
When a mixture of methanol and ethanol is heated in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, the resulting organic product or products is/are :
A. CH3OC2H5
B. CH3OCH3, C2H5OC2H5
C. CH3OC2H5, CH3OCH3
D. CH3OC2H5, CH3OCH3, and C2H5OC2H5.
Answer
371.1k+ views
Hint: Alcohols undergo dehydration in the presence of protonic acids to give alkenes or ethers. The product formation depends on the reaction conditions. Protonic acids involve concentrated sulfuric acids or phosphoric acid.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Symmetrical ethers may be formed by the dehydration of alcohols either in the presence of acids or heated alumina.
Dehydration means the loss of water.
Methanol and ethanol will undergo dehydration if heated in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid at 413 K.
For example, if excess ethanol is taken at 413 K, ethoxyethane is the main product.
This reaction is the acid-catalysed dehydration of alcohol.
This is a bimolecular substitution reaction involving the attack of the alcohol molecule on a protonated alcohol molecule.
This reaction occurs in three steps:
1. Protonation of alcohol
The presence of two lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom of alcohol makes it a Lewis base.
So, they react with strong mineral acids like sulfuric acid to form oxonium salts.
Ethanol forms protonated ethanol and methanol forms protonated methanol.
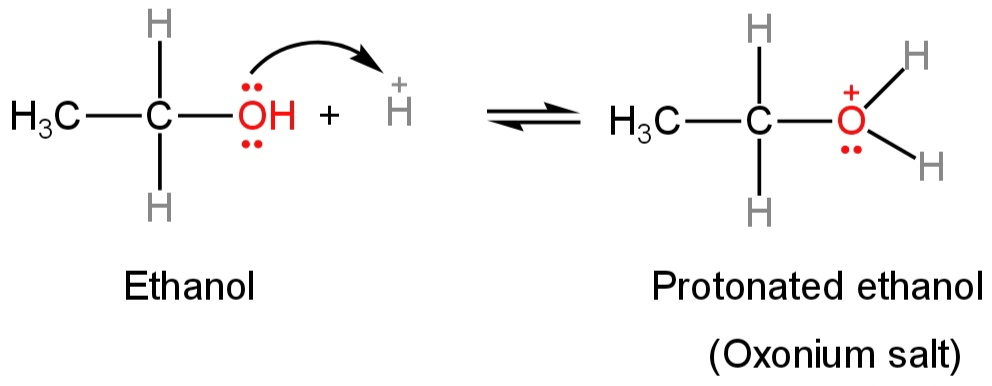
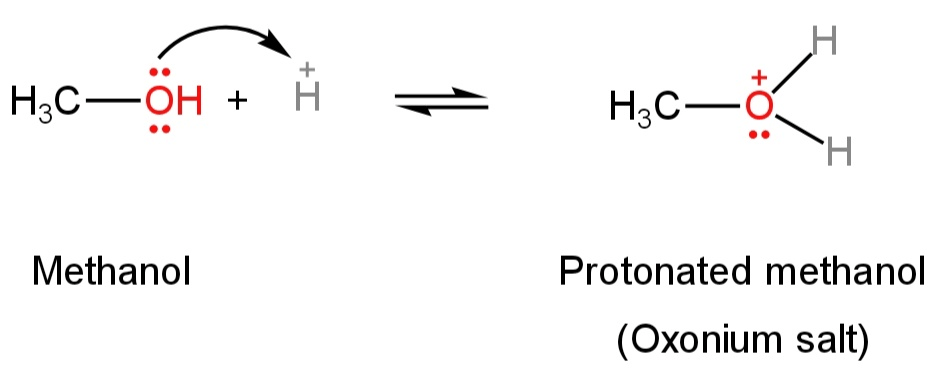
Image: Formation of protonated alcohol
2. Due to the presence of a positive charge on the oxygen atom, the carbon next to the oxygen atom becomes electron deficient.
So, nucleophilic attack by the deprotonated alcohol molecule occurs on the protonated alcohol to form protonated ether molecules with the loss of water.
