
An electric dipole is placed in a uniform electric field. The net electric force on the dipole
A. is always zero
B. depends on the orientation of the dipole
C. depends on the dipole moment
D. is always finite but non zero
Answer
592.2k+ views
Hint: Use the theory that for a charge +q the direction of the electric force is in the direction of the electric field and for a charge -q the direction of the electric force is in the opposite direction of the electric field. Calculate the force on both charges of the dipole by using F=qE and find the net force on the dipole.
Formula used:
F=qE
Complete answer:
Let us first understand what is meant by a dipole. Then we can easily calculate the net force on the dipole when it is placed in a uniform electric field.
A dipole is a combination of a pair of charges of equal magnitudes. However, in this combination, one charge is positive and the other charge is a negative charge. Suppose of the charge is +q then the other charge will be –q.
These two charges are separated by distance of 2a.
A diagram of a dipole is given below.
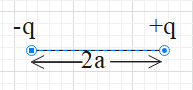
When a charge q is placed in a uniform electric field, the electric field exerts an electric force on the charge of magnitude F=qE.
The direction of the electric force depends on the nature of charge. If the charge is positive, then the direction of the electric force is in the direction of the electric field.
If the charge is negative, then the direction of the electric force is in the opposite direction of the electric field.
Now, let us place the dipole in a uniform electric field $\overrightarrow{E}$ as shown in the figure.
As per discussed information, the electric force on the +q charge is F=qE towards right and the electric force on the –q charge is F=qE towards left.
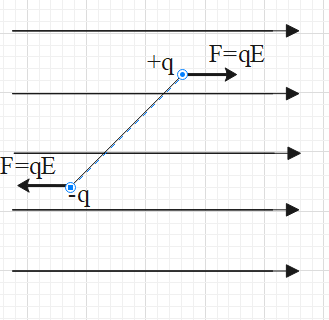
Therefore, there are two forces acting on the dipole. However, these two forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in directions. Therefore, the net force on the dipole is zero.
Even if we change the orientation, the length and the charge of the dipole, the net force on the dipole will be equal to zero.
Hence, the electric force on a dipole when it is placed in a uniform electric field is always zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The dipole moment of a dipole is a vector with a magnitude equal to 2aq and directed from the negative to the positive charge.
Note that although the net electric force on the dipole is zero, the dipole is not in equilibrium. The two electric forces will create a torque on the dipole.
Therefore, the dipole will not have translational motion and will only have a rotational motion.
Formula used:
F=qE
Complete answer:
Let us first understand what is meant by a dipole. Then we can easily calculate the net force on the dipole when it is placed in a uniform electric field.
A dipole is a combination of a pair of charges of equal magnitudes. However, in this combination, one charge is positive and the other charge is a negative charge. Suppose of the charge is +q then the other charge will be –q.
These two charges are separated by distance of 2a.
A diagram of a dipole is given below.
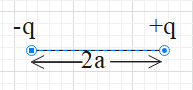
When a charge q is placed in a uniform electric field, the electric field exerts an electric force on the charge of magnitude F=qE.
The direction of the electric force depends on the nature of charge. If the charge is positive, then the direction of the electric force is in the direction of the electric field.
If the charge is negative, then the direction of the electric force is in the opposite direction of the electric field.
Now, let us place the dipole in a uniform electric field $\overrightarrow{E}$ as shown in the figure.
As per discussed information, the electric force on the +q charge is F=qE towards right and the electric force on the –q charge is F=qE towards left.

Therefore, there are two forces acting on the dipole. However, these two forces are equal in magnitude but opposite in directions. Therefore, the net force on the dipole is zero.
Even if we change the orientation, the length and the charge of the dipole, the net force on the dipole will be equal to zero.
Hence, the electric force on a dipole when it is placed in a uniform electric field is always zero.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The dipole moment of a dipole is a vector with a magnitude equal to 2aq and directed from the negative to the positive charge.
Note that although the net electric force on the dipole is zero, the dipole is not in equilibrium. The two electric forces will create a torque on the dipole.
Therefore, the dipole will not have translational motion and will only have a rotational motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




