
All the bonds (metal-ligand) are perpendicular to each other.
A. True
B. False
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: A metal–ligand multiple bond describes the interaction of certain ligands by a metal with a bond order greater than one. Ligands may be an ion or a molecule. Perpendicular means it should have ${90^ \circ }$ angle.
Complete step by step answer:
Explaining this question with the help of one metal ligand example
Now I am choosing example as ${[FeC{l_6}]^{3 - }}$
The electronic configuration of Iron is : $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2}3{d^6}$
And the ionic configuration becomes: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^0}3{d^5}$
The electronic configuration of Chlorine will be: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^5}$ Sulphur also has vacant $3d$ orbitals which can take part in bonding. Hence, the outer orbitals which take part in the reaction will be $s,p\,and\,d$ and the number of the orbitals participating will be $1,2\,and\,2$ respectively.
Hence the hybridisation of the complex will be : $s{p^3}{d^2}$ which has an octahedral geometry.
$4$ Chlorine occupy the $4$ corner and is in the same plane.
$2$ additional chlorine bonds are perpendicular to the plane above and below the plane
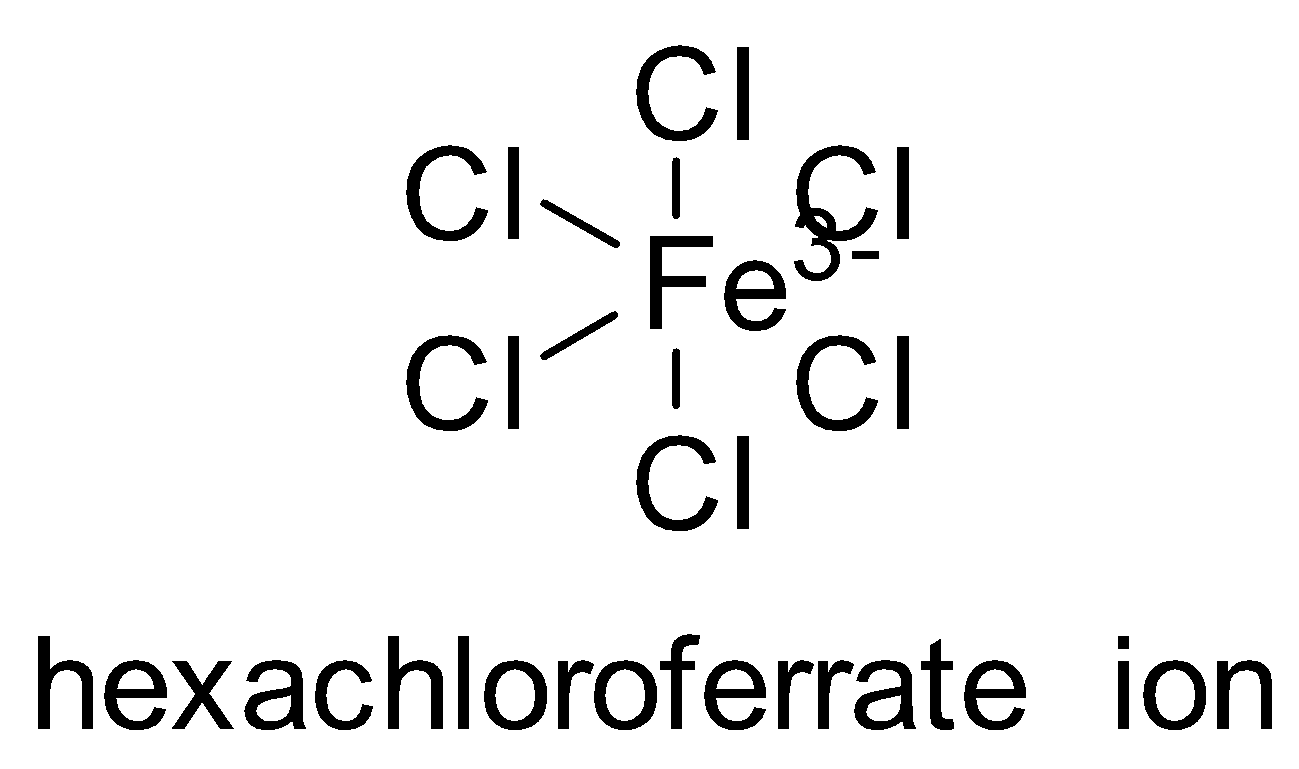
The bonds have to be arranged in such a way that there is minimum interaction between them.
Hence the statement is True they all are perpendicular to each other.
Note:The angle between two bonds is known as the bond angle. This has to be ${90^ \circ }$ or perpendicular since, any value less or more than this value will cause the bonds to come closer together.
This will lead to Bond Pair- Bond Pair repulsion and render the molecule unstable.
In case, the molecule has a lone pair, then also the arrangement doesn’t change. Only difference will be that the lone pair occupies the position of the bond pair, but the lone pair will also be perpendicular to the other bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
Explaining this question with the help of one metal ligand example
Now I am choosing example as ${[FeC{l_6}]^{3 - }}$
The electronic configuration of Iron is : $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^2}3{d^6}$
And the ionic configuration becomes: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^6}4{s^0}3{d^5}$
The electronic configuration of Chlorine will be: $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}3{p^5}$ Sulphur also has vacant $3d$ orbitals which can take part in bonding. Hence, the outer orbitals which take part in the reaction will be $s,p\,and\,d$ and the number of the orbitals participating will be $1,2\,and\,2$ respectively.
Hence the hybridisation of the complex will be : $s{p^3}{d^2}$ which has an octahedral geometry.
$4$ Chlorine occupy the $4$ corner and is in the same plane.
$2$ additional chlorine bonds are perpendicular to the plane above and below the plane

The bonds have to be arranged in such a way that there is minimum interaction between them.
Hence the statement is True they all are perpendicular to each other.
Note:The angle between two bonds is known as the bond angle. This has to be ${90^ \circ }$ or perpendicular since, any value less or more than this value will cause the bonds to come closer together.
This will lead to Bond Pair- Bond Pair repulsion and render the molecule unstable.
In case, the molecule has a lone pair, then also the arrangement doesn’t change. Only difference will be that the lone pair occupies the position of the bond pair, but the lone pair will also be perpendicular to the other bonds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