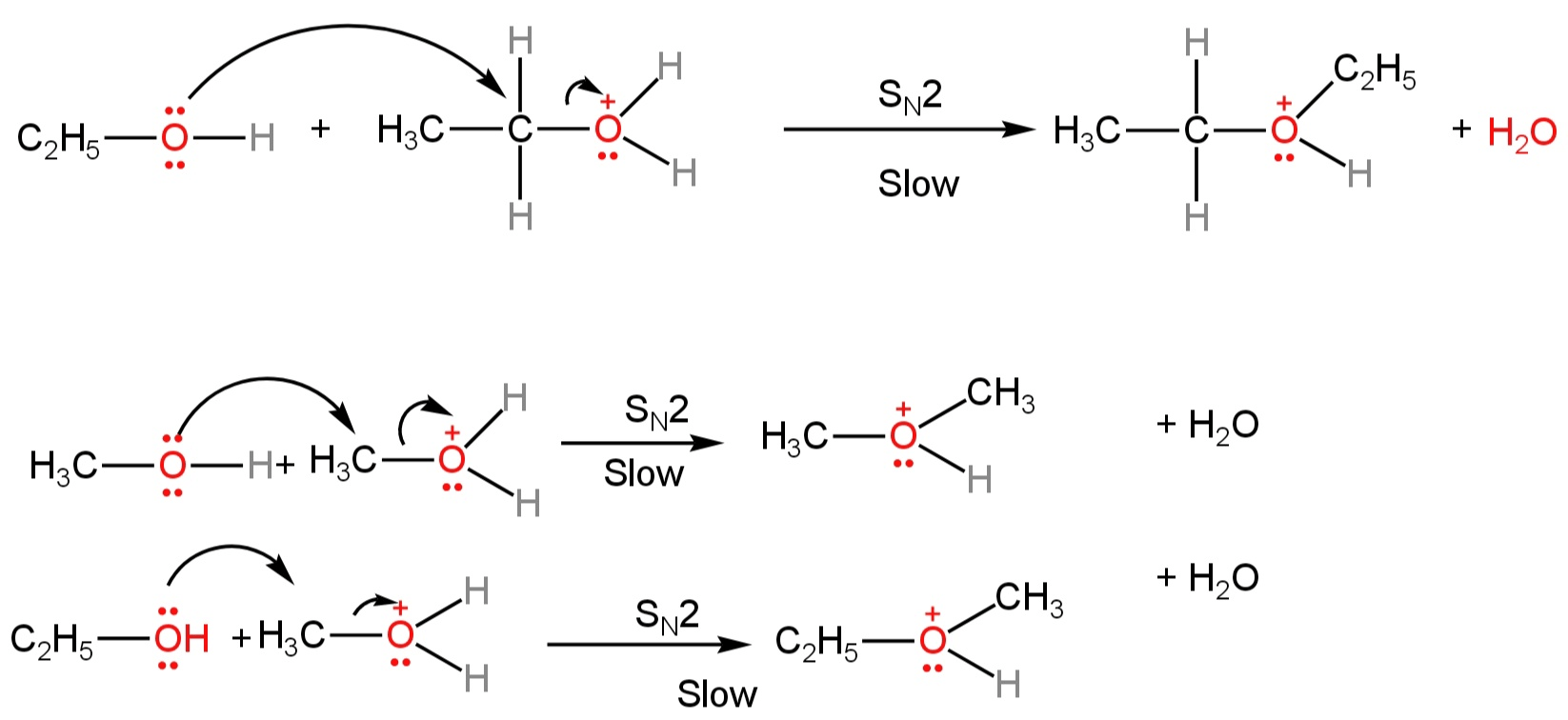
Image: Formation of protonated ether.
3. The alcohol molecule finally abstracts a proton from the protonated ether to form ethoxyethane, methoxymethane and methoxyethane.
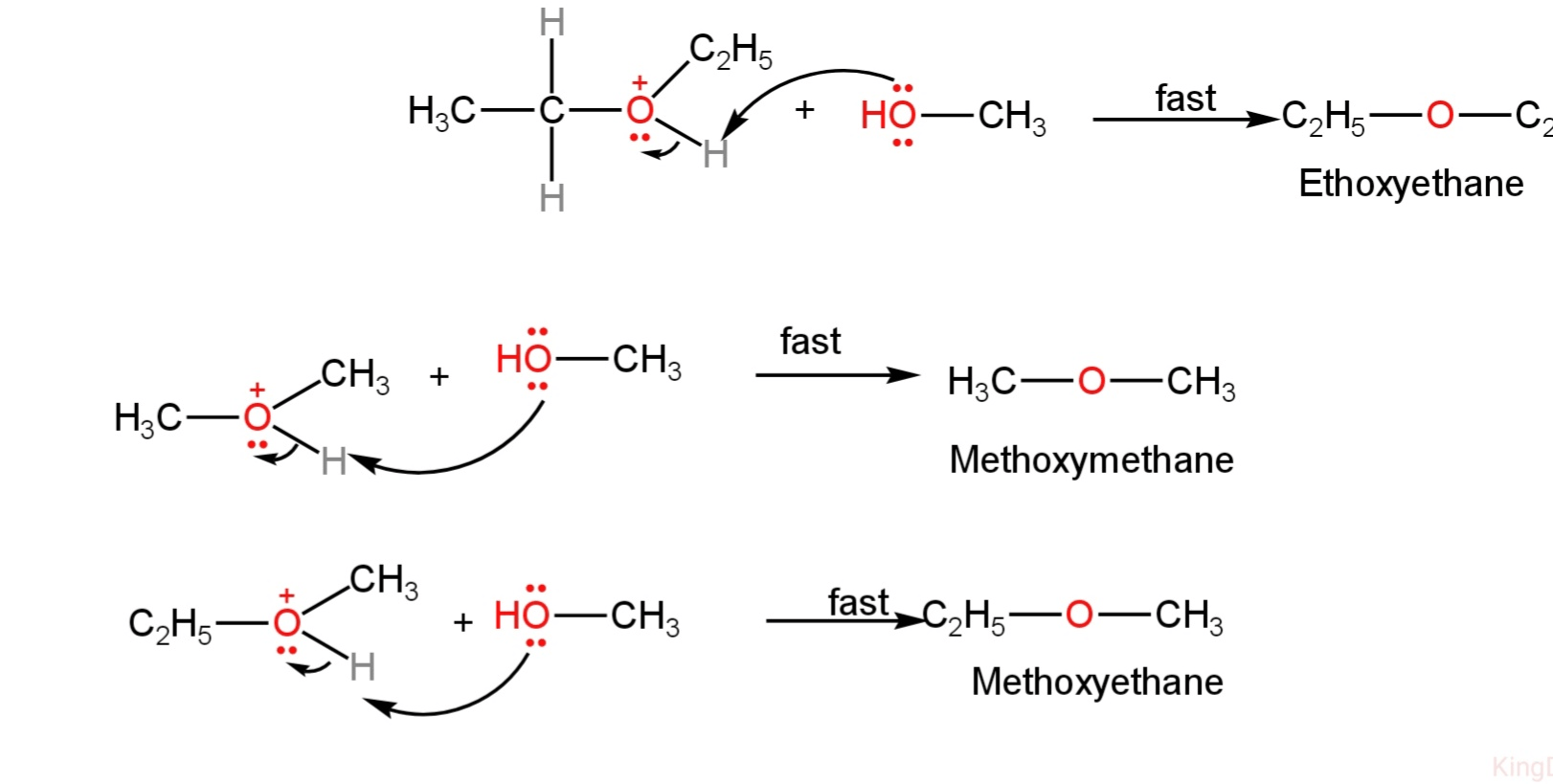
Image: Formation of ether
So, ethoxyethane, methoxymethane and methoxyethane are formed when a mixture of methanol and ethanol is heated in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid.
So, option D is correct.
Note: At 413 K, formation of ethers from primary alcohols is accompanied by formation of small amounts of alkenes. Therefore, it is the suitable way of preparation of ethers having unhindered primary alkyl groups. For secondary and tertiary alcohols due to presence of bulky alkyl groups, nucleophilic attack of lone pair of oxygen is not possible due to steric hindrance. So, alkenes are formed in large amounts.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Symmetrical ethers may be formed by the dehydration of alcohols either in the presence of acids or heated alumina.
Dehydration means the loss of water.
Methanol and ethanol will undergo dehydration if heated in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid at 413 K.
For example, if excess ethanol is taken at 413 K, ethoxyethane is the main product.
This reaction is the acid-catalysed dehydration of alcohol.
This is a bimolecular substitution reaction involving the attack of the alcohol molecule on a protonated alcohol molecule.
This reaction occurs in three steps:
1. Protonation of alcohol
The presence of two lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom of alcohol makes it a Lewis base.
So, they react with strong mineral acids like sulfuric acid to form oxonium salts.
Ethanol forms protonated ethanol and methanol forms protonated methanol.


Image: Formation of protonated alcohol
2. Due to the presence of a positive charge on the oxygen atom, the carbon next to the oxygen atom becomes electron deficient.
So, nucleophilic attack by the deprotonated alcohol molecule occurs on the protonated alcohol to form protonated ether molecules with the loss of water.

Image: Formation of protonated ether.
3. The alcohol molecule finally abstracts a proton from the protonated ether to form ethoxyethane, methoxymethane and methoxyethane.

Image: Formation of ether
So, ethoxyethane, methoxymethane and methoxyethane are formed when a mixture of methanol and ethanol is heated in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid.
So, option D is correct.
Note: At 413 K, formation of ethers from primary alcohols is accompanied by formation of small amounts of alkenes. Therefore, it is the suitable way of preparation of ethers having unhindered primary alkyl groups. For secondary and tertiary alcohols due to presence of bulky alkyl groups, nucleophilic attack of lone pair of oxygen is not possible due to steric hindrance. So, alkenes are formed in large amounts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE




