
What are the products when ethyl isopropyl ether is cleaved with concentrated $HI$?
A.Ethanol and 2-iodo-2- methylpropane
B.Ethanol and 2- methylpropane
C.Iodoethane and isopropyl alcohol
D.Iodoethane and 2-methylpropane
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: During the reaction of unsymmetrical ether having a different alkyl group with halogen acid, there is a formation of alcohol and alkyl halide and it also depends upon the nature of the alkyl group.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of ethyl isopropyl ether with concentrated $HI$ involves the formation of ethyl iodide and isopropyl alcohol. The chemical reaction of ethyl isopropyl alcohol with concentrated $HI$ is given as:
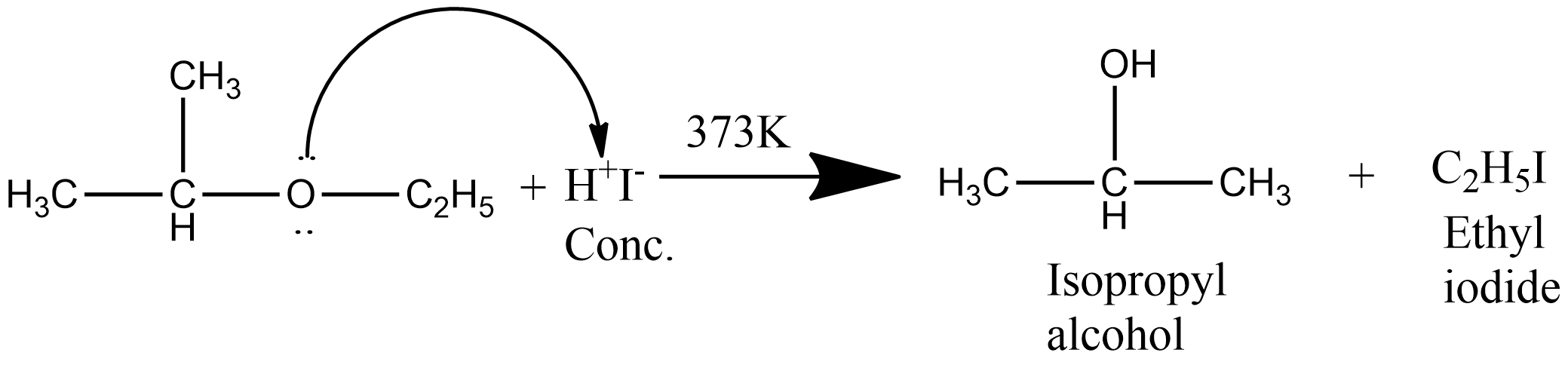
Here a secondary alkyl group is present hence the reaction occurs through the $S_N^2$ mechanism and due to steric hindrance, the halide ion attacks the smaller alkyl group as a result alkyl halide is formed from the smaller alkyl group. The cleavage of ether by concentrated $HI$ occur by the following mechanism:
