
A population of organisms has a gene for which there are two alleles, D and d. The allele frequency of D = 0.8. If this population satisfies all five of the Hardy-Weinberg conditions, what are the genotype frequencies that are expected in the next generation?
A. DD = 0.04; Dd = 0.32; dd = 0.64
B. DD = 0.64; Dd = 0.32; dd = 0.64
C. DD = 0.04; Dd= 0.64; dd= 0.32
D. DD = 0.64; Dd = 0.32; dd = 0.04
Answer
367.2k+ views
Hint: The Hardy-Weinberg model explains how a population can remain at genetic equilibrium, known as Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Genetic equilibrium takes place when there is no evolution within the population. In other words, the frequency of alleles (variants of a gene) will be similar from one generation to another.
Complete Step-by-step answer:
The Hardy–Weinberg principle relates allele frequencies to genotype frequencies in a randomly reproducing population. Consider a population with two alleles (A and B) that segregate at one locus. The frequency of allele A signified by p and the frequency of allele B is signified by q. The Hardy–Weinberg principle declares that after one generation of random breeding genotype frequencies will be
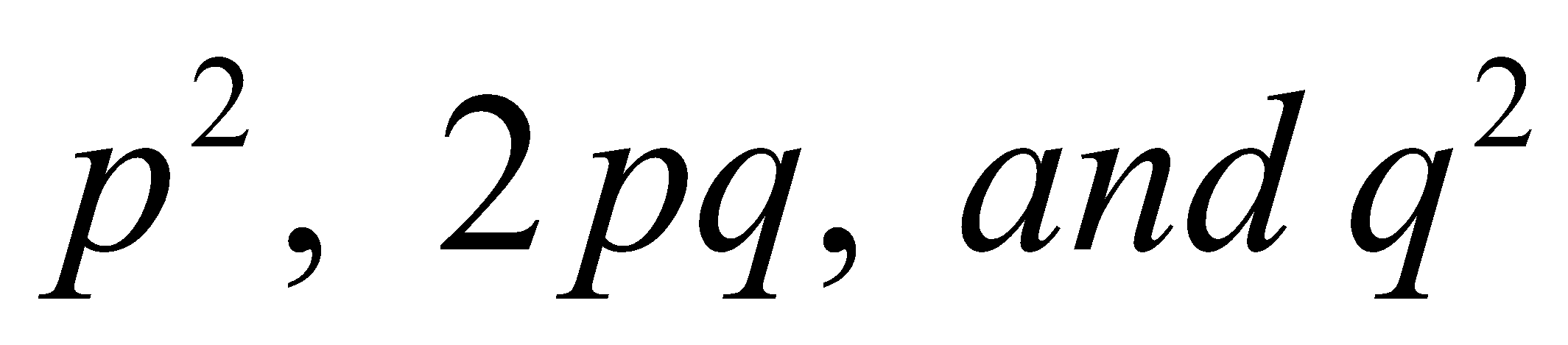 .
.
In the absence of other evolutionary forces (like natural selection), genotype frequencies should remain constant, and the population is said to be at Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium.
