
What is the action of ammonia $N{{H}_{3}}$ on benzoic acid? Write equations.
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Benzoic acid has carboxyl group and ammonia is a base, so acid donates Hydrogen ion and ammonia accepts hydrogen ion to form ammonium salt and on heating high temperature, amide is formed.
Complete step by step answer:
- The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid. Benzoic acid is naturally present in many plants.
- Molar mass of benzoic acid is 122.
- Benzoic acid is prepared by oxidation of Toluene. On hydrolysis of Benzonitrile and Benzamide leads to formation of Benzoic acid.
- Benzyl alcohol on oxidation produces Benzoic acid.
- Benzoic acid is meta directing, so substituent is added to meta position to carboxyl group.
-benzoic acid is a weak acid and ammonia is a weak base, acid and base react to form salt and water.
-Benzoic acid is a weak acid, so it donates proton to ammonia and ammonia is a weak base, it accepts proton to form salt Ammonium Benzoate.
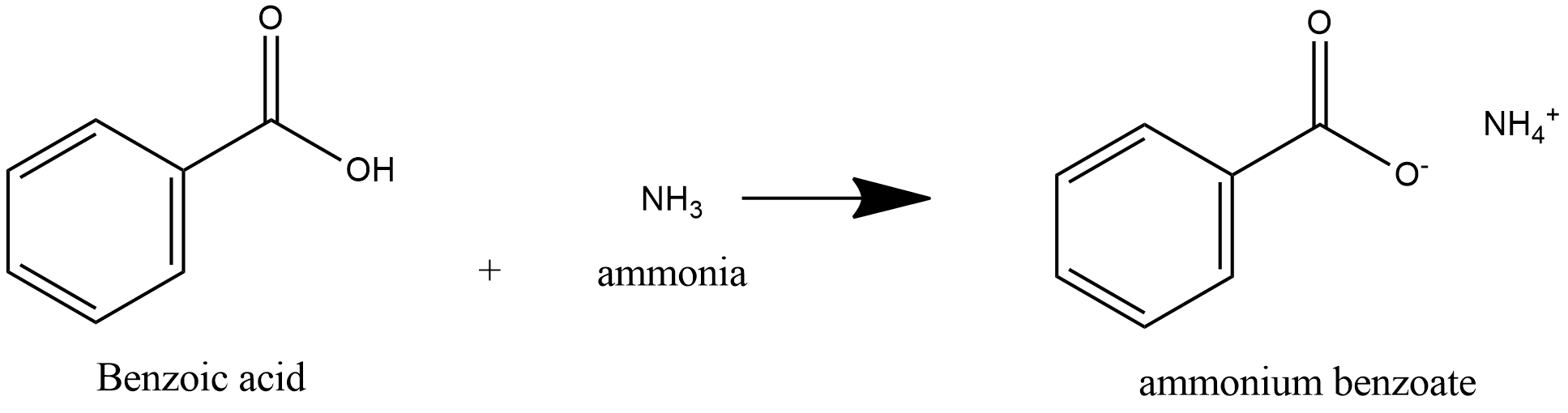
Further heating of ammonium benzoate leads to loss of water and leads to formation of Benzamide.
