
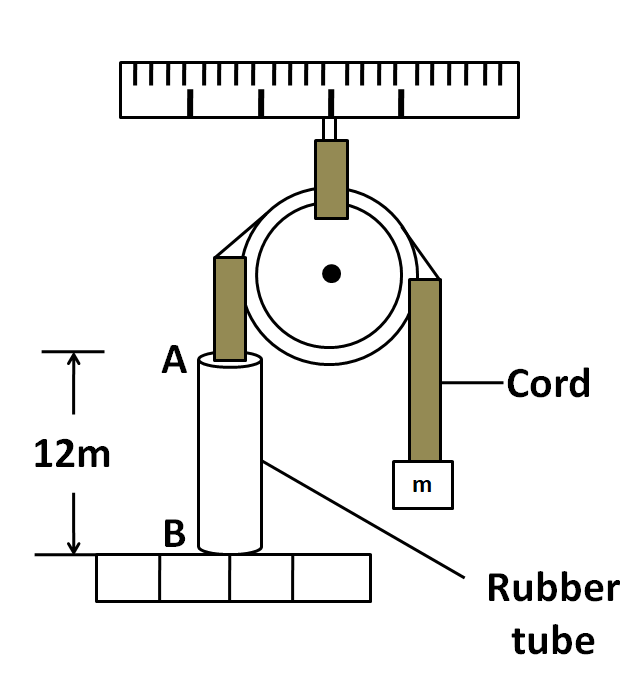
A long rubber tube having mass $ 0.9kg $ is fastened to a fixed support and the free end of the tube is attached to a chord which passes over a pulley and supports an object, with a mass of $ 5kg $ as shown in figure. If the tube is struck by a transverse blow at one end, the time required for the pulse to reach the other end is (neglect the variation of speed due to the mass of the tube)
(A) $ 5s $
(B) $ 0.48s $
(C) $ 4.8s $
(D) $ 3.2s $

Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint To solve this question, we have to determine the speed of the sound in the rubber tube from the formula given as $ v = \sqrt {\dfrac{T}{\mu }} $ . Then using the general formula of the speed in terms of the distance covered, we can find out the value of the time required for the pulse to reach the other end.
Formula Used The formula used in solving this question is given by
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{T}{\mu }} $, here $ v $ is the speed of the wave in a string having the mass density of $ \mu $, which is stretched by a tension of $ T $ .
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the tension in the cord as $ T $
So the free body diagram for the mass $ 5kg $ will be as,
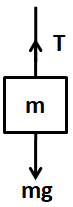
From the condition of vertical equilibrium we get,
$\Rightarrow T = mg $
According to the question $ m = 5kg $ . So we have
$\Rightarrow T = 5g $ ….(1)
Now, the velocity of sound in a stretched string is given by the formula,
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{T}{\mu }} $ …...(2)
We know that $ \mu $ is the mass per unit length. So the mass per unit length for the rubber tube, which is of length $ 12m $ is and mass $ 0.9kg $ is
$\therefore \mu = \dfrac{M}{l} $
$\Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{0.9}}{{12}} = 0.075kg/m $ …….(3)
Putting (1) and (3) in (2) we get
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{5g}}{{0.075}}} $
Putting $ g = 9.8m/{s^2} $ we get,
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{49}}{{0.075}}} $
On solving we get the value of the velocity as,
$\Rightarrow v = 25.56m/s $ …...(4)
Now, the rubber tube is struck by the transverse blow at one end. The total distance covered to reach the other end will be equal to the length of the tube. So we have
$\Rightarrow d = 12m $ …..(5)
So, the time required for the wave to reach the other end is given by the formula
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{d}{v} $
Putting (4) and (5) in the above formula we get,
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{12}}{{25.56}} $
On solving we get,
$\Rightarrow t = 0.47s $
From the options the nearest matching value is $ 0.48s $ . So we take
$\Rightarrow t \approx 0.48s $
Hence the correct answer is option (B).
Note
We should not calculate the tension in the rubber tube separately. This is because the tube is not freely hanging but it is fastened to the fixed support below it. So, its weight does not increase the tension in it. Hence, the tension in the tube will be equal to the tension due to the weight of the hanging block.
Formula Used The formula used in solving this question is given by
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{T}{\mu }} $, here $ v $ is the speed of the wave in a string having the mass density of $ \mu $, which is stretched by a tension of $ T $ .
Complete step by step answer
Let us consider the tension in the cord as $ T $
So the free body diagram for the mass $ 5kg $ will be as,

From the condition of vertical equilibrium we get,
$\Rightarrow T = mg $
According to the question $ m = 5kg $ . So we have
$\Rightarrow T = 5g $ ….(1)
Now, the velocity of sound in a stretched string is given by the formula,
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{T}{\mu }} $ …...(2)
We know that $ \mu $ is the mass per unit length. So the mass per unit length for the rubber tube, which is of length $ 12m $ is and mass $ 0.9kg $ is
$\therefore \mu = \dfrac{M}{l} $
$\Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{0.9}}{{12}} = 0.075kg/m $ …….(3)
Putting (1) and (3) in (2) we get
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{5g}}{{0.075}}} $
Putting $ g = 9.8m/{s^2} $ we get,
$\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {\dfrac{{49}}{{0.075}}} $
On solving we get the value of the velocity as,
$\Rightarrow v = 25.56m/s $ …...(4)
Now, the rubber tube is struck by the transverse blow at one end. The total distance covered to reach the other end will be equal to the length of the tube. So we have
$\Rightarrow d = 12m $ …..(5)
So, the time required for the wave to reach the other end is given by the formula
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{d}{v} $
Putting (4) and (5) in the above formula we get,
$\Rightarrow t = \dfrac{{12}}{{25.56}} $
On solving we get,
$\Rightarrow t = 0.47s $
From the options the nearest matching value is $ 0.48s $ . So we take
$\Rightarrow t \approx 0.48s $
Hence the correct answer is option (B).
Note
We should not calculate the tension in the rubber tube separately. This is because the tube is not freely hanging but it is fastened to the fixed support below it. So, its weight does not increase the tension in it. Hence, the tension in the tube will be equal to the tension due to the weight of the hanging block.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




