
A newspaper agent sells \[TOI\], \[HT\] and \[NBT\] in equal numbers to \[302\] persons. Seven got \[HT\] and \[NBT\], twelve got \[TOI\] and \[NBT\], nine got \[TOI\] and \[HT\] & three got all the three newspapers. The details are given in the Venn diagram.
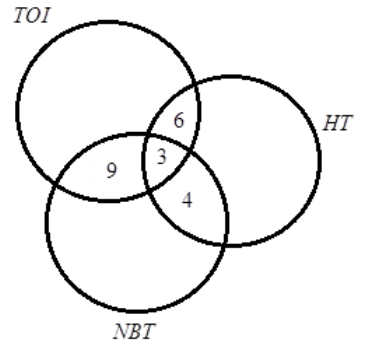
What percentage gets \[TOI\] or \[HT\] but not \[NBT\]?
A). More than \[65\% \]
B). Less than\[60\% \]
C). \[ \cong 64\% \]
D). None of these

Answer
520.2k+ views
Hint: Here, in the question, we have been given a Venn diagram which represents the data of the newspaper readers of three different brands. We are asked to find the percentage of people who read \[TOI\] or \[HT\] but not \[NBT\]. To find that, we will first find the number of persons who read only \[TOI\], only \[HT\] and only \[NBT\] and then reach the desired result.
Formula used:
\[n\left( {A \cup B \cup C} \right) = n\left( A \right) + n\left( B \right) + n\left( C \right) - n\left( {A \cap B} \right) - n\left( {B \cap C} \right) - n\left( {A \cap C} \right) + n\left( {A \cap B \cap C} \right)\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given, Total number of persons who read newspaper, \[n\left( {TOI \cup HT \cup NBT} \right)\]=\[302\]
\[
n\left( {HT \cap NBT} \right) = 7 \\
n\left( {TOI \cap NBT} \right) = 12 \\
n\left( {TOI \cap HT} \right) = 9 \\
n\left( {TOI \cap HT \cap NBT} \right) = 3 \]
Now, using identity, \[n\left( {A \cup B \cup C} \right) = n\left( A \right) + n\left( B \right) + n\left( C \right) - n\left( {A \cap B} \right) - n\left( {B \cap C} \right) - n\left( {A \cap C} \right) + n\left( {A \cap B \cap C} \right)\]
\[n\left( {TOI \cup HT \cup NBT} \right) = n\left( {TOI} \right) + n\left( {HT} \right) + n\left( {NBT} \right) - n\left( {TOI \cap HT} \right) - n\left( {HT \cap NBT} \right) - n\left( {TOI \cap NBT} \right) + n\left( {TOI \cap HT \cap NBT} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 302 = n\left( {TOI} \right) + n\left( {HT} \right) + n\left( {NBT} \right) - 9 - 7 - 12 + 3\]
Now, we are given that \[n\left( {TOI} \right) = n\left( {HT} \right) = n\left( {NBT} \right)\]
Therefore, \[ \Rightarrow 302 = 3 \times n\left( {TOI} \right) - 25\]
Simplifying it, we get,
\[
\Rightarrow n\left( {TOI} \right) = \dfrac{{327}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {TOI} \right) = 109 \]
Hence, \[n\left( {TOI} \right) = n\left( {HT} \right) = n\left( {NBT} \right) = 109\]
Now, we will calculate the number of persons who read only \[TOI\], only \[HT\] and only \[NBT\] using Venn diagram
\[
n\left( {TOI\;only} \right) = 109 - \left( {6 + 9 + 3} \right) \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {TOI\;only} \right) = 91 \]
Similarly, we get,
\[
n\left( {HT\;only} \right) = 109 - \left( {6 + 4 + 3} \right) \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {HT\;only} \right) = 96 \],
and
\[
n\left( {NBT\;only} \right) = 109 - \left( {9 + 4 + 3} \right) \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {NBT\;only} \right) = 93 \]
Let us draw a fresh Venn diagram again and shade the required region,
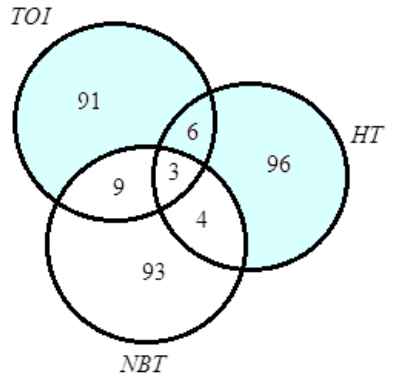
Now, using Venn diagram, No. of persons reading \[TOI \text{ or }HT\text{ but not }NBT\] is calculated as:
\[
n\left( {TOI \text{ or }HT\text{ but not }NBT} \right) = 91 + 96 + 6 \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {TOI \text{ or }HT\text{ but not }NBT} \right) = 193 \\
\]
Percentage of persons reading \[TOI \text{ or }HT\text{ but not }NBT\]=\[\dfrac{{193}}{{302}} \times 100\% \]
\[ = 63.907\]
Hence the correct option is C, \[ \cong 64\% \] is the correct option.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions, we should try to solve the question using Venn diagram to a possible extent. Venn diagrams are easy to read and understand. We can understand the data just by looking at the Venn diagram. And it is equally important to remember and understand the basic formula related to Venn diagram problems.
