface area of the molecule will decrease and cause decrease in intermolecular attraction forces. Boiling point is directly proportional to intermolecular attraction force and with increase in branching, boiling point of the molecules will decrease.
For example: boiling point of n-Hexane is more than that of neo-Hexane because in neo-hexane due to branching, surface area is lesser than that of n-Hexane and results in less intermolecular van der waals force of attraction between the molecules of neo-hexane as compared to n-Hexane.
Amount of heat required to boil the compound depends upon the intermolecular force of attraction and boiling enthalpy is inversely proportional to the intermolecular force of attraction. Hence, for isomeric alkanes branching decreases the boiling point, because branching lowers the intermolecular van der waals force of attraction.
Therefore, Correct answer is (D) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
Note :
Branching affects the surface area and surface area affects intermolecular force of attraction. If intermolecular force of attraction is weaker, then it needs less temperature or heat to boil the compound.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




