
An unknown transistor needs to be identified as a npn or pnp type. A multimeter, with +ve and –ve terminals, is used to measure resistance between different terminals. If terminal 2 is the base of the transistor then which of the following is correct for a pnp transistor?
A. +ve terminal 1, -ve terminal 2, resistance high
B. +ve terminal 2, -ve terminal 3, resistance low
C. +ve terminal 3, -ve terminal 2, resistance high
D. +ve terminal 2, -ve terminal 1, resistance high
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: For a high resistance in the circuit, the base-emitter and base-collector junctions must be reverse biased. For this, the base (cathode) must be at higher potential and both emitter and collector (anodes) must be at lower potential.
Complete step by step answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device, which is formed by fusing two junction diodes. When the anodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called a npn transistor. When the cathodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called a pnp transistor.
A transistor consists of three parts – a collector, an emitter and a base. The middle part is base.
Whether a given transistor is a p-n-p or a n-p-n transistor can be identified with help of a multimeter.
In the case of a p-n-p transistor, the emitter and the collector terminals are anodes. And the base terminal is a cathode.
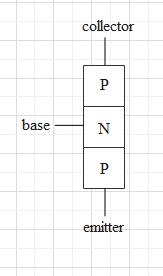
The positive and negative terminals of the multimeter are at higher and lower potentials respectively.
For a high resistance in the circuit, the base-emitter and base-collector junctions must be reverse biased. For this, the base (cathode) must be at higher potential and both emitter and collector (anodes) must be at lower potential.
This means that the +ve terminal of the multimeter must be connected to base (i.e. terminal 2) and the –ve terminal must be connected to either the emitter or the collector. (i.e. either terminal 2 or terminal 3).
Out of the given options, D satisfies this condition.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note:
For low resistance in the circuit, the base-emitter and base-collector junctions must be forward biased. For this, the base (cathode) must be at lower potential and both emitter and collector (anodes) must be at higher potential. This means that the -ve terminal of the multimeter must be connected to base (i.e. terminal 2) and the +ve terminal must be connected to either the emitter or the collector. (i.e. either terminal 2 or terminal 3).
Complete step by step answer:
A transistor is a semiconductor device, which is formed by fusing two junction diodes. When the anodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called a npn transistor. When the cathodes of the two diodes are fused, the transistor is called a pnp transistor.
A transistor consists of three parts – a collector, an emitter and a base. The middle part is base.
Whether a given transistor is a p-n-p or a n-p-n transistor can be identified with help of a multimeter.
In the case of a p-n-p transistor, the emitter and the collector terminals are anodes. And the base terminal is a cathode.

The positive and negative terminals of the multimeter are at higher and lower potentials respectively.
For a high resistance in the circuit, the base-emitter and base-collector junctions must be reverse biased. For this, the base (cathode) must be at higher potential and both emitter and collector (anodes) must be at lower potential.
This means that the +ve terminal of the multimeter must be connected to base (i.e. terminal 2) and the –ve terminal must be connected to either the emitter or the collector. (i.e. either terminal 2 or terminal 3).
Out of the given options, D satisfies this condition.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note:
For low resistance in the circuit, the base-emitter and base-collector junctions must be forward biased. For this, the base (cathode) must be at lower potential and both emitter and collector (anodes) must be at higher potential. This means that the -ve terminal of the multimeter must be connected to base (i.e. terminal 2) and the +ve terminal must be connected to either the emitter or the collector. (i.e. either terminal 2 or terminal 3).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