Step 1: This step is the protonation step, since ether is a lewis base, undergoes protonation to form oxonium ions as:
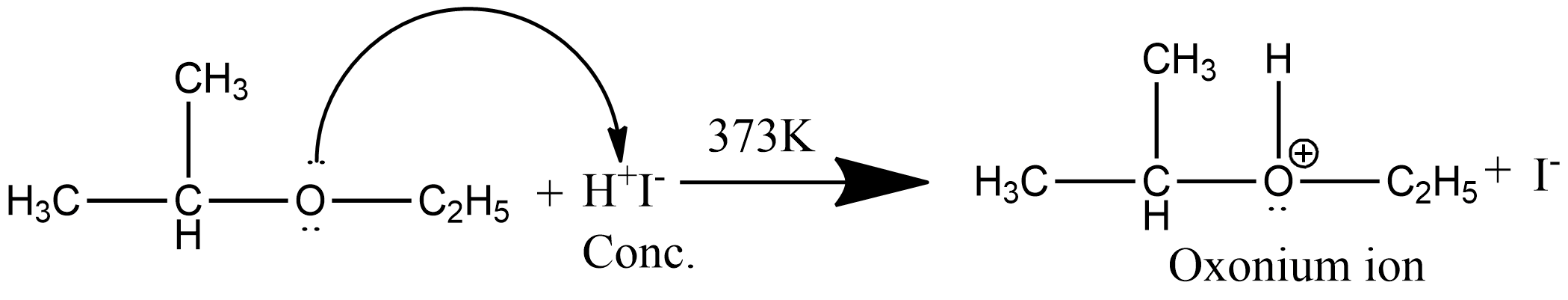
Step 2: Since the iodide ion is a good nucleophile and due to steric hindrance of alkyl group iodide ion attacks the smaller alkyl group of the oxonium ion formed in step 1and displace the alcohol molecule by $S_N^2$ mechanism as:
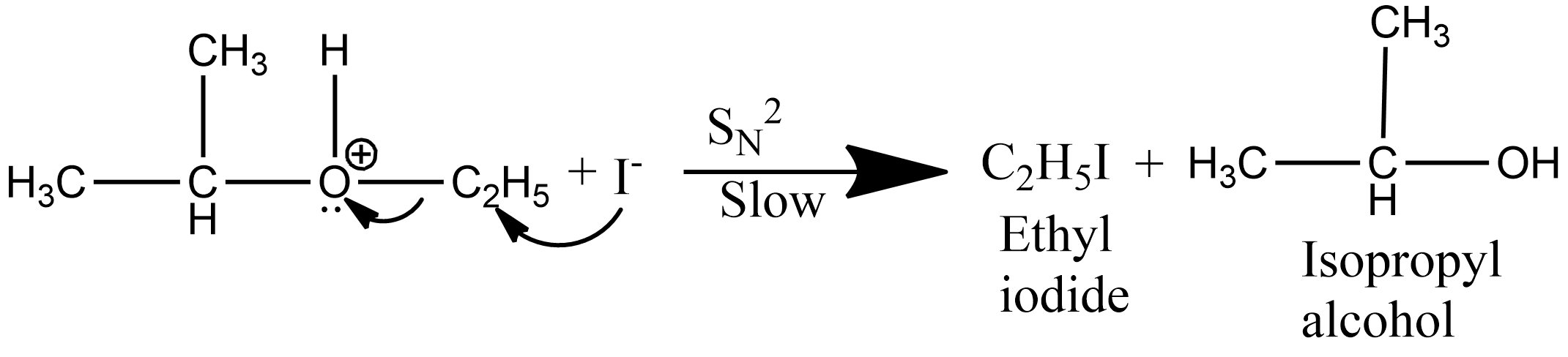
Hence the correct answer is option C.
Additional information:
If there is an excess of concentrated $HI$, then the ethanol formed during the reaction reacts with another molecule of concentrated $HI$ to form isopropyl iodide as:
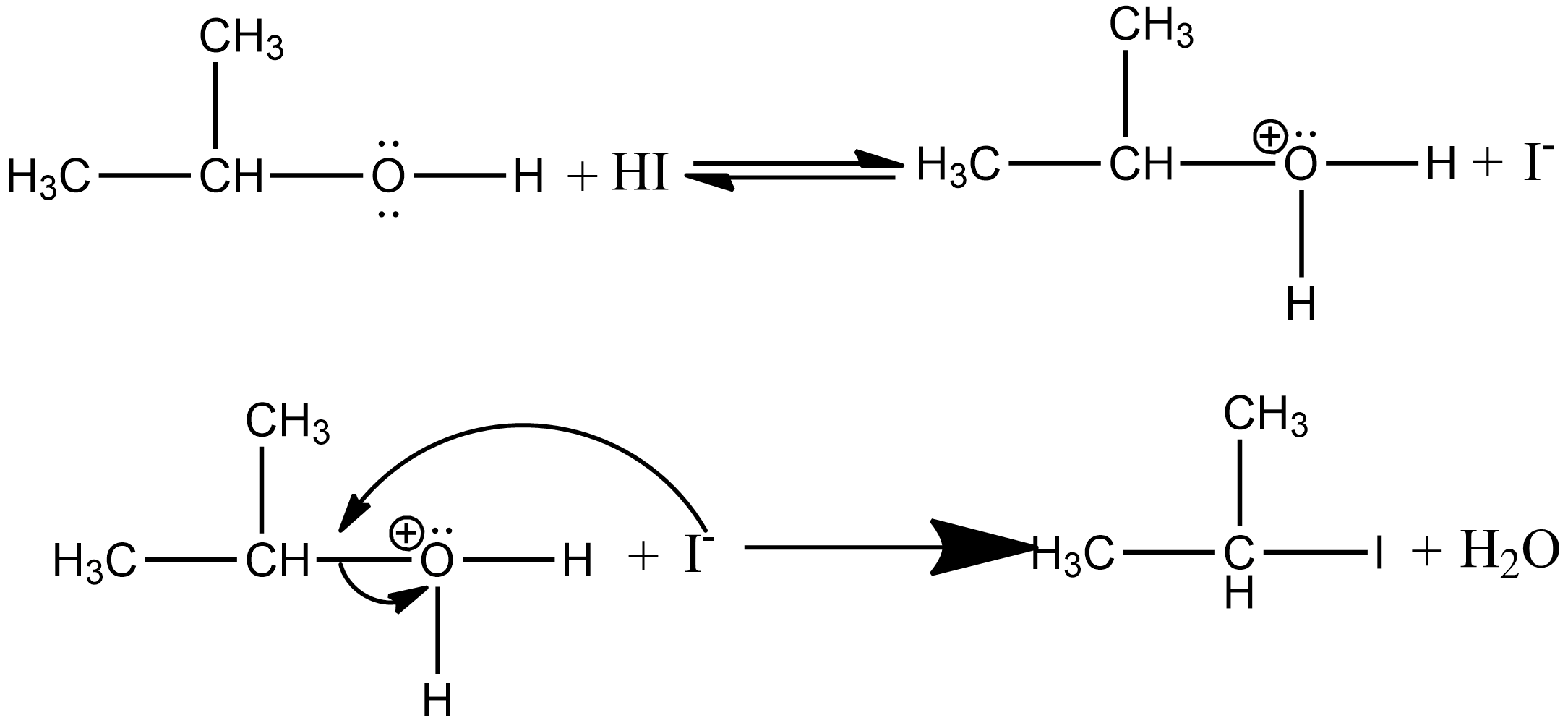
Note:
The reactivity of halogen acids towards the cleavage of ether follows the following order
$HI > HBr > HCl$
Since the cleavage of ether by halogen acids involves the nucleophilic attack by the halide ion on the protonated ether molecule. Hence greater the nucleophilicity of the halide ion, the greater will be the reactivity of halogen acid. The order of nucleophilicity of halide ion is as given:
