
A prism has a refracting angle of ${60^0}$. When placed in the position of minimum deviation, it produces a deviation of ${30^0}$. The angle of incidence is
A. ${30^0}$
B. ${45^0}$
C. ${15^0}$
D. ${60^0}$
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: White light is an EM wave which is made up of various colored rays with different wavelengths. Now when this light wave is passed into any transparent material time of interaction of individual constituent rays with atoms of that material determines the structure of the light coming out the prism. But when a light of only one color(monochromatic light) is passed into prism that light suffers deviation. There will be some minimum value for this deviation.
Formula used:
$i + e = A + \delta $
Complete step-by-step answer:
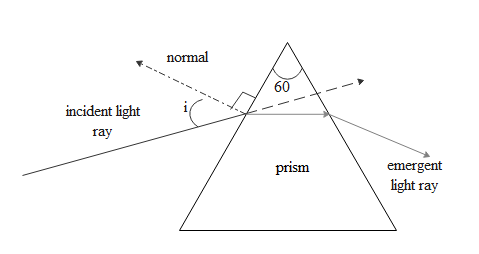
Let us assume incident ray is incident at an angle $i$ with the normal and it emerged out with the angle $e$deviation of $\delta $.
Now in case of minimum deviation the incident angle and the emergent angle will be the same. Let $A$ be the refractive angle of a prism.
Then there is a relation $i + e = A + \delta $
In case of minimum deviation as incident angle is equal to emerging angle we have $i = e$
so we get
$\eqalign{
& 2i = A + \delta \cr
& i = \dfrac{{A + \delta }}{2} \cr
& A = {60^0},\delta = {30^0} \cr
& i = \dfrac{{{{60}^0} + {{30}^0}}}{2} \cr
& i = {45^0} \cr} $
Hence angle of incidence will be ${45^0}$
Additional Information: We considered monochromatic light only because when white light is passed through prism the light gets separated into its individual component colors and gets out of that prism. This process of separation of light into its individual components is called dispersion of light. In case of monochromatic light only deviation happens and dispersion can’t happen.
Note: It is observed during the experiment that for a prism when incident and emerging angles become equal, we get minimum deviation hence it is totally experimental and no derivation for this. But if we place another prism closer to this prism in an inverted position with the same refracting angle then the final ray coming out of the second prism will have zero deviation with incident ray.
Formula used:
$i + e = A + \delta $
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume incident ray is incident at an angle $i$ with the normal and it emerged out with the angle $e$deviation of $\delta $.
Now in case of minimum deviation the incident angle and the emergent angle will be the same. Let $A$ be the refractive angle of a prism.
Then there is a relation $i + e = A + \delta $
In case of minimum deviation as incident angle is equal to emerging angle we have $i = e$

so we get
$\eqalign{
& 2i = A + \delta \cr
& i = \dfrac{{A + \delta }}{2} \cr
& A = {60^0},\delta = {30^0} \cr
& i = \dfrac{{{{60}^0} + {{30}^0}}}{2} \cr
& i = {45^0} \cr} $
Hence angle of incidence will be ${45^0}$
Additional Information: We considered monochromatic light only because when white light is passed through prism the light gets separated into its individual component colors and gets out of that prism. This process of separation of light into its individual components is called dispersion of light. In case of monochromatic light only deviation happens and dispersion can’t happen.
Note: It is observed during the experiment that for a prism when incident and emerging angles become equal, we get minimum deviation hence it is totally experimental and no derivation for this. But if we place another prism closer to this prism in an inverted position with the same refracting angle then the final ray coming out of the second prism will have zero deviation with incident ray.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




