
A particle of mass $1\times {{10}^{-26}}Kg$ and charge $1.6\times {{10}^{-19}}C$ travelling with a velocity $1.28\times {{10}^{6}}m{{s}^{-1}}$ along the positive X-axis enters a region in which a uniform electric field E and a uniform magnetic field of induction B are present. If $E=-102.4\times {{10}^{3}}\widehat{k}N{{C}^{-1}}$ and $B=8\times {{10}^{-2}}\widehat{j}Wb{{m}^{-2}}$, the direction of motion of the particles is
A. along the positive x-axis
B. along the negative x-axis
C. at $45{}^\circ $to the positive x-axis
D. at $135{}^\circ $to the positive x-axis
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: Newton’s first law will be helpful in solving this question. The first law states that ‘each and every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force’. This is known as inertia.
Complete answer:
On the behalf of Newton's law of motion, we can say that until the force is being zero the direction of motion cannot be varied according to the law of motion by Newton.
So let us calculate the force involved here. In this case we can see that the particle is residing in a region of both electric and magnetic fields. So the force will be the resultant of these two.
Let F be the force acting on the particle due to electric and magnetic fields.
Mass
$m=1\times {{10}^{-26}}Kg$
Velocity
$v=1.28\times {{10}^{6}}m{{s}^{-1}}$
Electric field is
$E=-102.4\times {{10}^{3}}\widehat{k}N{{C}^{-1}}$
And magnetic field is given as
$B=8\times {{10}^{-2}}\widehat{j}Wb{{m}^{-2}}$
Therefore we can write that,
$F=q\left( v\times B \right)+qE$
Substituting the given values will give,
\[F=0N\]
So here it is clear now that no force is acting. So the particle will continue to move in its previous direction of motion. That will move in the positive x-axis.
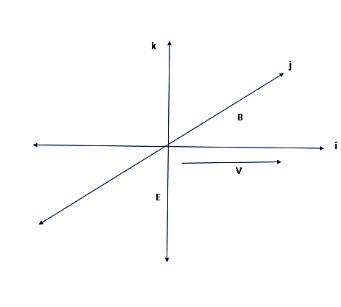
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
A book kept on the table remains at rest as long as net force acting on it is zero. A moving object cannot stop motion by itself. A rolling ball on a rough surface or ground stops earlier than on a smooth surface because rough surfaces is offering more friction than a smooth surface.
Complete answer:
On the behalf of Newton's law of motion, we can say that until the force is being zero the direction of motion cannot be varied according to the law of motion by Newton.
So let us calculate the force involved here. In this case we can see that the particle is residing in a region of both electric and magnetic fields. So the force will be the resultant of these two.
Let F be the force acting on the particle due to electric and magnetic fields.
Mass
$m=1\times {{10}^{-26}}Kg$
Velocity
$v=1.28\times {{10}^{6}}m{{s}^{-1}}$
Electric field is
$E=-102.4\times {{10}^{3}}\widehat{k}N{{C}^{-1}}$
And magnetic field is given as
$B=8\times {{10}^{-2}}\widehat{j}Wb{{m}^{-2}}$
Therefore we can write that,
$F=q\left( v\times B \right)+qE$
Substituting the given values will give,
\[F=0N\]
So here it is clear now that no force is acting. So the particle will continue to move in its previous direction of motion. That will move in the positive x-axis.

So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
A book kept on the table remains at rest as long as net force acting on it is zero. A moving object cannot stop motion by itself. A rolling ball on a rough surface or ground stops earlier than on a smooth surface because rough surfaces is offering more friction than a smooth surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




