
$\alpha$-Amino acids in heating with $Ba{{(OH)}_{2}}$ shows decarboxylation to produce primary amines:
(A) True
(B) False
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Decarboxylation reaction means the release of carbon dioxide. $\alpha$-amino acids are those amino acids which are made up of central carbon atom attached with hydrogen, alkyl or aryl group (R), primary amine ($N{{H}_{2}}$) and carboxylic acid ($COOH$) which on reaction with barium hydroxide gives $R-C{{H}_{2}}-N{{H}_{2}}$ and carbon dioxide.
Complete step by step solution:
From your chemistry lessons, you have learned about the decarboxylation of amine
Decarboxylation is a type of chemical reaction in which carboxylic groups are removed and releases carbon dioxide.
Amino acids are organic compounds which contain both amine groups as well as carboxylic groups with them and an R group which forms the side chain. Protein and peptides are the polymers of amino acids and hence protein are the polyamides.
In our body approximately 20 amino acids are present and all of them varies in their side chain, the side chain may be hydrophilic (water-loving) or hydrophobic (water-hating) and the side chains are bounded with the backbone of the molecule and thus determines the properties of amino acids made with different side chains.
Alpha-amino acids are those amino acids which are made up of central carbon atom attached with hydrogen, alkyl or aryl group (R), primary amine ($N{{H}_{2}}$) and carboxylic acid ($COOH$). They can exist as enantiomers and most of the alpha-amino acids present in nature have L-configuration and also known as L-amino acids.
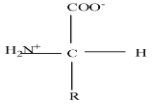
Here we are going to deal with the decarboxylation reaction of $\alpha$-amino acid,
$\alpha$-amino acids, when heated with barium hydroxide ($Ba{{(OH)}_{2}}$), undergoes decarboxylation reaction and produces primary amine.
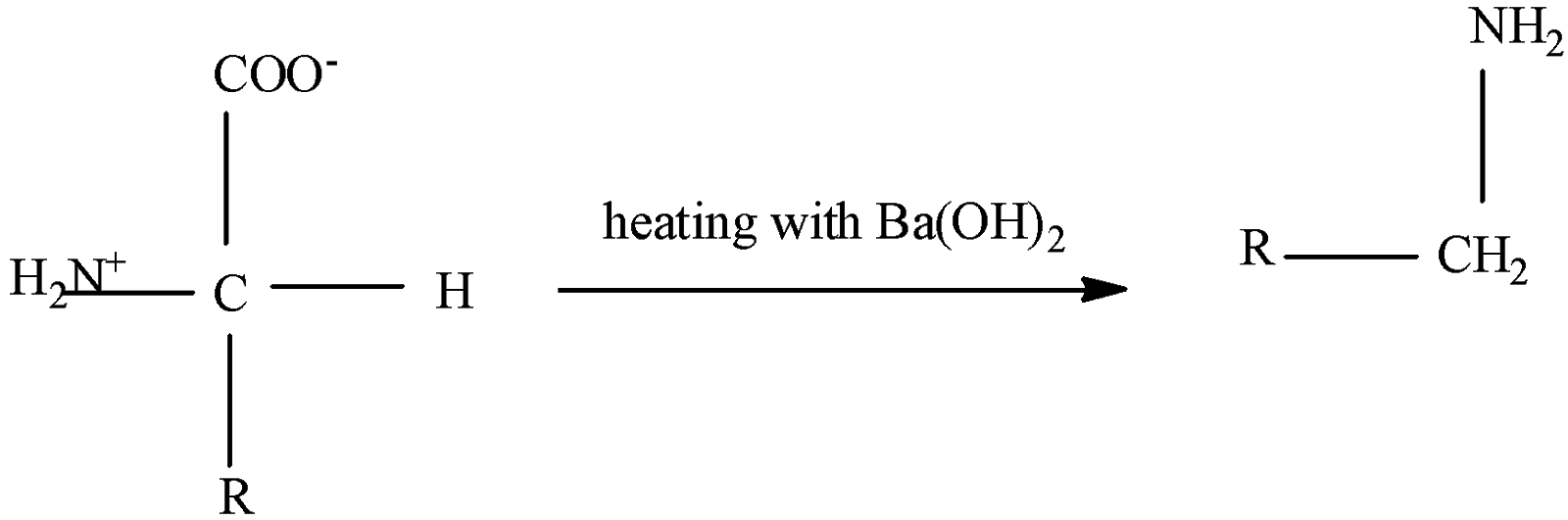
Thus it is true that it produces primary amine.