Formula used:
\[n\left( {A \cup B \cup C} \right) = n\left( A \right) + n\left( B \right) + n\left( C \right) - n\left( {A \cap B} \right) - n\left( {B \cap C} \right) - n\left( {A \cap C} \right) + n\left( {A \cap B \cap C} \right)\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given, Total number of persons who read newspaper, \[n\left( {TOI \cup HT \cup NBT} \right)\]=\[302\]
\[
n\left( {HT \cap NBT} \right) = 7 \\
n\left( {TOI \cap NBT} \right) = 12 \\
n\left( {TOI \cap HT} \right) = 9 \\
n\left( {TOI \cap HT \cap NBT} \right) = 3 \]
Now, using identity, \[n\left( {A \cup B \cup C} \right) = n\left( A \right) + n\left( B \right) + n\left( C \right) - n\left( {A \cap B} \right) - n\left( {B \cap C} \right) - n\left( {A \cap C} \right) + n\left( {A \cap B \cap C} \right)\]
\[n\left( {TOI \cup HT \cup NBT} \right) = n\left( {TOI} \right) + n\left( {HT} \right) + n\left( {NBT} \right) - n\left( {TOI \cap HT} \right) - n\left( {HT \cap NBT} \right) - n\left( {TOI \cap NBT} \right) + n\left( {TOI \cap HT \cap NBT} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow 302 = n\left( {TOI} \right) + n\left( {HT} \right) + n\left( {NBT} \right) - 9 - 7 - 12 + 3\]
Now, we are given that \[n\left( {TOI} \right) = n\left( {HT} \right) = n\left( {NBT} \right)\]
Therefore, \[ \Rightarrow 302 = 3 \times n\left( {TOI} \right) - 25\]
Simplifying it, we get,
\[
\Rightarrow n\left( {TOI} \right) = \dfrac{{327}}{3} \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {TOI} \right) = 109 \]
Hence, \[n\left( {TOI} \right) = n\left( {HT} \right) = n\left( {NBT} \right) = 109\]
Now, we will calculate the number of persons who read only \[TOI\], only \[HT\] and only \[NBT\] using Venn diagram
\[
n\left( {TOI\;only} \right) = 109 - \left( {6 + 9 + 3} \right) \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {TOI\;only} \right) = 91 \]
Similarly, we get,
\[
n\left( {HT\;only} \right) = 109 - \left( {6 + 4 + 3} \right) \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {HT\;only} \right) = 96 \],
and
\[
n\left( {NBT\;only} \right) = 109 - \left( {9 + 4 + 3} \right) \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {NBT\;only} \right) = 93 \]
Let us draw a fresh Venn diagram again and shade the required region,

Now, using Venn diagram, No. of persons reading \[TOI \text{ or }HT\text{ but not }NBT\] is calculated as:
\[
n\left( {TOI \text{ or }HT\text{ but not }NBT} \right) = 91 + 96 + 6 \\
\Rightarrow n\left( {TOI \text{ or }HT\text{ but not }NBT} \right) = 193 \\
\]
Percentage of persons reading \[TOI \text{ or }HT\text{ but not }NBT\]=\[\dfrac{{193}}{{302}} \times 100\% \]
\[ = 63.907\]
Hence the correct option is C, \[ \cong 64\% \] is the correct option.
Note: Whenever we face such types of questions, we should try to solve the question using Venn diagram to a possible extent. Venn diagrams are easy to read and understand. We can understand the data just by looking at the Venn diagram. And it is equally important to remember and understand the basic formula related to Venn diagram problems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




