
What are essential and non-essential amino acids? Give two examples of each type.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Amino acids are those organic compounds which contain amino groups and carboxyl groups as functional groups. Depending upon the relative position of the amino group with respect to the carboxyl group, the amino acids are classified as alpha-, beta-, gamma-, delta- etc. amino acids.
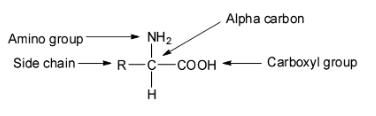
The hydrolysis of proteins gives only the alpha amino acids. Thus, the alpha amino acids are considered to be the building blocks of proteins. The term ‘amino acid’ is used to refer specifically to these alpha amino acids.
Complete step by step answer:
- There are twenty two proteinogenic or protein-building amino acids and they combine into peptide chains to form the building blocks of various types of proteins. All these amino acids differ from one another in the nature of the side chain groups attached to the alpha carbon. Therefore, the properties of the side chains of the amino acids determine the properties of the proteins they create.
- Out of these, twenty are standard amino acids and the rest two are non-standard amino acids.
- Out of the twenty one amino acids common to all life forms, human body cannot synthesize nine amino acids. These nine proteinogenic amino acids cannot be produced from other compounds by the human body and so must be supplied in the human diet. They are required for the growth of the body and their deficiency causes diseases. Hence, they are termed as ‘essential’ or ‘indispensable’ amino acids. Two examples of essential amino acids are valine and leucine.
- Six amino acids can be synthesized by the human body. These six proteinogenic amino acids can be produced from other compounds by the human body and so there is no need of supplying them externally. Hence, they are termed as ‘non-essential’ or ‘dispensable’ amino acids. Two examples of non-essential amino acids are alanine and asparagine.
Note:
- Apart from valine and leucine, the other seven essential amino acids are isoleucine, phenylalanine, methionine, tryptophan, threonine, lysine and histidine.
- Apart from alanine and asparagine, the other four non-essential amino acids are aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine and selenocysteine.
- The synthesis of the other six amino acids can be limited under special pathophysiological conditions and hence are called conditionally essential. These are arginine, cysteine, glycine, proline, glutamine and tyrosine.
The hydrolysis of proteins gives only the alpha amino acids. Thus, the alpha amino acids are considered to be the building blocks of proteins. The term ‘amino acid’ is used to refer specifically to these alpha amino acids.

Complete step by step answer:
- There are twenty two proteinogenic or protein-building amino acids and they combine into peptide chains to form the building blocks of various types of proteins. All these amino acids differ from one another in the nature of the side chain groups attached to the alpha carbon. Therefore, the properties of the side chains of the amino acids determine the properties of the proteins they create.
- Out of these, twenty are standard amino acids and the rest two are non-standard amino acids.
- Out of the twenty one amino acids common to all life forms, human body cannot synthesize nine amino acids. These nine proteinogenic amino acids cannot be produced from other compounds by the human body and so must be supplied in the human diet. They are required for the growth of the body and their deficiency causes diseases. Hence, they are termed as ‘essential’ or ‘indispensable’ amino acids. Two examples of essential amino acids are valine and leucine.
- Six amino acids can be synthesized by the human body. These six proteinogenic amino acids can be produced from other compounds by the human body and so there is no need of supplying them externally. Hence, they are termed as ‘non-essential’ or ‘dispensable’ amino acids. Two examples of non-essential amino acids are alanine and asparagine.
Note:
- Apart from valine and leucine, the other seven essential amino acids are isoleucine, phenylalanine, methionine, tryptophan, threonine, lysine and histidine.
- Apart from alanine and asparagine, the other four non-essential amino acids are aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine and selenocysteine.
- The synthesis of the other six amino acids can be limited under special pathophysiological conditions and hence are called conditionally essential. These are arginine, cysteine, glycine, proline, glutamine and tyrosine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