We are told that the allele frequency for D = 0.8; thus, the frequency of d= 0.2. These values are the p and q that we have to calculate the genotype frequencies in the next generation. By using a Hardy- Weinberg equation,
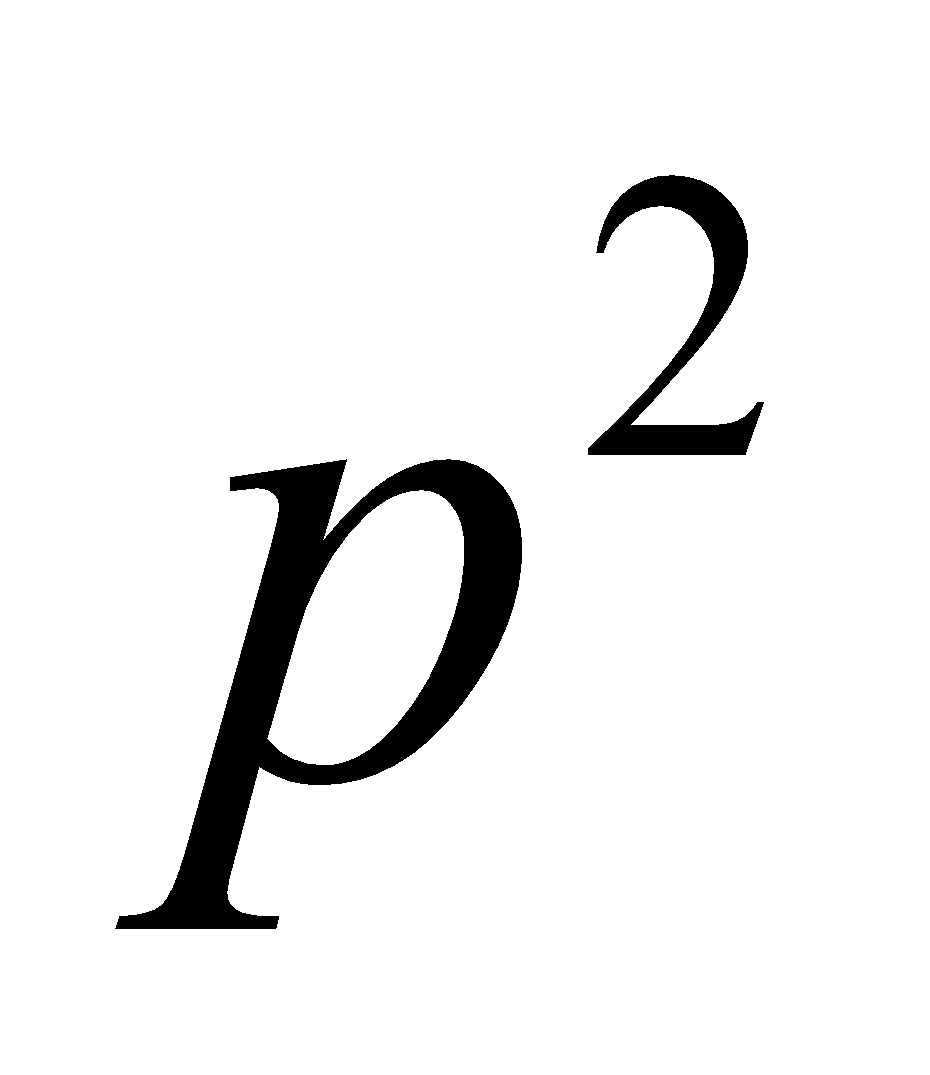 |(DD) = 0.64,
|(DD) = 0.64,
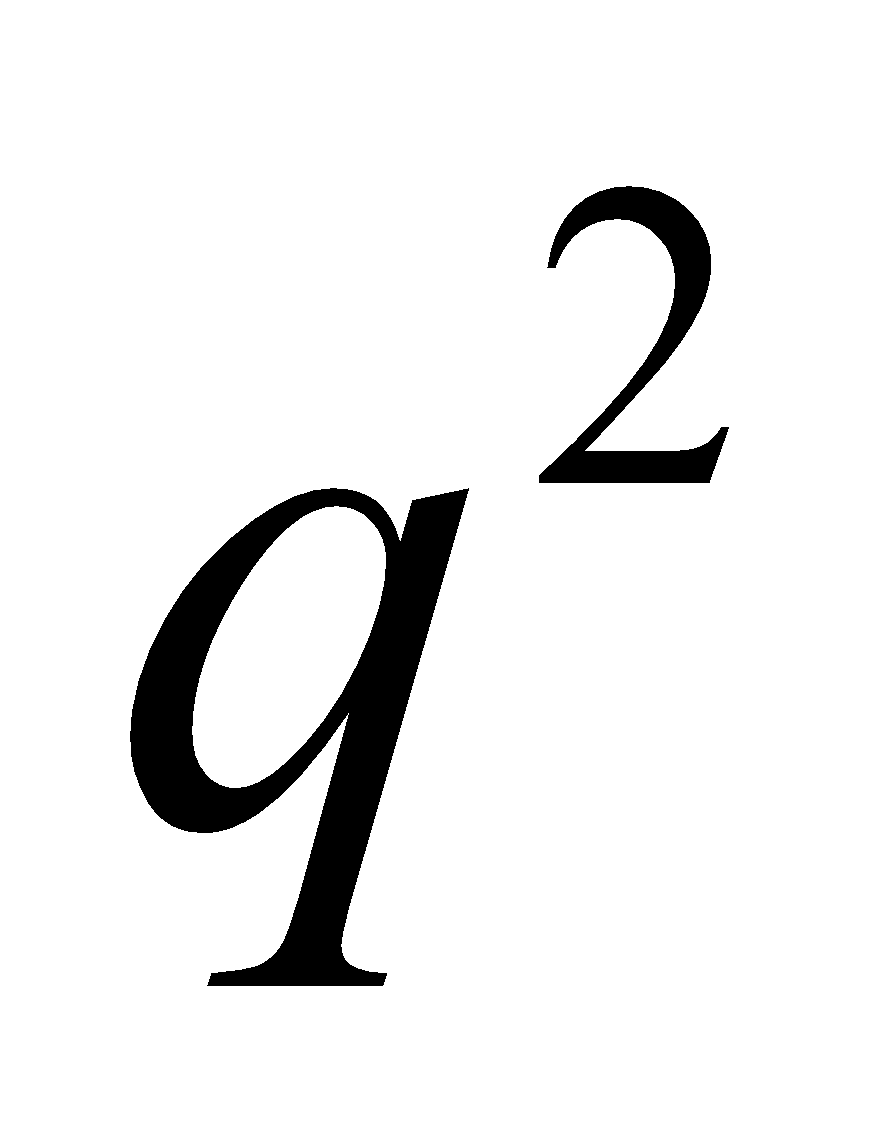 |(dd) = 0.04 and 2pq (Dd) = 0.32.
|(dd) = 0.04 and 2pq (Dd) = 0.32.
Therefore the correct answer is Option D.
Note: The Hardy–Weinberg principle is based on a number of assumptions like random mating (i.e, population structure is not present and mating takes place in direct proportion to genotype frequencies), the lack of natural selection, very high population size (i.e., genetic drift is negligible), no gene flow or migration, no mutation, and the locus is autosomal.