Note: Decarboxylation takes place due to the carboxyl group of amino acids. L-amino acids are those amino acids in which amine group is present on the left and in D-amino acid it is present on the right side. Deamination is the reaction of an amino group of amino acids. Decarboxylation is the reaction used for the purification process by the bacteria of the large intestine to form primary amines.
Complete step by step solution:
From your chemistry lessons, you have learned about the decarboxylation of amine
Decarboxylation is a type of chemical reaction in which carboxylic groups are removed and releases carbon dioxide.
Amino acids are organic compounds which contain both amine groups as well as carboxylic groups with them and an R group which forms the side chain. Protein and peptides are the polymers of amino acids and hence protein are the polyamides.
In our body approximately 20 amino acids are present and all of them varies in their side chain, the side chain may be hydrophilic (water-loving) or hydrophobic (water-hating) and the side chains are bounded with the backbone of the molecule and thus determines the properties of amino acids made with different side chains.
Alpha-amino acids are those amino acids which are made up of central carbon atom attached with hydrogen, alkyl or aryl group (R), primary amine ($N{{H}_{2}}$) and carboxylic acid ($COOH$). They can exist as enantiomers and most of the alpha-amino acids present in nature have L-configuration and also known as L-amino acids.

Here we are going to deal with the decarboxylation reaction of $\alpha$-amino acid,
$\alpha$-amino acids, when heated with barium hydroxide ($Ba{{(OH)}_{2}}$), undergoes decarboxylation reaction and produces primary amine.
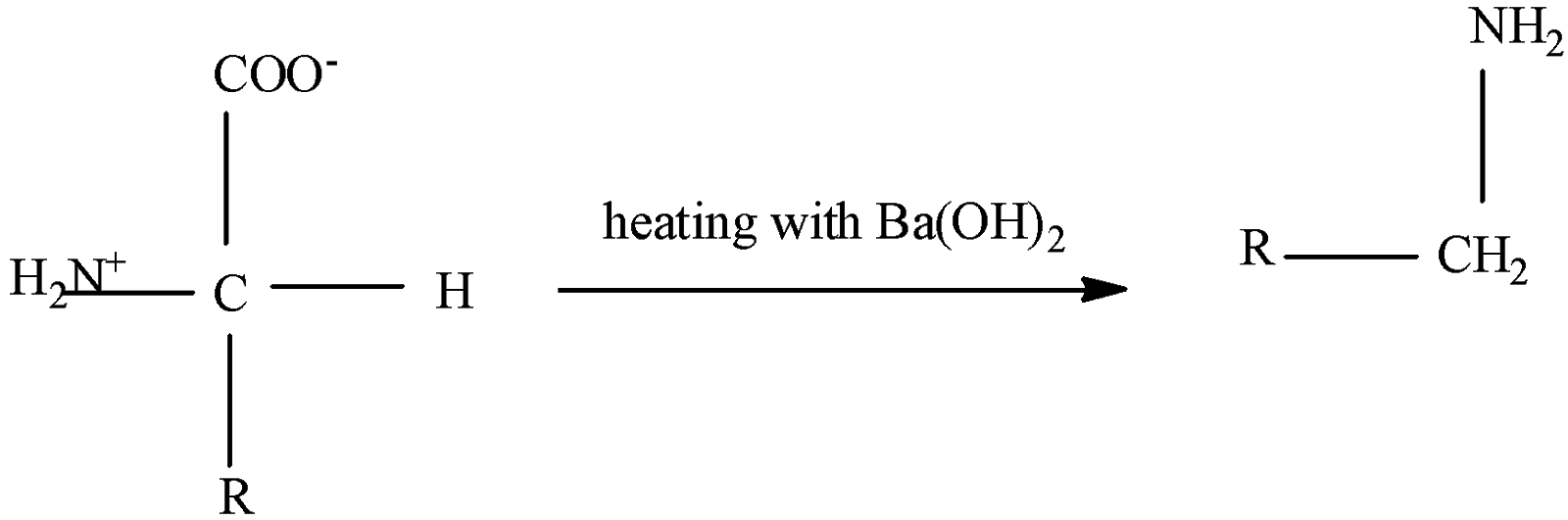
Thus it is true that it produces primary amine.
Note: Decarboxylation takes place due to the carboxyl group of amino acids. L-amino acids are those amino acids in which amine group is present on the left and in D-amino acid it is present on the right side. Deamination is the reaction of an amino group of amino acids. Decarboxylation is the reaction used for the purification process by the bacteria of the large intestine to form primary amines.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the class 12 chemistry CBSE

Define Vant Hoff factor How is it related to the degree class 12 chemistry CBSE




