
What is the action of the silver acetate on ethyl bromide?
Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: When silver acetate and ethyl bromide react with each other, an ester is formed. This reaction takes place through a nucleophilic substitution reaction. In silver acetate, acetate is the negative part.
Complete step by step answer:
Ethyl bromide is a haloalkane and haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The halogen atom in haloalkane is more electronegative than the carbon atom attached to it. As a result, the carbon atom acquires a partial positive charge and the halogen atom acquires a partial negative charge. The presence of this small positive charge on the carbon atom makes it susceptible to attack by nucleophilic reagent (i.e. reagent possessing a negative charge or a lone pair of electrons). Thus, when a nucleophile stronger than the halide ion approaches the positively charged carbon atom of an alkyl halide, the halogen atom with its bonding pair of electrons is displaced and a new bond between the carbon atom and the incoming nucleophile is formed:
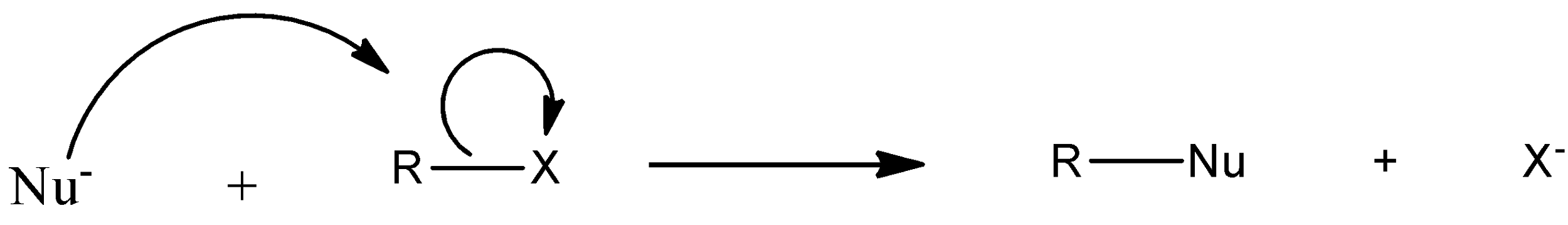
Such a reaction in which a stronger nucleophile displaces a weaker nucleophile is called nucleophilic substitution reactions.
So, the silver acetate is the reagent in which the acetate ion is the negative charge and displaces the bromide ion in the ethyl bromide. In this reaction, an ester is formed. The product formed will be ethyl acetate or ethyl ethanoate.
The reaction is given below:
$C{{H}_{3}}COOAg+Br-C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH}C{{H}_{3}}COOC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}+AgBr$
The mechanism of the reaction is:
The silver acetate will split into ions. The negative part is acetate. This negative acetate will attack the positive ethyl group in the bromoethane. This will lead to the formation of ethyl acetate.
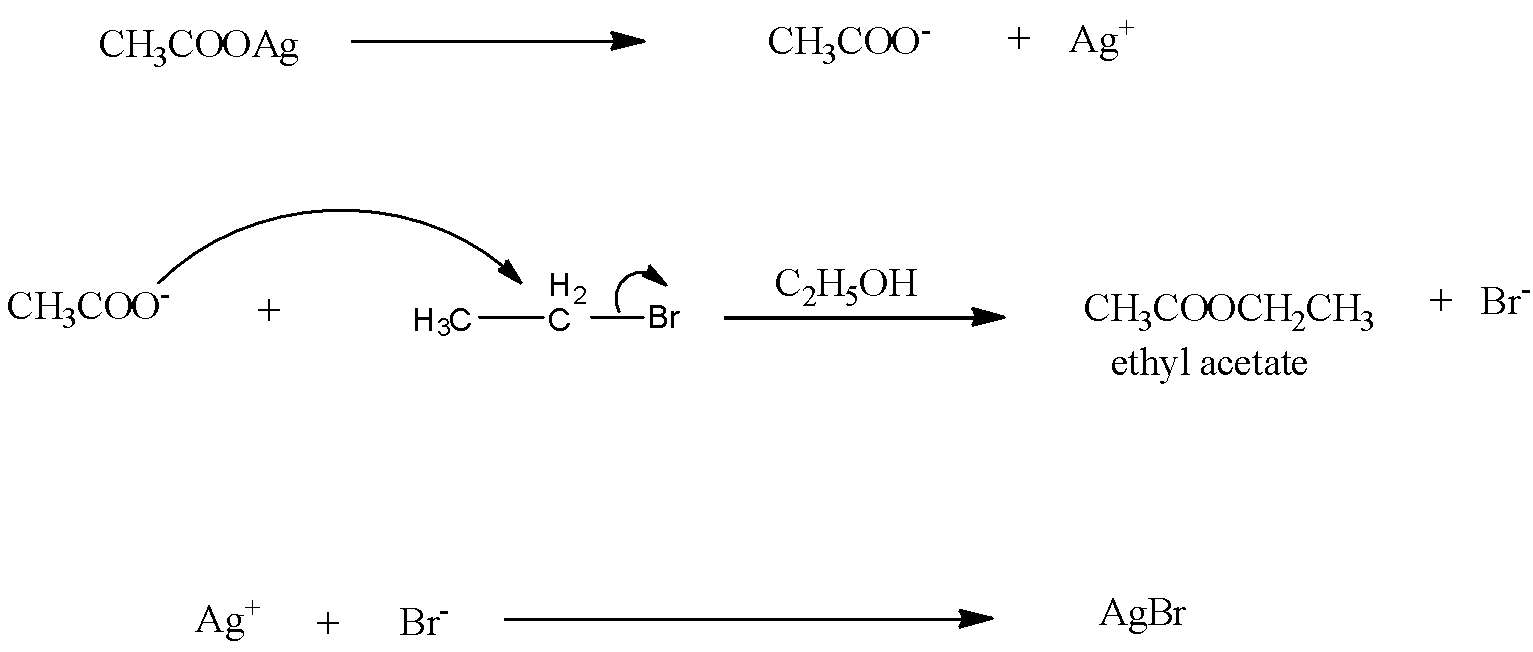
Note: Amongst the halide ions, the order in which the halogen ion departs follows the sequence:
