
A semiconductor of Ge can be made p-type by adding:
(A) Trivalent Impurity
(B) Tetravalent Impurity
(C) Pentavalent impurity
(D) Divalent impurity
Answer
592.5k+ views
Hint: p-type semiconductor has impurity of atoms having three electrons in the outermost shell. For Ex. Ga, In and Al. The trivalent impurity belongs to group 13 of periodic table. Valency of Ge is 4. Pentavalent impurities belong to Group 15 of periodic table. Ge belongs to Group 14 of periodic table.
Formula used:
Complete step by step answer:
- In pure state, Ge atoms share four outermost electrons with adjacent Ge atoms. Hence there are no free electrons at room temperature. This is an example of intrinsic or pure semiconductor. Intrinsic or pure semiconductors are those which are free from impurities or are free from dopants species.
The electronic configuration of Ge is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{2}}$
As valency of Ge is 4, it forms a covalent bond with adjacent Ge atoms.
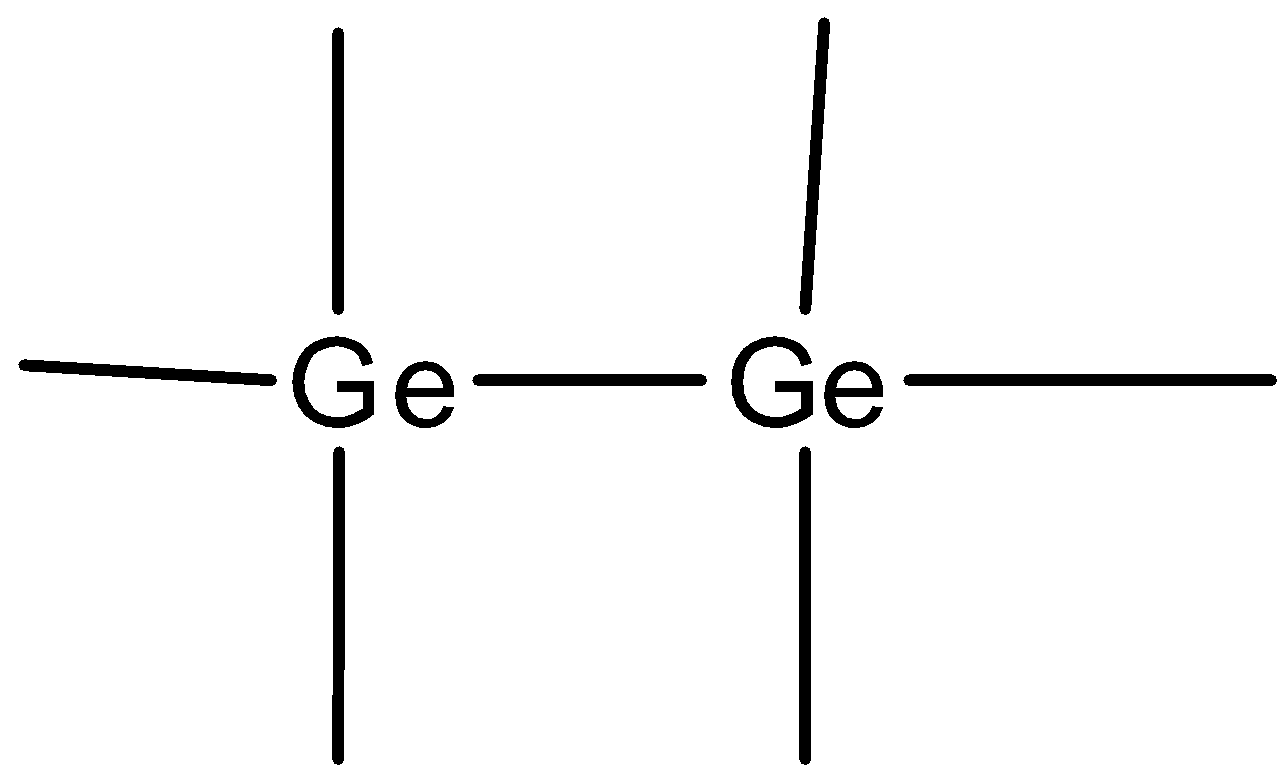
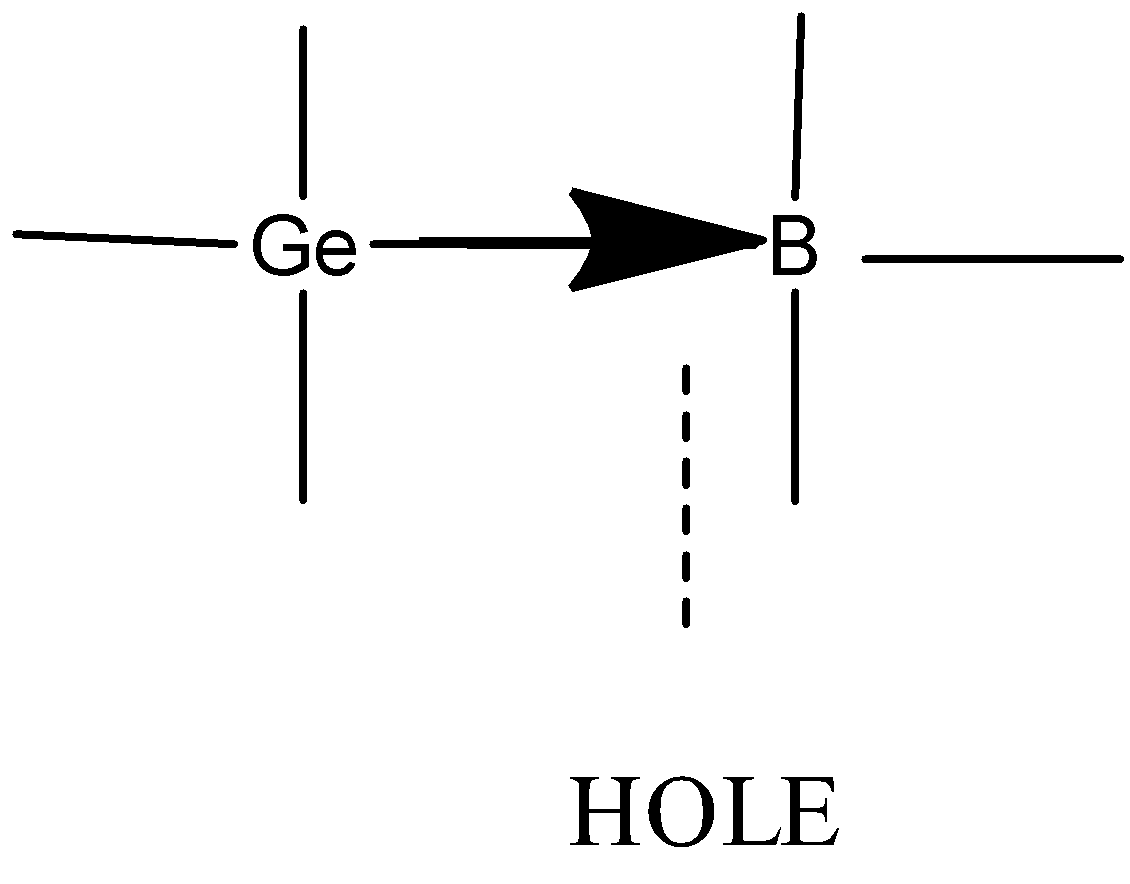
- When trivalent impurity (atom having three electrons in outermost shell Ex. Ga, In, Al) is added to an intrinsic semiconductor, Ge atom is replaced with trivalent atom , three electrons are paired and three covalent bonds are formed . One electron remains unpaired which creates a vacant state for electrons often called as hole.
The electronic configuration of boron is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$. Valency of boron is 3.
- When pentavalent impurity (atom having five electrons in outermost shell Ex. Phosphorous) is added to an intrinsic semiconductor, Ge atom is replaced with pentavalent atom which gives free electron.






