
Among the following ethers, which one will produce methyl alcohol on treatment with hot concentrated HI?
(A)- $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-C{{H}_{2}}-O-C{{H}_{3}}$
(B)- $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{H}_{2}}-CH(C{{H}_{3}})-O-C{{H}_{3}}$
(C)- $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}-O-C{{H}_{3}}$
(D)- $C{{H}_{3}}-CH(C{{H}_{3}})-C{{H}_{2}}-O-C{{H}_{3}}$
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: The strong concentrated acid causes the cleavage of the C-O bond in the ether, followed by the nucleophilic substitution reaction to form the alcohol and the alkyl halide. This substitution further depends on the stability of the carbocation formed in the higher degree of alkyl groups.
Complete step by step solution:
The reaction of ether with the strong hydriodic acid (HI), which causes the cleavage of the ether C-O bond, following the nucleophilic substitution reaction. This cleavage further depends on the degree of alkyl group present on the ether as the primary and the secondary alkyl ethers having less steric hindrance. Thus, shows the ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism.
So, in compound (A), through the ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism, having ${{1}^{\circ }}$ alkyl group, on reaction with HI, it forms butanol and methyl iodide.
Similarly, in compound (D), on reaction with HI, it forms 2-methyl propanol and methyl iodide.
In compound (B), having a ${{2}^{\circ }}$ alkyl group, on reaction it forms methyl iodide and isobutyl alcohol.
Whereas in case of the tertiary alkyl ether due to steric hindrance it follows the ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism through the formation of the stable carbocation intermediate. So, in compound (C), on reaction we get tertiary- butyl iodide and methanol. As follows:
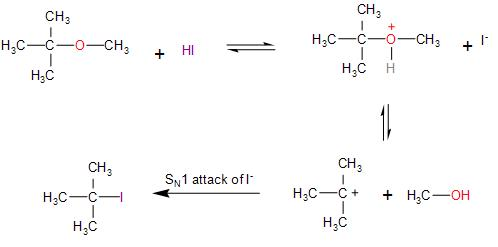
Therefore, the option (C)- $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}-O-C{{H}_{3}}$ ether will produce methyl alcohol on treatment with hot concentrated $HI$.
Note: It must be noted that in the primary and the secondary alkyl ethers, following the ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism, due to less hindrance, the iodide attaches to the smaller alkyl group, whereas in the tertiary alkyl ether following the ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism, the high stability of the tertiary carbocation the iodide attaches to it, and the smaller alkyl forms the alcohol.
Complete step by step solution:
The reaction of ether with the strong hydriodic acid (HI), which causes the cleavage of the ether C-O bond, following the nucleophilic substitution reaction. This cleavage further depends on the degree of alkyl group present on the ether as the primary and the secondary alkyl ethers having less steric hindrance. Thus, shows the ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism.
So, in compound (A), through the ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism, having ${{1}^{\circ }}$ alkyl group, on reaction with HI, it forms butanol and methyl iodide.
Similarly, in compound (D), on reaction with HI, it forms 2-methyl propanol and methyl iodide.
In compound (B), having a ${{2}^{\circ }}$ alkyl group, on reaction it forms methyl iodide and isobutyl alcohol.
Whereas in case of the tertiary alkyl ether due to steric hindrance it follows the ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism through the formation of the stable carbocation intermediate. So, in compound (C), on reaction we get tertiary- butyl iodide and methanol. As follows:

Therefore, the option (C)- $C{{H}_{3}}-C{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}-O-C{{H}_{3}}$ ether will produce methyl alcohol on treatment with hot concentrated $HI$.
Note: It must be noted that in the primary and the secondary alkyl ethers, following the ${{S}_{N}}2$ mechanism, due to less hindrance, the iodide attaches to the smaller alkyl group, whereas in the tertiary alkyl ether following the ${{S}_{N}}1$ mechanism, the high stability of the tertiary carbocation the iodide attaches to it, and the smaller alkyl forms the alcohol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




