
An iron chain lies on a rough horizontal table. It starts sliding when one-fourth of its length hangs over the edge of the table. The coefficient of static friction between the chain and surface of the table is
A. \[\dfrac{1}{2}\]
B. \[\dfrac{1}{3}\]
C. \[\dfrac{1}{4}\]
D. \[\dfrac{1}{5}\]
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: In this question we have been given that an iron chain on a table starts sliding down when one fourth of its length hangs over the edge of the table. We have been asked to calculate the static friction between the surface of the table and the chain. Static friction is the limiting frictional force above which the object starts to slide or move on a surface. We know that the maximum static friction will be equal to the weight of the hanging chain. Since the weight of the hanging chain is the force that is opposed by the static friction.
Complete answer:
It is given that one fourth of the length of chain is hanging from the side of the table as shown in the figure below.
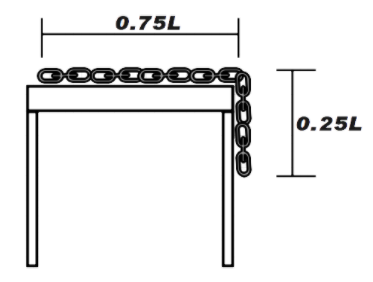
Now, let us assume that the chain has uniformly distributed mass. Therefore, we can say that one fourth of the mass of the chain is hanging from the side of the table.
Therefore,
Weight of chain hanging from the table \[=\dfrac{mg}{4}\]
Similarly,
Weight of chain on the table \[=\dfrac{3mg}{4}\]
Now, we know that
\[F=\mu N\] ……………… (1)
Where, F is the frictional force, N is the normal reaction and \[\mu \]is the coefficient of friction.
We know that
\[N=\dfrac{3mg}{4}\] ………………….. (2)
We also know that, the maximum frictional force is equal to the weight of the hanging chain
Therefore,
\[F=\dfrac{mg}{4}\] …………… (3)
Therefore, from (1), (2) and (3)
We get,
\[\dfrac{mg}{4}=\mu \dfrac{3mg}{4}\]
On solving
We get,
\[\mu =\dfrac{1}{3}\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
When we try to move an object, we experience a friction force. This force is known as static friction force. The static friction force keeps the object at rest. Therefore, it opposes motion. The friction force experienced when on a moving object is known as dynamic friction force. This force acts opposite to the direction of the motion of the object.
Complete answer:
It is given that one fourth of the length of chain is hanging from the side of the table as shown in the figure below.

Now, let us assume that the chain has uniformly distributed mass. Therefore, we can say that one fourth of the mass of the chain is hanging from the side of the table.
Therefore,
Weight of chain hanging from the table \[=\dfrac{mg}{4}\]
Similarly,
Weight of chain on the table \[=\dfrac{3mg}{4}\]
Now, we know that
\[F=\mu N\] ……………… (1)
Where, F is the frictional force, N is the normal reaction and \[\mu \]is the coefficient of friction.
We know that
\[N=\dfrac{3mg}{4}\] ………………….. (2)
We also know that, the maximum frictional force is equal to the weight of the hanging chain
Therefore,
\[F=\dfrac{mg}{4}\] …………… (3)
Therefore, from (1), (2) and (3)
We get,
\[\dfrac{mg}{4}=\mu \dfrac{3mg}{4}\]
On solving
We get,
\[\mu =\dfrac{1}{3}\]
Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Note:
When we try to move an object, we experience a friction force. This force is known as static friction force. The static friction force keeps the object at rest. Therefore, it opposes motion. The friction force experienced when on a moving object is known as dynamic friction force. This force acts opposite to the direction of the motion of the object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