${{I}^{-}}$ >$B{{r}^{-}}$ >$C{{l}^{-}}$ >${{F}^{-}}$ . it is because of this reason that the order of reactivity of haloalkanes follow the sequence: iodoalkanes > bromoalkanes > chloroalkanes > fluoroalkanes.
Complete step by step answer:
Ethyl bromide is a haloalkane and haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction.
The halogen atom in haloalkane is more electronegative than the carbon atom attached to it. As a result, the carbon atom acquires a partial positive charge and the halogen atom acquires a partial negative charge. The presence of this small positive charge on the carbon atom makes it susceptible to attack by nucleophilic reagent (i.e. reagent possessing a negative charge or a lone pair of electrons). Thus, when a nucleophile stronger than the halide ion approaches the positively charged carbon atom of an alkyl halide, the halogen atom with its bonding pair of electrons is displaced and a new bond between the carbon atom and the incoming nucleophile is formed:

Such a reaction in which a stronger nucleophile displaces a weaker nucleophile is called nucleophilic substitution reactions.
So, the silver acetate is the reagent in which the acetate ion is the negative charge and displaces the bromide ion in the ethyl bromide. In this reaction, an ester is formed. The product formed will be ethyl acetate or ethyl ethanoate.
The reaction is given below:
$C{{H}_{3}}COOAg+Br-C{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow[\Delta ]{{{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH}C{{H}_{3}}COOC{{H}_{2}}C{{H}_{3}}+AgBr$
The mechanism of the reaction is:
The silver acetate will split into ions. The negative part is acetate. This negative acetate will attack the positive ethyl group in the bromoethane. This will lead to the formation of ethyl acetate.

Note: Amongst the halide ions, the order in which the halogen ion departs follows the sequence:
${{I}^{-}}$ >$B{{r}^{-}}$ >$C{{l}^{-}}$ >${{F}^{-}}$ . it is because of this reason that the order of reactivity of haloalkanes follow the sequence: iodoalkanes > bromoalkanes > chloroalkanes > fluoroalkanes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