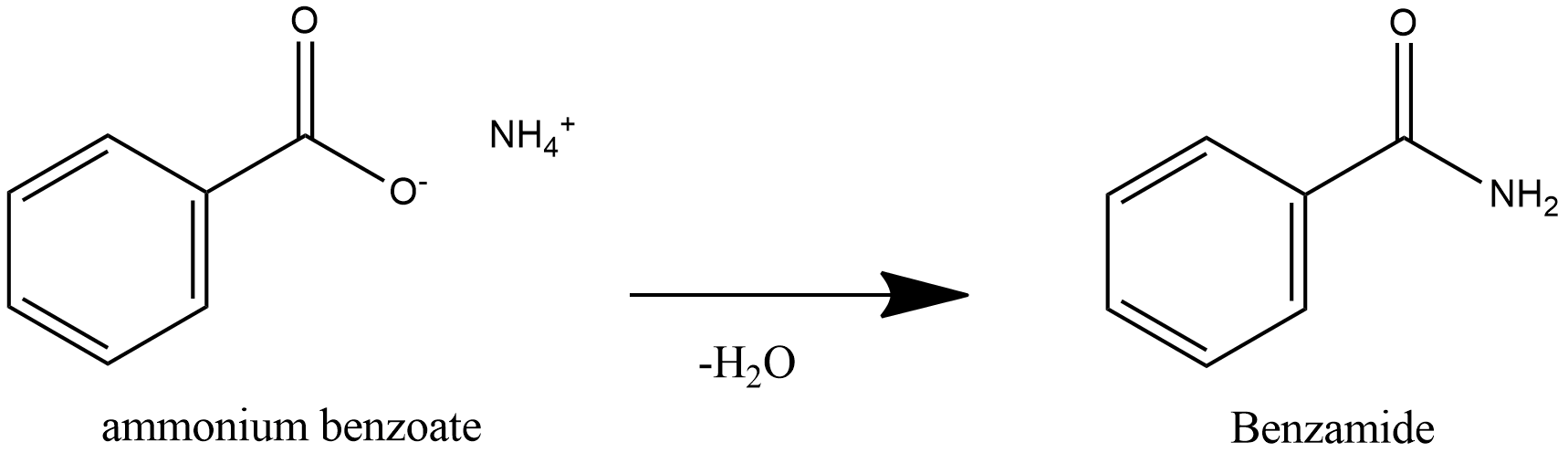
Benzamide on Hydrolysis produces Benzoic acid and Ammonia.
By carboxylation of phenyl magnesium halide, Benzoic acid is produced.
On vigorous oxidation of Alkyl benzene, benzoic acid is produced.
Ester, anhydride and acyl chloride on hydrolysis produces Carboxylic acid.
So, Benzoic acid reacts with ammonia to produce salt ammonium benzoate which on heating produces Benzamide.
Note: Benzoic acid is a weak acid and ammonia is weak base, acid and base react to form salt and water. Benzoic acid is a weak acid, so it donates proton to ammonia and ammonia is a weak base, it accepts proton to form salt Ammonium Benzoate. Further heating of ammonium benzoate leads to loss of water and leads to formation of Benzamide.
Complete step by step answer:
- The simplest aromatic carboxylic acid is benzoic acid. Benzoic acid is naturally present in many plants.
- Molar mass of benzoic acid is 122.
- Benzoic acid is prepared by oxidation of Toluene. On hydrolysis of Benzonitrile and Benzamide leads to formation of Benzoic acid.
- Benzyl alcohol on oxidation produces Benzoic acid.
- Benzoic acid is meta directing, so substituent is added to meta position to carboxyl group.
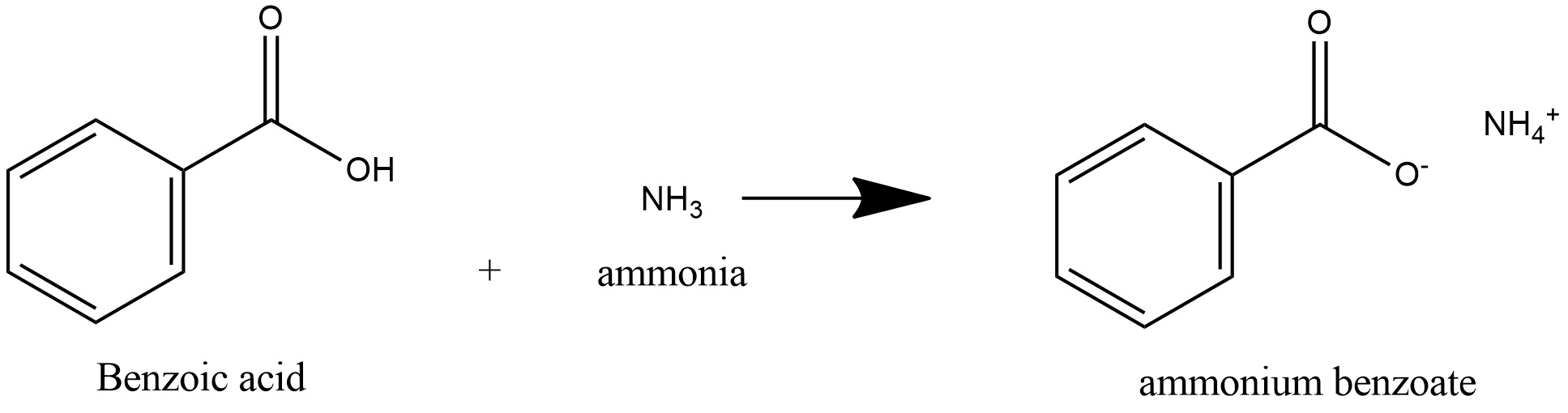
-benzoic acid is a weak acid and ammonia is a weak base, acid and base react to form salt and water.
