
Arrange the following compounds in the decreasing order of reactivity with NBS/heat.
A.\[1 > 2 > 3 > 4\]
B.\[2 > 1 > 3 > 4\]
C.\[1 > 2 > 4 > 3\]
D.\[4 > 3 > 2 > 1\]

Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint:NBS stands for N-Bromo-succinimide which is used for allylic and benzylic substitution. An allylic group has a structural formula of \[R - C{H_2} - CH = C{H_2}\].
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1:
The N-Bromo-succinimide or NBS is a Bromo derivative of succinic acid. The carbon atom present in the adjacent position to the double-bonded carbon atom is the allylic carbon atom the position is known as allylic position.
Step 2
NBS generates a free radical in the allylic position and a bromine atom gets added to that free radical center.
Step 3
As we see that the NBS mechanism proceeds via a free radical mechanism, so greater is the stability of the free radical greater will be the reactivity of the reaction.
Step 4
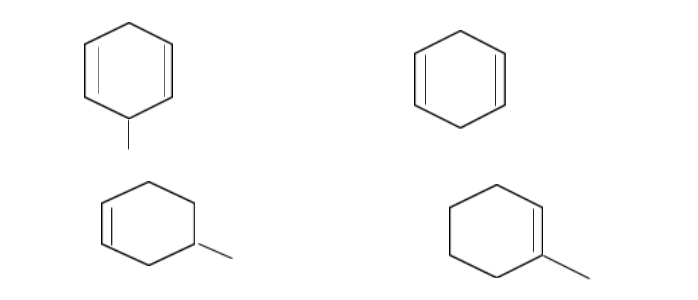
In structure 1,
The structure has 2 \[C = C\] double bonds. It forms a tertiary allylic free radical which is highly resonance stabilized as well as experiences the electron-donating effect or the \[ + I\]effect of the \[ - C{H_3}\] group.
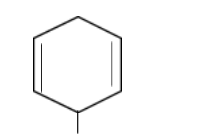
In structure 2,
As the structure is symmetrical, it forms two identical types of free radical centers. The free radical is present in the secondary carbon atom so experiences resonance from both sides.
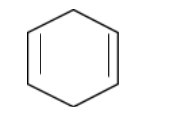
In structure 3,
In this case, the resonance experienced by the secondary carbon is only from one side.
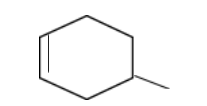
In structure 4,
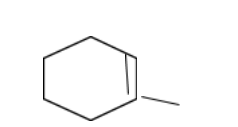
In this case, due to the presence of the methyl group exerting the \[ + I\]effect, the free radical becomes more stable than structure 3.
Hence, the free radical generated in structure 1 will be the most stabilized whereas the free radical generated in structure 3 will be the least stable. So, the reactivity of structure 1 will be the maximum, whereas for structure 3 it is the minimum. Thus, the correct order of reactivity is option c) which is \[1 > 2 > 4 > 3\].
Note: In alkenes, there are two positions named allylic and vinylic where a student gets confused. An allylic group has a structural formula \[R - C{H_2} - CH = C{H_2}\]. A vinylic group has a structural formula \[RCH = C{H_2}\].
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1:
The N-Bromo-succinimide or NBS is a Bromo derivative of succinic acid. The carbon atom present in the adjacent position to the double-bonded carbon atom is the allylic carbon atom the position is known as allylic position.
Step 2
NBS generates a free radical in the allylic position and a bromine atom gets added to that free radical center.
Step 3
As we see that the NBS mechanism proceeds via a free radical mechanism, so greater is the stability of the free radical greater will be the reactivity of the reaction.
Step 4
In structure 1,

The structure has 2 \[C = C\] double bonds. It forms a tertiary allylic free radical which is highly resonance stabilized as well as experiences the electron-donating effect or the \[ + I\]effect of the \[ - C{H_3}\] group.
In structure 2,

As the structure is symmetrical, it forms two identical types of free radical centers. The free radical is present in the secondary carbon atom so experiences resonance from both sides.
In structure 3,

In this case, the resonance experienced by the secondary carbon is only from one side.
In structure 4,

In this case, due to the presence of the methyl group exerting the \[ + I\]effect, the free radical becomes more stable than structure 3.
Hence, the free radical generated in structure 1 will be the most stabilized whereas the free radical generated in structure 3 will be the least stable. So, the reactivity of structure 1 will be the maximum, whereas for structure 3 it is the minimum. Thus, the correct order of reactivity is option c) which is \[1 > 2 > 4 > 3\].
Note: In alkenes, there are two positions named allylic and vinylic where a student gets confused. An allylic group has a structural formula \[R - C{H_2} - CH = C{H_2}\]. A vinylic group has a structural formula \[RCH = C{H_2}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