Complete Step-by-step answer:
The Hardy–Weinberg principle relates allele frequencies to genotype frequencies in a randomly reproducing population. Consider a population with two alleles (A and B) that segregate at one locus. The frequency of allele A signified by p and the frequency of allele B is signified by q. The Hardy–Weinberg principle declares that after one generation of random breeding genotype frequencies will be
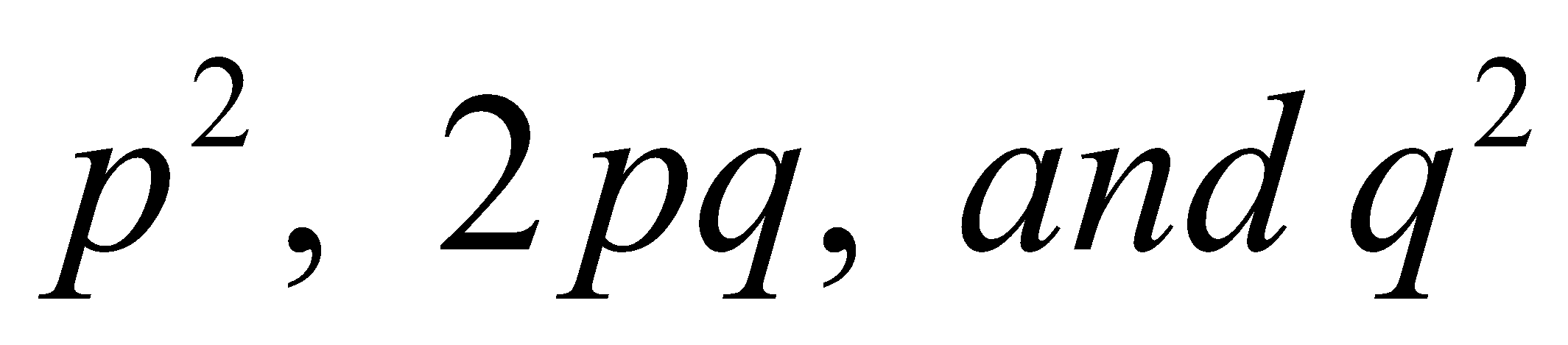
In the absence of other evolutionary forces (like natural selection), genotype frequencies should remain constant, and the population is said to be at Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium.
