
A uniform ladder of length L rests against the frictionless wall. The floor is rough and the coefficient of static friction between the floor and ladder is μ. When the ladder is positioned at angle θ, as shown in the accompanying, it is just about to slip. What is θ?
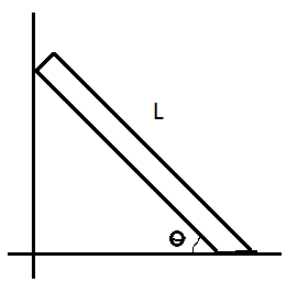
(A) \[\tan \theta =2\mu \]
(B) \[\cos \theta =\mu \]
(C) \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{1}{2\mu }\]
(D) \[\sin \theta =\dfrac{1}{\mu }\]

Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint:First all we have to make a free body diagram depicting clearly all the forces acting. Then we have to see whether any forces balance out each other or not. We have to then add the forces and arrive at our answer.
Complete step by step answer:
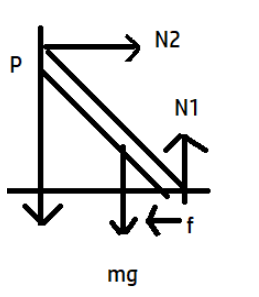
We have drawn a free body diagram and now we can easily solve this problem.
Since the body is in equilibrium, so sum of all the forces must be zero
In horizontal direction:
\[\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=f \\
&\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\mu mg \\
\end{align}\]
where f is the frictional force due to the floor whose coefficient of friction is \[\mu \]
In vertical direction:
\[\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=mg\]
Since the body is inclined it has the tendency to rotate but there is no rotation so the sum of all torque acting on the body is zero.
\[\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow \sum{\tau }=0 \\
&\Rightarrow \dfrac{mgL\cos \theta }{2}+fL\sin \theta ={{N}_{1}}L\cos \theta \\
&\Rightarrow \dfrac{mgL\cos \theta }{2}+\mu mgL\sin \theta =mgL\cos \theta \\
&\Rightarrow \mu mgL\sin \theta =\dfrac{mgL\cos \theta }{2} \\
&\therefore \tan \theta =\dfrac{1}{2\mu } \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct option comes out to be (C).
Note:Always keep in mind that frictional force opposes the relative motion of the two bodies. Here the ladder has the tendency to move leftwards, so frictional force acts towards right. Also, in accordance with Newton’s third law forces occur in pairs, that is the cause of origin of normal reaction.
Complete step by step answer:

We have drawn a free body diagram and now we can easily solve this problem.
Since the body is in equilibrium, so sum of all the forces must be zero
In horizontal direction:
\[\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=f \\
&\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\mu mg \\
\end{align}\]
where f is the frictional force due to the floor whose coefficient of friction is \[\mu \]
In vertical direction:
\[\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=mg\]
Since the body is inclined it has the tendency to rotate but there is no rotation so the sum of all torque acting on the body is zero.
\[\begin{align}
&\Rightarrow \sum{\tau }=0 \\
&\Rightarrow \dfrac{mgL\cos \theta }{2}+fL\sin \theta ={{N}_{1}}L\cos \theta \\
&\Rightarrow \dfrac{mgL\cos \theta }{2}+\mu mgL\sin \theta =mgL\cos \theta \\
&\Rightarrow \mu mgL\sin \theta =\dfrac{mgL\cos \theta }{2} \\
&\therefore \tan \theta =\dfrac{1}{2\mu } \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct option comes out to be (C).
Note:Always keep in mind that frictional force opposes the relative motion of the two bodies. Here the ladder has the tendency to move leftwards, so frictional force acts towards right. Also, in accordance with Newton’s third law forces occur in pairs, that is the cause of origin of normal reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




