
A particle projected from ground moves at angle \[45^\circ \] with horizontal one second after the projection and speed is minimum two seconds after the projection. The angle of projection of particle is (Neglect the effect of air resistance)
A. \[{\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( 3 \right)\]
B. \[{\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( 2 \right)\]
C. \[{\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\sqrt 2 } \right)\]
D. \[{\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( 4 \right)\]
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Use the formula for the time of ascent of the projectile.
Also, use the kinematic equation relating initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration and time.
Formula used:
The time of ascent of the projectile is given by
\[t = \dfrac{{u\sin \theta }}{g}\] …… (1)
Here, \[t\] is the time of ascent of the projectile, \[u\] is the speed of projection, \[\theta \] is the angle
of projection and \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity.
The kinematic equation relating the final vertical velocity \[{v_y}\], initial vertical velocity \[{u_y}\], acceleration \[g\] and time \[t\] of a particle in projectile motion is
\[{v_y} = {u_y} - gt\] …… (2)
The angle of projection \[\theta \] of the projectile is given by
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{v_y}}}{{{v_x}}}} \right)\] …… (3)
Here, \[{v_x}\] and \[{v_y}\] are the horizontal and vertical components of velocity of the projectile at any time \[t\].
Complete step by step answer:
The particle projected in the air starts its projectile motion one second after the launch at an angle of projection \[45^\circ \] and attains the minimum speed two seconds after the projection.
The diagram representing the projectile motion of the particle is as follows:
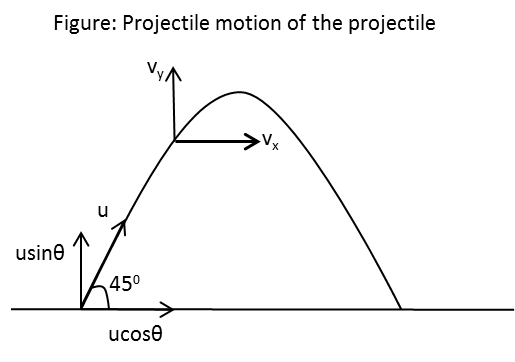
In the above figure, \[\theta \] is the angle of projection, \[u\] is the speed of projection and \[{v_x}\] and \[{v_y}\] are the horizontal and vertical components of velocity at any time.
The particle has a minimum velocity after two seconds of the projection. The projectile has the minimum speed at the maximum height as the vertical speed of the projectile becomes zero at maximum height.
The time taken by the particle to reach the maximum height is known as time of ascent.
The velocity of the particle becomes minimum i.e. zero after two seconds of projection.
Hence, the time of ascent of the particle is two seconds.
Substitute \[2\,{\text{s}}\] for \[t\] in equation (1).
\[2\,{\text{s}} = \dfrac{{u\sin \theta }}{g}\]
\[ \Rightarrow u\sin \theta = 2g\]
The horizontal and vertical components of the initial velocity of the projectile are \[u\cos \theta \] and \[u\sin \theta \].
\[{u_x} = u\cos \theta \]
\[{u_y} = u\sin \theta \]
The horizontal component of the speed \[{v_x}\] of projectile remains the same throughout the projectile motion.
\[{v_x} = u\cos \theta \]
Calculate the vertical component of the velocity of the projectile at any time.
Substitute \[u\sin \theta \] for \[{u_y}\] in equation (2).
\[{v_y} = u\sin \theta - gt\]
Calculate the vertical component of velocity \[{v_y}\] at time one second after the projection.
Substitute \[2g\] for \[u\sin \theta \] and \[1\,{\text{s}}\] for \[t\] in the above equation.
\[{v_y} = 2g - g\left( {1\,{\text{s}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_y} = g\]
Rewrite the equation for the angle of projection of the projectile one second after its projection.
Substitute \[45^\circ \] for \[\theta \], \[u\cos \theta \] for \[{v_x}\] and \[g\] for \[{v_y}\] in equation (3).
\[45^\circ = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{g}{{u\cos \theta }}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \tan 45^\circ = \dfrac{g}{{u\cos \theta }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow u\cos \theta = g\]
Now calculate the angle of projection of the projectile.
Substitute \[u\sin \theta \] for \[{v_y}\] and \[u\cos \theta \] for \[{v_x}\] in equation (3).
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{u\sin \theta }}{{u\cos \theta }}} \right)\
Substitute \[2g\] for \[u\sin \theta \] and \[g\] for \[u\cos \theta \] in the above equation.