${I^ - } > B{r^ - } > C{l^ - }$
So we can say iodide ions are most reactive towards cleavage of ether as compared to bromide and chloride ions.
Complete step by step answer:
The reaction of ethyl isopropyl ether with concentrated $HI$ involves the formation of ethyl iodide and isopropyl alcohol. The chemical reaction of ethyl isopropyl alcohol with concentrated $HI$ is given as:
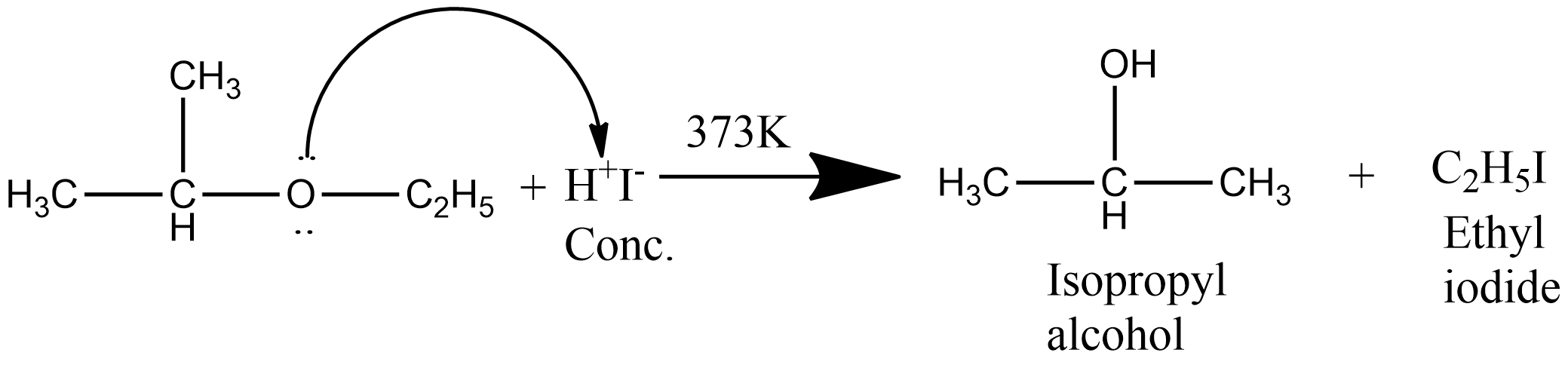
Here a secondary alkyl group is present hence the reaction occurs through the $S_N^2$ mechanism and due to steric hindrance, the halide ion attacks the smaller alkyl group as a result alkyl halide is formed from the smaller alkyl group. The cleavage of ether by concentrated $HI$ occur by the following mechanism:
Step 1: This step is the protonation step, since ether is a lewis base, undergoes protonation to form oxonium ions as:
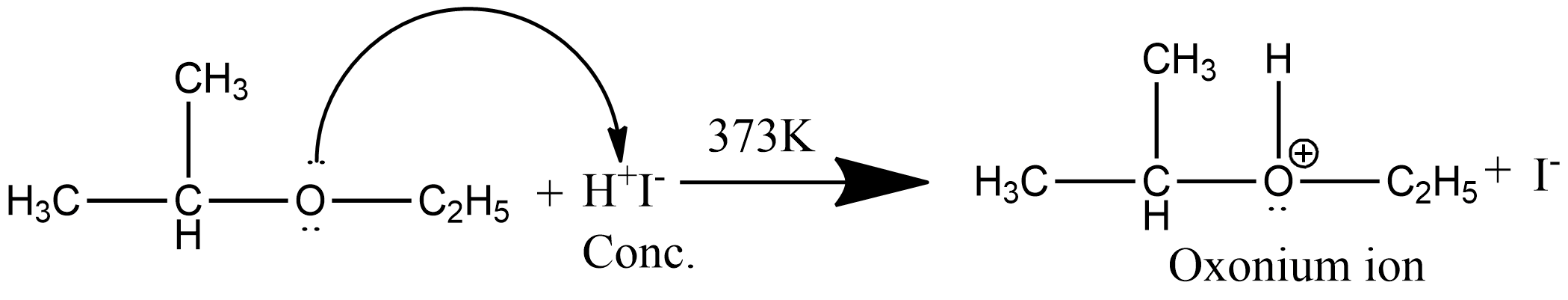
