
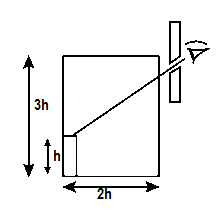
An observer can see through a pin-hole, the top of thin rod of height h, placed as shown in figure. The beaker height is 3h and its radius is h. When the beaker is filled with a liquid up to a height 2h, he can see the lower end of the rod. Then the refractive index of the liquid is
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A}.\text{ }\dfrac{5}{2} \\
& \text{B}\text{. }\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{2}} \\
& \text{C}\text{. }\sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2}} \\
& \text{D}\text{. }\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
526.5k+ views
Hint: With the help of simple trigonometry we can find the angle of incidence and angle of refraction. Then we can apply Snell’s law to find the refractive index of the water. Here when the beaker is filled with the liquid the ray bends towards the normal and the ray gets refracted.
Formula used:
\[{{n}_{1}}\sin i={{n}_{2}}\sin r\]
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{opposite}}{\text{hypotenuse}}\]
Complete answer:
The simplified way of the diagram can be given as
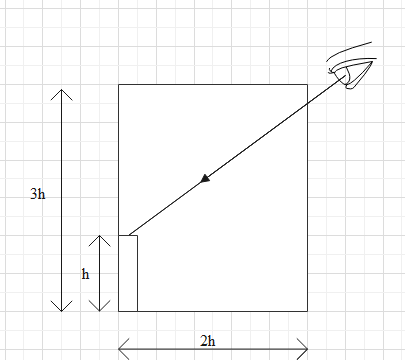
And when the liquid is filled then the diagram can be given as
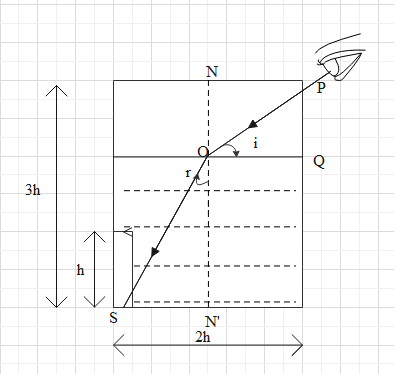
We can find the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction from the above diagram by applying a simple trigonometry rule. With the help of trigonometry, angle of incidence (i) can be given as
\[\sin i=\dfrac{\text{opposite(OQ)}}{\text{hypotenuse(OP)}}\]
Where, hypotenuse can be given as
\[\text{hypotenuse=}\sqrt{{{(\text{opposite)}}^{2}}+{{(\text{adjacent)}}^{2}}}\]
Hence we can write
\[\Rightarrow OP=\sqrt{O{{Q}^{2}}+P{{Q}^{2}}}\]
Where OQ=h and PQ=h
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow OP=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OP=\sqrt{2{{h}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OP=\sqrt{2}h \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore sine of angle of incidence is given as
\[\sin i=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{2}h}\Rightarrow \sin i=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
Now similarly for the sine of angle of refraction consider the triangle OSN’ then sin r can be given as
\[\sin r=\dfrac{SN'}{OS}\]
Where OS can again be written in terms of SN’ and ON’
\[\sin r=\dfrac{SN'}{\sqrt{SN{{'}^{2}}+ON{{'}^{2}}}}\]
Where SN’=h and ON’=2h
\[\begin{align}
& \sin r=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{(2h)}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin r=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{5}h}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, according to Snell’s law the ratio of the sine of angle of incidence and the angle of refraction is a constant and in terms of refractive indices it is given as
\[{{n}_{1}}\sin i={{n}_{2}}\sin r\]
Where \[{{n}_{1}}\] is the refractive index of the first medium and \[{{n}_{2}}\] is the refractive index of the second medium. We know the value of sini and sinr and the refractive index of the first medium will be equal to 1 as the first medium is air.
We have to find\[{{n}_{2}}\] which is a refractive index of liquid as per the question.
\[{{n}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{n}_{1}}\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{(1)(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}})}{(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}})}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{n}_{2}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{2}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
While using trigonometry formula we should be careful with the sides like which one is adjacent and which one is opposite at some places adjacent is taken as base and opposite is called height. Here we also directly apply the refractive index of air as when the medium is not given, air is always considered.
Formula used:
\[{{n}_{1}}\sin i={{n}_{2}}\sin r\]
\[\sin \theta =\dfrac{\text{opposite}}{\text{hypotenuse}}\]
Complete answer:
The simplified way of the diagram can be given as

And when the liquid is filled then the diagram can be given as

We can find the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction from the above diagram by applying a simple trigonometry rule. With the help of trigonometry, angle of incidence (i) can be given as
\[\sin i=\dfrac{\text{opposite(OQ)}}{\text{hypotenuse(OP)}}\]
Where, hypotenuse can be given as
\[\text{hypotenuse=}\sqrt{{{(\text{opposite)}}^{2}}+{{(\text{adjacent)}}^{2}}}\]
Hence we can write
\[\Rightarrow OP=\sqrt{O{{Q}^{2}}+P{{Q}^{2}}}\]
Where OQ=h and PQ=h
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow OP=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{h}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OP=\sqrt{2{{h}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow OP=\sqrt{2}h \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore sine of angle of incidence is given as
\[\sin i=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{2}h}\Rightarrow \sin i=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
Now similarly for the sine of angle of refraction consider the triangle OSN’ then sin r can be given as
\[\sin r=\dfrac{SN'}{OS}\]
Where OS can again be written in terms of SN’ and ON’
\[\sin r=\dfrac{SN'}{\sqrt{SN{{'}^{2}}+ON{{'}^{2}}}}\]
Where SN’=h and ON’=2h
\[\begin{align}
& \sin r=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{(2h)}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sin r=\dfrac{h}{\sqrt{5}h}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, according to Snell’s law the ratio of the sine of angle of incidence and the angle of refraction is a constant and in terms of refractive indices it is given as
\[{{n}_{1}}\sin i={{n}_{2}}\sin r\]
Where \[{{n}_{1}}\] is the refractive index of the first medium and \[{{n}_{2}}\] is the refractive index of the second medium. We know the value of sini and sinr and the refractive index of the first medium will be equal to 1 as the first medium is air.
We have to find\[{{n}_{2}}\] which is a refractive index of liquid as per the question.
\[{{n}_{2}}=\dfrac{{{n}_{1}}\sin i}{\sin r}=\dfrac{(1)(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}})}{(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{5}})}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{n}_{2}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{2}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
While using trigonometry formula we should be careful with the sides like which one is adjacent and which one is opposite at some places adjacent is taken as base and opposite is called height. Here we also directly apply the refractive index of air as when the medium is not given, air is always considered.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