We are told that the allele frequency for D = 0.8; thus, the frequency of d= 0.2. These values are the p and q that we have to calculate the genotype frequencies in the next generation. By using a Hardy- Weinberg equation,
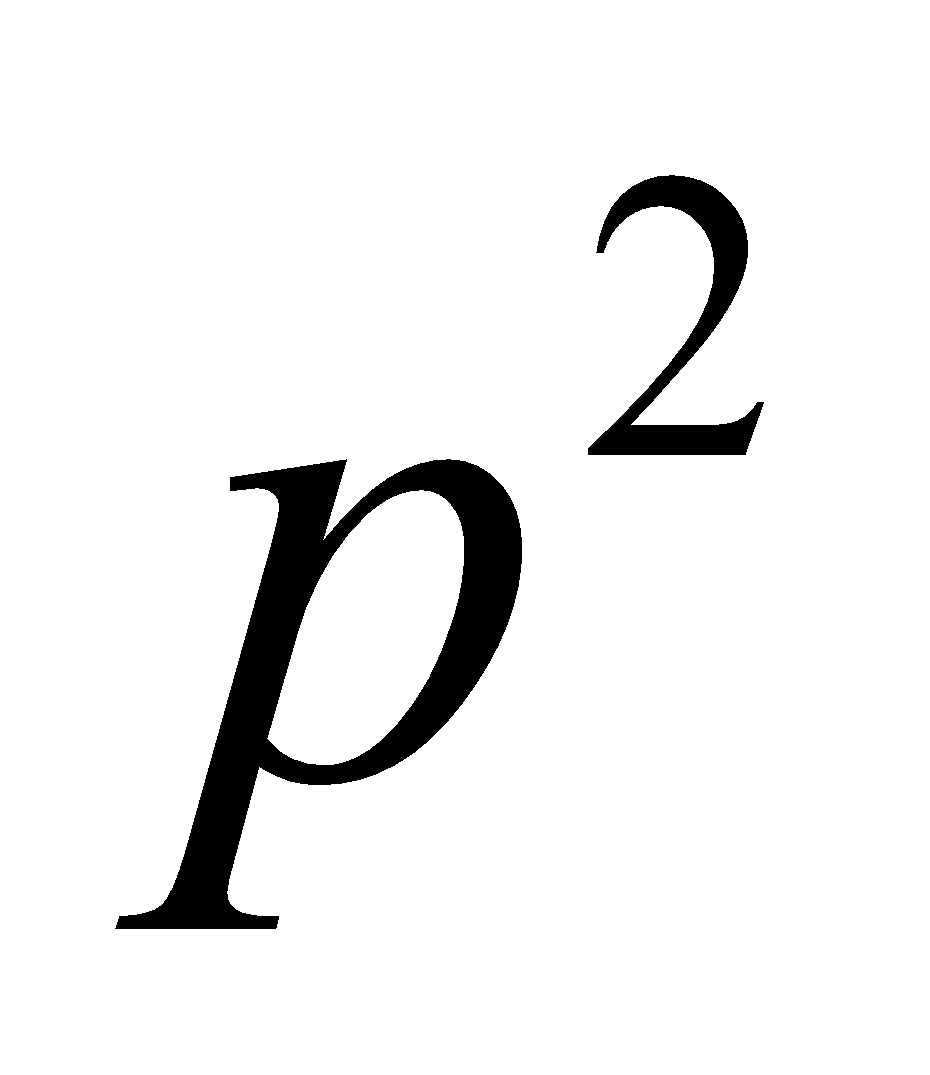
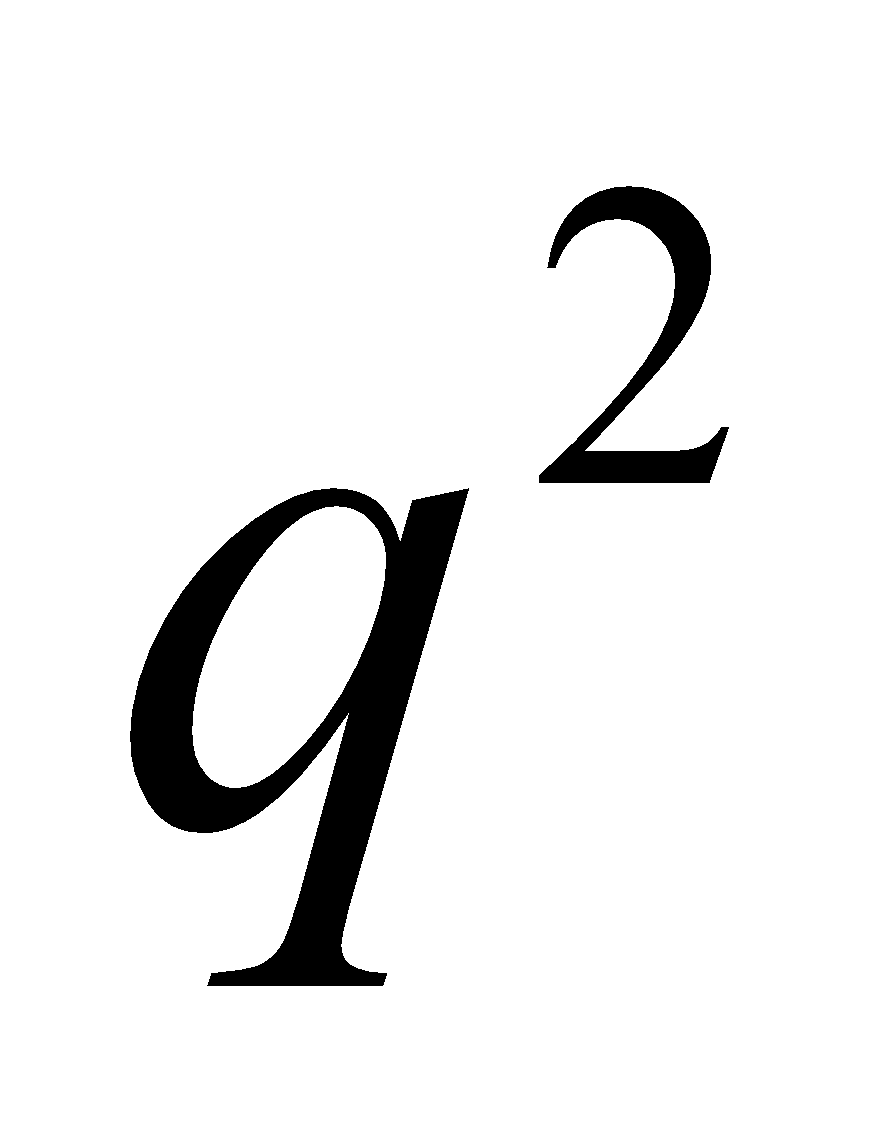
Therefore the correct answer is Option D.
Note: The Hardy–Weinberg principle is based on a number of assumptions like random mating (i.e, population structure is not present and mating takes place in direct proportion to genotype frequencies), the lack of natural selection, very high population size (i.e., genetic drift is negligible), no gene flow or migration, no mutation, and the locus is autosomal.
Recently Updated Pages
Choose the incorrect statement regarding the HardyWeinberg class 12 biology NEET_UG

Explain in brief the separation and isolation of DNA class 12 biology NEET_UG

Number of testicular lobules in testes is A 250 B 500 class 12 biology NEET_UG

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE