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{2g}}{g}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( 2 \right)\]
Therefore, the angle of projection of the particle is \[{\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( 2 \right)\].
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
\[u\sin \theta \] and \[u\cos \theta \] are the vertical and horizontal components of only initial velocity of projection. For the rest of the projectile motion, the vertical component of the velocity of the projectile changes continuously and the horizontal component remains the same. The projectile motion of the particle in the present example starts after the one second of projection.
Also, use the kinematic equation relating initial velocity, final velocity, acceleration and time.
Formula used:
The time of ascent of the projectile is given by
\[t = \dfrac{{u\sin \theta }}{g}\] …… (1)
Here, \[t\] is the time of ascent of the projectile, \[u\] is the speed of projection, \[\theta \] is the angle
of projection and \[g\] is the acceleration due to gravity.
The kinematic equation relating the final vertical velocity \[{v_y}\], initial vertical velocity \[{u_y}\], acceleration \[g\] and time \[t\] of a particle in projectile motion is
\[{v_y} = {u_y} - gt\] …… (2)
The angle of projection \[\theta \] of the projectile is given by
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{v_y}}}{{{v_x}}}} \right)\] …… (3)
Here, \[{v_x}\] and \[{v_y}\] are the horizontal and vertical components of velocity of the projectile at any time \[t\].
Complete step by step answer:
The particle projected in the air starts its projectile motion one second after the launch at an angle of projection \[45^\circ \] and attains the minimum speed two seconds after the projection.
The diagram representing the projectile motion of the particle is as follows:

In the above figure, \[\theta \] is the angle of projection, \[u\] is the speed of projection and \[{v_x}\] and \[{v_y}\] are the horizontal and vertical components of velocity at any time.
The particle has a minimum velocity after two seconds of the projection. The projectile has the minimum speed at the maximum height as the vertical speed of the projectile becomes zero at maximum height.
The time taken by the particle to reach the maximum height is known as time of ascent.
The velocity of the particle becomes minimum i.e. zero after two seconds of projection.
Hence, the time of ascent of the particle is two seconds.
Substitute \[2\,{\text{s}}\] for \[t\] in equation (1).
\[2\,{\text{s}} = \dfrac{{u\sin \theta }}{g}\]
\[ \Rightarrow u\sin \theta = 2g\]
The horizontal and vertical components of the initial velocity of the projectile are \[u\cos \theta \] and \[u\sin \theta \].
\[{u_x} = u\cos \theta \]
\[{u_y} = u\sin \theta \]
The horizontal component of the speed \[{v_x}\] of projectile remains the same throughout the projectile motion.
\[{v_x} = u\cos \theta \]
Calculate the vertical component of the velocity of the projectile at any time.
Substitute \[u\sin \theta \] for \[{u_y}\] in equation (2).
\[{v_y} = u\sin \theta - gt\]
Calculate the vertical component of velocity \[{v_y}\] at time one second after the projection.
Substitute \[2g\] for \[u\sin \theta \] and \[1\,{\text{s}}\] for \[t\] in the above equation.
\[{v_y} = 2g - g\left( {1\,{\text{s}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_y} = g\]
Rewrite the equation for the angle of projection of the projectile one second after its projection.
Substitute \[45^\circ \] for \[\theta \], \[u\cos \theta \] for \[{v_x}\] and \[g\] for \[{v_y}\] in equation (3).
\[45^\circ = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{g}{{u\cos \theta }}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \tan 45^\circ = \dfrac{g}{{u\cos \theta }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow u\cos \theta = g\]
Now calculate the angle of projection of the projectile.
Substitute \[u\sin \theta \] for \[{v_y}\] and \[u\cos \theta \] for \[{v_x}\] in equation (3).
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{u\sin \theta }}{{u\cos \theta }}} \right)\
Substitute \[2g\] for \[u\sin \theta \] and \[g\] for \[u\cos \theta \] in the above equation.
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{2g}}{g}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( 2 \right)\]
Therefore, the angle of projection of the particle is \[{\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( 2 \right)\].
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
\[u\sin \theta \] and \[u\cos \theta \] are the vertical and horizontal components of only initial velocity of projection. For the rest of the projectile motion, the vertical component of the velocity of the projectile changes continuously and the horizontal component remains the same. The projectile motion of the particle in the present example starts after the one second of projection.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




