
What is the action of bromine water on benzylamine (aniline) at room temperature?
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: In electrophilic aromatic substitution, an incoming electrophile is added to the aromatic ring which replaces the hydrogen atom of the aromatic ring. This is due to the electron density present in the benzene ring, it is able to attract an electrophile group.
Complete step by step answer:
Aniline is an aromatic compound in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by the amine group $ - N{H_2}$. The amine group is a ring activating group. This means that the amine group will increase the electron density on the benzene ring. As a result, the reaction will become much faster and the incoming electrophile will attach to the ring more fastly. This reaction is known as the electrophilic substitution reaction.
The reaction of bromine water with benzylamine is shown below.
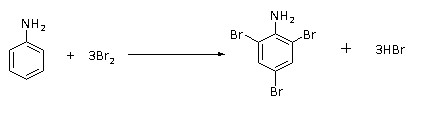
In this reaction, aniline reacts with bromine water with no catalyst involved to give tri substituted compound called 2,4,6-tribromoaniline by replacing three hydrogen atom of aniline ring with three bromine atom and the byproduct formed is hydrogen bromide.
The white precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline is formed.
Additional information: The $ - N{H_2}$ group present in the aromatic ring is a 2,4-directing effect. This means the incoming electrophile will get attached to the second position and the fourth position of the aromatic ring.
Note:
The bromine water is usually used for testing the double bond $C = C$. When bromine water is added to the benzylamine or phenol, the color of the bromine water decolorizes, and a white precipitate is formed. The formation of white precipitate predicts the presence of a double bond. To differentiate phenol from benzylamine, a solubility test is performed. Phenol is generally acidic in nature so when dissolved in sodium hydroxide forms a colorless solution on the other hand benzylamine is slightly basic in nature so it gives colorless (or pale brown solution) when reacted with hydrochloric acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Aniline is an aromatic compound in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by the amine group $ - N{H_2}$. The amine group is a ring activating group. This means that the amine group will increase the electron density on the benzene ring. As a result, the reaction will become much faster and the incoming electrophile will attach to the ring more fastly. This reaction is known as the electrophilic substitution reaction.
The reaction of bromine water with benzylamine is shown below.

In this reaction, aniline reacts with bromine water with no catalyst involved to give tri substituted compound called 2,4,6-tribromoaniline by replacing three hydrogen atom of aniline ring with three bromine atom and the byproduct formed is hydrogen bromide.
The white precipitate of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline is formed.
Additional information: The $ - N{H_2}$ group present in the aromatic ring is a 2,4-directing effect. This means the incoming electrophile will get attached to the second position and the fourth position of the aromatic ring.
Note:
The bromine water is usually used for testing the double bond $C = C$. When bromine water is added to the benzylamine or phenol, the color of the bromine water decolorizes, and a white precipitate is formed. The formation of white precipitate predicts the presence of a double bond. To differentiate phenol from benzylamine, a solubility test is performed. Phenol is generally acidic in nature so when dissolved in sodium hydroxide forms a colorless solution on the other hand benzylamine is slightly basic in nature so it gives colorless (or pale brown solution) when reacted with hydrochloric acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

How was the Civil Disobedience Movement different from class 12 social science CBSE

How is democracy better than other forms of government class 12 social science CBSE