Step 2: Since the iodide ion is a good nucleophile and due to steric hindrance of alkyl group iodide ion attacks the smaller alkyl group of the oxonium ion formed in step 1and displace the alcohol molecule by $S_N^2$ mechanism as:
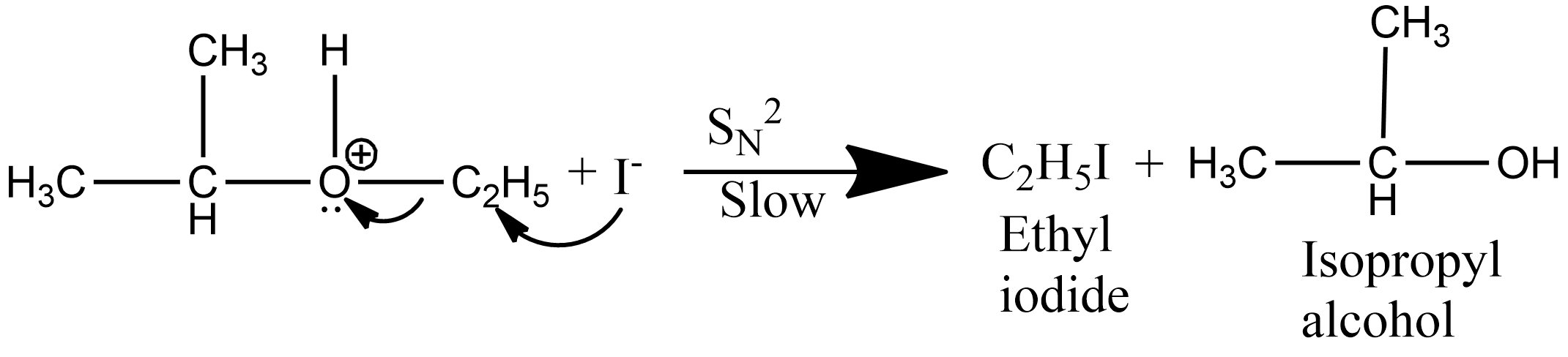
Hence the correct answer is option C.
Additional information:
If there is an excess of concentrated $HI$, then the ethanol formed during the reaction reacts with another molecule of concentrated $HI$ to form isopropyl iodide as:

Note:
The reactivity of halogen acids towards the cleavage of ether follows the following order
$HI > HBr > HCl$
Since the cleavage of ether by halogen acids involves the nucleophilic attack by the halide ion on the protonated ether molecule. Hence greater the nucleophilicity of the halide ion, the greater will be the reactivity of halogen acid. The order of nucleophilicity of halide ion is as given:
${I^ - } > B{r^ - } > C{l^ - }$
So we can say iodide ions are most reactive towards cleavage of ether as compared to bromide and chloride ions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




