
What are the various steps involved in biological nitrogen fixation in plants?
Answer
546.3k+ views
Hint: The conversion of molecular nitrogen present in the atmosphere to ammonia or ammonium compounds in the soil is known as nitrogen fixation. The molecular nitrogen is mostly converted into utilisable form by the help of microorganisms.
Complete answer:
The atmosphere contains about 78% of the molecular nitrogen. This nitrogen is non-reactive and cannot be easily absorbed by the plants. This nitrogen is converted into ammonia or ammonium salts by the help of bacteria. This is known as nitrogen fixation. The cyanobacteria convert nitrogen into ammonia by the help of nitrogenase enzyme.
The steps involved in the fixation are:
1)Nitrification: It is the process of conversion of ammonia into nitrates. The ammonia is converted into nitrites by Nitrosomonas and nitrococcus. The nitrites are converted into nitrates by Nitrobacter.
2)Assimilation: In this the ammonia and nitrates are utilised by the plants. The roots help in absorbing these nutrients which are taken up by plants.
3)Ammonification: By this process, nitrogen present in the living matter is converted into ammonia. The ammonia is further released into the environment and is reused.
4)Denitrification: In this process, the nitrates are broken down back to nitrogen gas by the help of anaerobic bacteria.
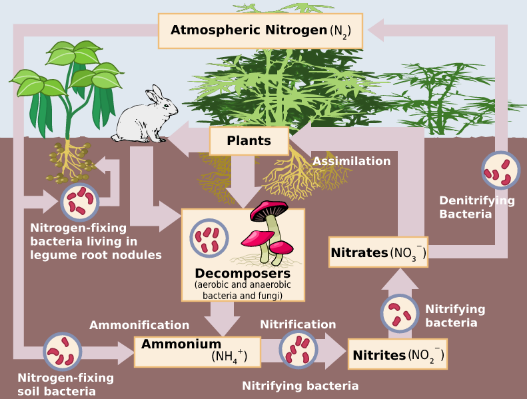
Note: Leguminous plants help in fixing free nitrogen present in the air. The Rhizobium bacteria present in the roots of these plants help in converting the free nitrogen into nitrates, nitrites and ammonia. This relationship is known as symbiosis. Through this both the organism and the plants are benefitted. This symbiosis helps in increasing the fertility of the soil.
Complete answer:
The atmosphere contains about 78% of the molecular nitrogen. This nitrogen is non-reactive and cannot be easily absorbed by the plants. This nitrogen is converted into ammonia or ammonium salts by the help of bacteria. This is known as nitrogen fixation. The cyanobacteria convert nitrogen into ammonia by the help of nitrogenase enzyme.
The steps involved in the fixation are:
1)Nitrification: It is the process of conversion of ammonia into nitrates. The ammonia is converted into nitrites by Nitrosomonas and nitrococcus. The nitrites are converted into nitrates by Nitrobacter.
2)Assimilation: In this the ammonia and nitrates are utilised by the plants. The roots help in absorbing these nutrients which are taken up by plants.
3)Ammonification: By this process, nitrogen present in the living matter is converted into ammonia. The ammonia is further released into the environment and is reused.
4)Denitrification: In this process, the nitrates are broken down back to nitrogen gas by the help of anaerobic bacteria.

Note: Leguminous plants help in fixing free nitrogen present in the air. The Rhizobium bacteria present in the roots of these plants help in converting the free nitrogen into nitrates, nitrites and ammonia. This relationship is known as symbiosis. Through this both the organism and the plants are benefitted. This symbiosis helps in increasing the fertility of the soil.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