-Benzoic acid is a weak acid, so it donates proton to ammonia and ammonia is a weak base, it accepts proton to form salt Ammonium Benzoate.

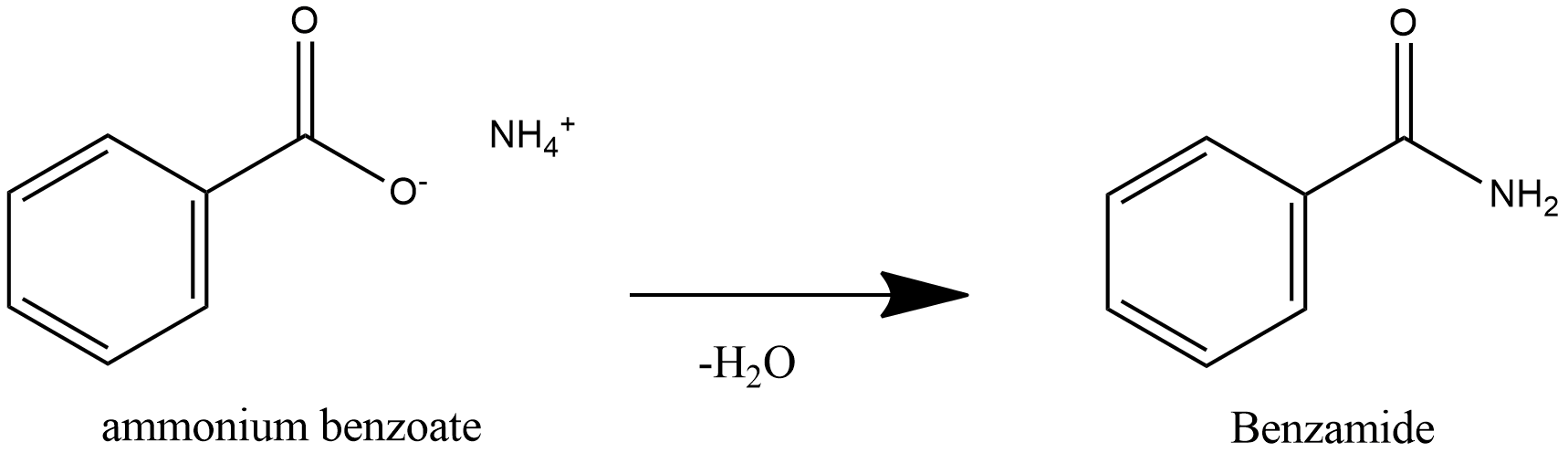
Further heating of ammonium benzoate leads to loss of water and leads to formation of Benzamide.

Benzamide on Hydrolysis produces Benzoic acid and Ammonia.
By carboxylation of phenyl magnesium halide, Benzoic acid is produced.
On vigorous oxidation of Alkyl benzene, benzoic acid is produced.
Ester, anhydride and acyl chloride on hydrolysis produces Carboxylic acid.
So, Benzoic acid reacts with ammonia to produce salt ammonium benzoate which on heating produces Benzamide.


Note: Benzoic acid is a weak acid and ammonia is weak base, acid and base react to form salt and water. Benzoic acid is a weak acid, so it donates proton to ammonia and ammonia is a weak base, it accepts proton to form salt Ammonium Benzoate. Further heating of ammonium benzoate leads to loss of water and leads to formation of Benzamide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




