
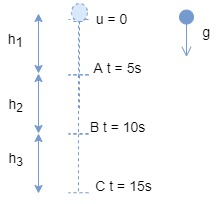
A stone falls freely under gravity. It covers distance $ {{h}_{1}} $ $ {{h}_{2}} $ and $ {{h}_{3}} $ in the first 5 seconds, the next 5 seconds and the next 5 seconds respectively. The relation between $ {{h}_{1}} $ , $ {{h}_{2}} $ and $ {{h}_{3}} $ is:
(A) $ {{h}_{1}}=2{{h}_{2}}=3{{h}_{3}} $
(B) $ {{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{{{h}_{2}}}{3}=\dfrac{{{h}_{3}}}{5} $
(C) $ {{h}_{2}}=3{{h}_{1}}\text{ }and\text{ }{{h}_{3}}=3{{h}_{2}} $
(D) $ {{h}_{1}}={{h}_{2}}={{h}_{3}} $
Answer
553.8k+ views
Hint: We can use position time relation which is given by
$ S=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}} $
Here, S is distance travelled in time t,
u is the initial velocity,
a is the acceleration and t is time taken.
In case of free fall, if downward direction is taken positive and object is released from rest, then
$ u=0,\text{ }a=g=10m/{{s}^{2}},\text{ }S=h $
In case of free fall, if downward direction is taken negative and object is released from set, then
$ u=0,\text{ }a=-g=-10m/{{s}^{2}},\text{ }S=-h $ .
Complete step by step solution
We have, given
Stone is falling freely under gravity.
It means, if we will take downward as negative
Then, $ a=-g $
$ S=-{{h}_{1}} $
Case I: Where $ {{h}_{1}} $ is the distance covered in first seconds,
Here, stone is falling freely hence take initial velocity as zero.
$ u=0 $ , t=5s is given
Then use distance/position-time relation
$ S=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}} $
Here, $ a=-g $ , means acceleration due to gravity.
Put all the above values:
$ {{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{25}{2}g $ ; $ -{{h}_{1}}=0\left( 5 \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( -g \right){{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}} $
$ -{{h}_{1}}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\times g{{\left( 25 \right)}^{{}}} $
$ {{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{25}{2}g $ ----------(2)
Now in Case II:
Distance travelled by stone in next 5 seconds,
Now total distance covered will be, $ S=-\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right) $ [negative sign shows just direction of measurement]
And total time taken, t=5+5=10s
Put the above values in eq, (1)
$ -\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right)=0\left( 10 \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( -g \right){{\left( 10 \right)}^{2}} $
$ \left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}g\left( 100 \right)=\dfrac{100}{2}g $ ---------(3)
Case III:
Distance travelled by stone in next 5 seconds,
Total distance covered $ S=-\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{3}} \right) $
Total time taken $ t=5+5+5=15s $
Put the values in eq. (1)
$ -\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{3}} \right)=-\dfrac{1}{2}g{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}} $
$ \left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{3}} \right)=\dfrac{225}{2}g $ ------- (4)
Solve eq. (2) and (3)
$ \left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right)-{{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{100}{2}g-\dfrac{25}{2}g $
$ {{h}_{2}}=\dfrac{75}{2}g $ -------- (5)
Solve eq. (3) and (4),
$ \left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{3}} \right)-\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right)=\dfrac{225}{2}g-\dfrac{100}{2}g $
$ {{h}_{3}}=\dfrac{125}{2}g $ --------- (6)
Write eq. (5) and (6) in terms of
$ {{h}_{2}}=\dfrac{25}{2}\times 3g\to {{h}_{2}}=3{{h}_{1}} $ ---------- (7)
$ {{h}_{3}}=\dfrac{25}{2}\times 5g\to {{h}_{3}}=5{{h}_{1}} $ ----------- (8)
From eq. (7) and (8),
$ {{h}_{1}}={{\dfrac{{{h}_{2}}}{3}}_{{}}}=\dfrac{{{h}_{3}}}{5} $ This is required result.
