
Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissues?
(a)Both xylem and phloem consist of one type of cells which coordinate to perform a common function
(b)Both xylem and phloem consist of more than one type of cells which coordinate to perform a common function
(c)Both xylem and phloem consist of more than one type of cells which do not coordinate
(d)Both xylem and phloem consist of one type of cells which gives strength to the plants
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: Xylem and phloem are collectively known as vascular bundles. Xylem transport water and minerals from the roots to the entire plant body while phloem has the responsibility to transport the organic food inside the body of the plant.
Complete answer:
Xylem and phloem are an example of complex permanent tissues. These tissues are named so because they are made up of more than one type of cells and all these different types of cells coordinate to perform the same function. They ultimately achieve the same goal despite their different structures and function.
Additional Information:
Just any complex tissue, xylem and phloem are also made up of 4 types of cell and are a mixture of living and dead cells.
Xylem consists of :
Tracheids: They are elongated dead cells with wide lumen surrounded by hard lignified cell walls. The end walls are narrow and this unthickened part allows the rapid movement of water between tracheidsTheir walls have thickening to provide mechanical strength to the plants.
Vessels: They are much elongated and the end walls are transverse or oblique. Sometimes the end walls are completely dissolved while at times it is intact but possesses several pores. This type of end wall is referred to as multiple perforation plates. Like tracheids, it is also dead with lignin deposition in cell walls.
Xylem parenchyma: These are parenchymatous cells with simple pits for lateral conduction of xylem sap. It stores food(starch or fat) and at times tannins too.
Xylem fibres: These are sclerenchymatous fibres that are mainly mechanical in function. They may be septate or nonseptate with a narrow lumen.
Phloem consists of :
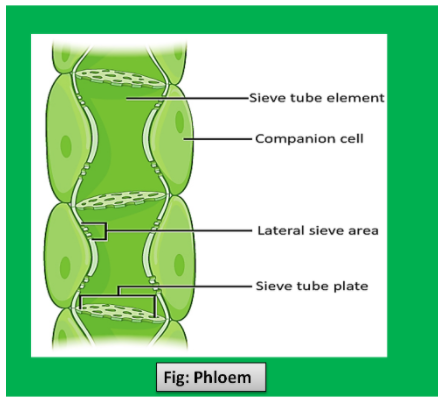
Sieve tubes: A sieve tube is made of sorter segments or cells called sieve tube elements or members. They are placed end to end. The end walls contain sieve pits and it is the reason it is also known as sieve plate. Also, the sieve member is enucleated.
Companion cells: narrow, elongated, thin-walled living cells which lie beside the sieve tubes. Their close companionship is maintained by plasmodesmata. Its nuclei control the activities of sieve cells also. Phloem Parenchyma: They are living and elongated parenchymatous cells which store food, resins, latex etc. It has abundant plasmodesmata for lateral conduction of food.
Phloem or Bast Fibres: They are absent in primary phloem but abundant in secondary phloem. They provide mechanical strength and occur in sheets or cylinders. The fibres of jute and hemp are phloem fibres.
So, the correct answer is ‘Both xylem and phloem consist of more than one type of cells
which coordinate to perform a common function’.
Note: Gymnosperms(nonflowering plants) and angiosperms (flowering plants) are quite different in terms of their types of vascular tissues. Gymnosperms are devoid of vessels but they are abundant in angiosperms. In gymnosperms, sieve cells do not fuse to form a sieve tube, instead, they remain solitary. Though the individual sieve cells are more elongated compared to the individual sieve tube member of angiosperms. Companion cells are absent in gymnosperms and are replaced by albuminous cells, modified parenchyma cells.
Complete answer:
Xylem and phloem are an example of complex permanent tissues. These tissues are named so because they are made up of more than one type of cells and all these different types of cells coordinate to perform the same function. They ultimately achieve the same goal despite their different structures and function.
Additional Information:
Just any complex tissue, xylem and phloem are also made up of 4 types of cell and are a mixture of living and dead cells.
Xylem consists of :
Tracheids: They are elongated dead cells with wide lumen surrounded by hard lignified cell walls. The end walls are narrow and this unthickened part allows the rapid movement of water between tracheidsTheir walls have thickening to provide mechanical strength to the plants.
Vessels: They are much elongated and the end walls are transverse or oblique. Sometimes the end walls are completely dissolved while at times it is intact but possesses several pores. This type of end wall is referred to as multiple perforation plates. Like tracheids, it is also dead with lignin deposition in cell walls.
Xylem parenchyma: These are parenchymatous cells with simple pits for lateral conduction of xylem sap. It stores food(starch or fat) and at times tannins too.
Xylem fibres: These are sclerenchymatous fibres that are mainly mechanical in function. They may be septate or nonseptate with a narrow lumen.
Phloem consists of :
Sieve tubes: A sieve tube is made of sorter segments or cells called sieve tube elements or members. They are placed end to end. The end walls contain sieve pits and it is the reason it is also known as sieve plate. Also, the sieve member is enucleated.
Companion cells: narrow, elongated, thin-walled living cells which lie beside the sieve tubes. Their close companionship is maintained by plasmodesmata. Its nuclei control the activities of sieve cells also. Phloem Parenchyma: They are living and elongated parenchymatous cells which store food, resins, latex etc. It has abundant plasmodesmata for lateral conduction of food.
Phloem or Bast Fibres: They are absent in primary phloem but abundant in secondary phloem. They provide mechanical strength and occur in sheets or cylinders. The fibres of jute and hemp are phloem fibres.

So, the correct answer is ‘Both xylem and phloem consist of more than one type of cells
which coordinate to perform a common function’.
Note: Gymnosperms(nonflowering plants) and angiosperms (flowering plants) are quite different in terms of their types of vascular tissues. Gymnosperms are devoid of vessels but they are abundant in angiosperms. In gymnosperms, sieve cells do not fuse to form a sieve tube, instead, they remain solitary. Though the individual sieve cells are more elongated compared to the individual sieve tube member of angiosperms. Companion cells are absent in gymnosperms and are replaced by albuminous cells, modified parenchyma cells.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




