
A uniform wire of length L is bent in the form of a circle. The shift in its centre of mass is
\[A.\,\dfrac{L}{\pi }\]
\[B.\,\dfrac{2L}{\pi }\]
\[C.\,\dfrac{L}{2\pi }\]
\[D.\,\dfrac{L}{3\pi }\]
Answer
523k+ views
Hint: It will be easy to solve this problem, by drawing the given situation, the shift in the centre of mass the mass can be determined. The length of the wire equals the circumference of the circle. Thus, using this, we will find the value of the radius of the circle, which equals the shift in its centre of the mass.
Formula used:
\[C=2\pi R\]
Complete answer:
The uniform wire is bent to form a circle. The length of the wire equals the circumference of the circle. As the circumference of the circle is the value of its boundary. In simple words, if we reform the circle into a straight wire, then, the length of the wire will be equal to that of the circumference of the circle.
The circumference of the circle is given by the formula as follows.
\[C=2\pi R\]
Where R is the radius of the circle.
The diagram representing the conversion of the uniform wire into a circle is as follows.
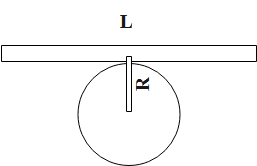
From given, we have the length of the wire to be equal to “L”.
So, we have, the circumference of the circle is equal to the length of the wire.
\[\begin{align}
& C=L \\
& \Rightarrow L=2\pi R \\
\end{align}\]
Now, rearrange the terms to find the equation, in terms of the length of the wire. So, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& L=2\pi R \\
& R=\dfrac{L}{2\pi } \\
\end{align}\]
We have found the equation in terms of the radius, because the centre of the mass shifts by a value equal to that of the radius of the circle.
At the value of the shift in the centre of the mass equals \[\dfrac{L}{2\pi }\].
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In this case, we are asked to find the value of the shift in the centre of the mass. In order to confuse us, instead of the circumference of the circle, it is being asked as the shift in the centre of the mass.
Formula used:
\[C=2\pi R\]
Complete answer:
The uniform wire is bent to form a circle. The length of the wire equals the circumference of the circle. As the circumference of the circle is the value of its boundary. In simple words, if we reform the circle into a straight wire, then, the length of the wire will be equal to that of the circumference of the circle.
The circumference of the circle is given by the formula as follows.
\[C=2\pi R\]
Where R is the radius of the circle.
The diagram representing the conversion of the uniform wire into a circle is as follows.

From given, we have the length of the wire to be equal to “L”.
So, we have, the circumference of the circle is equal to the length of the wire.
\[\begin{align}
& C=L \\
& \Rightarrow L=2\pi R \\
\end{align}\]
Now, rearrange the terms to find the equation, in terms of the length of the wire. So, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& L=2\pi R \\
& R=\dfrac{L}{2\pi } \\
\end{align}\]
We have found the equation in terms of the radius, because the centre of the mass shifts by a value equal to that of the radius of the circle.
At the value of the shift in the centre of the mass equals \[\dfrac{L}{2\pi }\].
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
In this case, we are asked to find the value of the shift in the centre of the mass. In order to confuse us, instead of the circumference of the circle, it is being asked as the shift in the centre of the mass.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