- The process of adding impurities in pure semiconductors is called doping which leads to formation of Extrinsic semiconductors.
So, a semiconductor of Ge can be made p type by adding trivalent impurity, so option A is correct.
Note: Group IV Elements like Si, Ge are semiconductors which have conductivity between Conductors and Insulators. They have Four Valence electrons, when trivalent (Group lll) impurity is added, it forms three covalent bonds and leaves a hole leading to formation of. P-type or Positive Semiconductor. When pentavalent impurity (group V) is added, it forms four covalent bonds which give free electrons to the semiconductor. As electrons are negative, it produces n type semiconductor. P-type impurities are called acceptors and n-type semiconductors are called donors as it gives free electrons to the semiconductor.
Formula used:
Complete step by step answer:
- In pure state, Ge atoms share four outermost electrons with adjacent Ge atoms. Hence there are no free electrons at room temperature. This is an example of intrinsic or pure semiconductor. Intrinsic or pure semiconductors are those which are free from impurities or are free from dopants species.
The electronic configuration of Ge is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{6}}3{{s}^{2}}3{{p}^{6}}3{{d}^{10}}4{{s}^{2}}4{{p}^{2}}$
As valency of Ge is 4, it forms a covalent bond with adjacent Ge atoms.

- When trivalent impurity (atom having three electrons in outermost shell Ex. Ga, In, Al) is added to an intrinsic semiconductor, Ge atom is replaced with trivalent atom , three electrons are paired and three covalent bonds are formed . One electron remains unpaired which creates a vacant state for electrons often called as hole.
The electronic configuration of boron is $1{{s}^{2}}2{{s}^{2}}2{{p}^{1}}$. Valency of boron is 3.

- When pentavalent impurity (atom having five electrons in outermost shell Ex. Phosphorous) is added to an intrinsic semiconductor, Ge atom is replaced with pentavalent atom which gives free electron.






- The process of adding impurities in pure semiconductors is called doping which leads to formation of Extrinsic semiconductors.
So, a semiconductor of Ge can be made p type by adding trivalent impurity, so option A is correct.
Note: Group IV Elements like Si, Ge are semiconductors which have conductivity between Conductors and Insulators. They have Four Valence electrons, when trivalent (Group lll) impurity is added, it forms three covalent bonds and leaves a hole leading to formation of. P-type or Positive Semiconductor. When pentavalent impurity (group V) is added, it forms four covalent bonds which give free electrons to the semiconductor. As electrons are negative, it produces n type semiconductor. P-type impurities are called acceptors and n-type semiconductors are called donors as it gives free electrons to the semiconductor.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




