
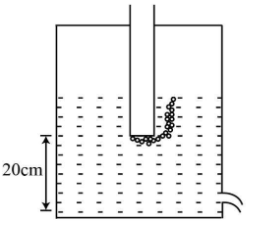
A tube is attached as shown in a closed vessel containing water. The velocity of water coming out from a small hole is
\[A.\,\sqrt{2}{m}/{s}\;\]
\[B.\,2{m}/{s}\;\]
C. Depends on the pressure of the air inside the vessel
D. none of these

Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: This problem can be solved using the concept of Bernoulli’s theorem. Bernoulli's theorem states that "The decrease in the pressure (or potential energy) of a fluid is the effect of the increase in its speed." that is, the reduction in the pressure of fluid occurs when that fluid speeds up.
Formula used:
\[{{P}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{1}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{2}}\]
Complete answer:
From given, we have,
The height of the water level = 20 cm
Therefore, the height = 0.2 m
The velocity of water coming out from a small hole, \[{{v}_{2}}\]= ?
The pressure at the bottom of the tube inserted in a closed vessel is equal to the pressure at a small hole present at the bottom of the closed vessel.
Let the velocity of the water at the bottom of the test tube be \[{{v}_{1}}\]
Let the velocity of the water at the small hole of the closed vessel be \[{{v}_{2}}\]
The velocity \[{{v}_{1}}\] is so small that it can be considered to be equal to zero.
We use Bernoulli’s theorem to solve this problem. Bernoulli’s equation is given by,
Energy per unit volume before = Energy per unit volume after
\[{{P}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{1}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{2}}\]
Where \[P\]is the pressure energy, \[\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}^{2}}\]is the kinetic energy per unit volume and \[\rho gh\]is the potential energy per unit volume.
As the position of the small hole is at the bottom, thus the height is considered to be zero.
From given conditions, we have,
\[{{P}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}\], \[{{h}_{2}}=0\]and \[{{v}_{1}}=0\]
Substitute these values in the above equation.
\[\begin{align}
& {{P}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{1}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{2}} \\
& P+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{(0)}^{2}}+\rho g{{h}_{1}}=P+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2}+\rho g(0) \\
& \rho g{{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Rearrange the above terms to obtain the expression in terms of \[{{v}_{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& {{v}_{2}}^{2}=2g{{h}_{1}} \\
& {{v}_{2}}=\sqrt{2g{{h}_{1}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Substitute the given values in the above equation to find the velocity of the water coming out from a small hole.
\[\begin{align}
& {{v}_{2}}=\sqrt{2\times 10\times 0.2} \\
& {{v}_{2}}=\sqrt{4} \\
& {{v}_{2}}=2{m}/{s}\; \\
\end{align}\]
As the value of the velocity of the water coming out from a small hole is equal to\[2{m}/{s}\;\] .
Thus, the option (B) is correct.
Note: The things to be on your finger-tips for further information on solving these types of problems are: The heights should also be considered, as in this case, the small hole was at the bottom of the vessel, so considered to be zero. Even the units of the height should be considered.
Formula used:
\[{{P}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{1}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{2}}\]
Complete answer:
From given, we have,
The height of the water level = 20 cm
Therefore, the height = 0.2 m
The velocity of water coming out from a small hole, \[{{v}_{2}}\]= ?
The pressure at the bottom of the tube inserted in a closed vessel is equal to the pressure at a small hole present at the bottom of the closed vessel.
Let the velocity of the water at the bottom of the test tube be \[{{v}_{1}}\]
Let the velocity of the water at the small hole of the closed vessel be \[{{v}_{2}}\]
The velocity \[{{v}_{1}}\] is so small that it can be considered to be equal to zero.
We use Bernoulli’s theorem to solve this problem. Bernoulli’s equation is given by,
Energy per unit volume before = Energy per unit volume after
\[{{P}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{1}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{2}}\]
Where \[P\]is the pressure energy, \[\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}^{2}}\]is the kinetic energy per unit volume and \[\rho gh\]is the potential energy per unit volume.
As the position of the small hole is at the bottom, thus the height is considered to be zero.
From given conditions, we have,
\[{{P}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}\], \[{{h}_{2}}=0\]and \[{{v}_{1}}=0\]
Substitute these values in the above equation.
\[\begin{align}
& {{P}_{1}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{1}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2}+\rho g{{h}_{2}} \\
& P+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{(0)}^{2}}+\rho g{{h}_{1}}=P+\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2}+\rho g(0) \\
& \rho g{{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\rho {{v}_{2}}^{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Rearrange the above terms to obtain the expression in terms of \[{{v}_{2}}\]
\[\begin{align}
& {{v}_{2}}^{2}=2g{{h}_{1}} \\
& {{v}_{2}}=\sqrt{2g{{h}_{1}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Substitute the given values in the above equation to find the velocity of the water coming out from a small hole.
\[\begin{align}
& {{v}_{2}}=\sqrt{2\times 10\times 0.2} \\
& {{v}_{2}}=\sqrt{4} \\
& {{v}_{2}}=2{m}/{s}\; \\
\end{align}\]
As the value of the velocity of the water coming out from a small hole is equal to\[2{m}/{s}\;\] .
Thus, the option (B) is correct.
Note: The things to be on your finger-tips for further information on solving these types of problems are: The heights should also be considered, as in this case, the small hole was at the bottom of the vessel, so considered to be zero. Even the units of the height should be considered.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