Therefore option (B) is the correct answer.
Note
We can also, use direct formula, Distance travelled in the second by,
$ {{D}_{n}}=u+\dfrac{a}{2}\left( 2n-1 \right) $
Here, n is nth second, above question n is given as 5s.
Using the above formula we will get the same answer.
$ S=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}} $
Here, S is distance travelled in time t,
u is the initial velocity,
a is the acceleration and t is time taken.
In case of free fall, if downward direction is taken positive and object is released from rest, then
$ u=0,\text{ }a=g=10m/{{s}^{2}},\text{ }S=h $
In case of free fall, if downward direction is taken negative and object is released from set, then
$ u=0,\text{ }a=-g=-10m/{{s}^{2}},\text{ }S=-h $ .
Complete step by step solution
We have, given
Stone is falling freely under gravity.
It means, if we will take downward as negative
Then, $ a=-g $
$ S=-{{h}_{1}} $
Case I: Where $ {{h}_{1}} $ is the distance covered in first seconds,
Here, stone is falling freely hence take initial velocity as zero.
$ u=0 $ , t=5s is given
Then use distance/position-time relation
$ S=ut+\dfrac{1}{2}a{{t}^{2}} $
Here, $ a=-g $ , means acceleration due to gravity.
Put all the above values:

$ {{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{25}{2}g $ ; $ -{{h}_{1}}=0\left( 5 \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( -g \right){{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}} $
$ -{{h}_{1}}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\times g{{\left( 25 \right)}^{{}}} $
$ {{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{25}{2}g $ ----------(2)
Now in Case II:
Distance travelled by stone in next 5 seconds,
Now total distance covered will be, $ S=-\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right) $ [negative sign shows just direction of measurement]
And total time taken, t=5+5=10s
Put the above values in eq, (1)
$ -\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right)=0\left( 10 \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left( -g \right){{\left( 10 \right)}^{2}} $
$ \left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}g\left( 100 \right)=\dfrac{100}{2}g $ ---------(3)
Case III:
Distance travelled by stone in next 5 seconds,
Total distance covered $ S=-\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{3}} \right) $
Total time taken $ t=5+5+5=15s $
Put the values in eq. (1)
$ -\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{3}} \right)=-\dfrac{1}{2}g{{\left( 15 \right)}^{2}} $
$ \left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{3}} \right)=\dfrac{225}{2}g $ ------- (4)
Solve eq. (2) and (3)
$ \left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right)-{{h}_{1}}=\dfrac{100}{2}g-\dfrac{25}{2}g $
$ {{h}_{2}}=\dfrac{75}{2}g $ -------- (5)
Solve eq. (3) and (4),
$ \left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}}+{{h}_{3}} \right)-\left( {{h}_{1}}+{{h}_{2}} \right)=\dfrac{225}{2}g-\dfrac{100}{2}g $
$ {{h}_{3}}=\dfrac{125}{2}g $ --------- (6)
Write eq. (5) and (6) in terms of
$ {{h}_{2}}=\dfrac{25}{2}\times 3g\to {{h}_{2}}=3{{h}_{1}} $ ---------- (7)
$ {{h}_{3}}=\dfrac{25}{2}\times 5g\to {{h}_{3}}=5{{h}_{1}} $ ----------- (8)
From eq. (7) and (8),
$ {{h}_{1}}={{\dfrac{{{h}_{2}}}{3}}_{{}}}=\dfrac{{{h}_{3}}}{5} $ This is required result.
Therefore option (B) is the correct answer.
Note
We can also, use direct formula, Distance travelled in the second by,
$ {{D}_{n}}=u+\dfrac{a}{2}\left( 2n-1 \right) $
Here, n is nth second, above question n is given as 5s.
Using the above formula we will get the same answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




