
A locomotive approaching a crossing at a speed of 80 mile/hr, sounds a whistle of frequency 400 Hz when 1 mile from the crossing. There is no wind, and the speed of sound in air is 0.200 miles/s. What frequency is heard by an observer 0.60 miles from the crossing on the straight road which crosses the railroad at right angles?
A. 440 Hz
B. 442 Hz
C. 444 Hz
D. 446 Hz
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: Determine the speed of source along the line of sight of the observer. To do so, you have to determine the angle made by the speed of the locomotive and speed of the locomotive along the line of sight of the observer. Use Doppler’s formula for apparent frequency when both source and observer are moving towards each other.
Formula used:
Apparent frequency, \[{f_{app}} = f\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v - {v_S}}}} \right)\]
Here, f is the original frequency, v is the speed of sound and \[{v_S}\] is the speed of source.
Complete step by step answer:
As we can see this is the case of both observer and source are moving towards each other but the direction is perpendicular to each other. We have to determine the speed of the source along the line of sight of the observer.
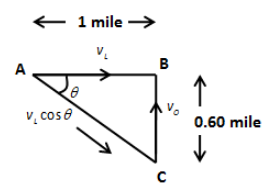
Let’s determine the distance AC using Pythagoras theorem as follows,
\[AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {AB} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {BC} \right)}^2}} \]
Substituting 1 mile for AB and 0.60 mile for BC in the above equation, we get,
\[AC = \sqrt {{{\left( 1 \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0.6} \right)}^2}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow AC = 1.166\,{\text{mile}}\]
Let’s determine the angle \[\theta \] as follows,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
Substituting 1 mile for AB and 1.166 mile for AC in the above equation, we get,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{1.166}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = 0.857\]
We have the speed of the source along the line of sight is,
\[{v_S} = {v_L}\cos \theta \]
Substituting 80 miles/hr for \[{v_L}\] and 0.857 for \[\cos \theta \] in the above equation, we get,
\[{v_S} = \left( {80\,{\text{mile/hr}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{1\,{\text{hr}}}}{{3600\,{\text{s}}}}} \right)\left( {0.857} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_S} = \left( {80\,{\text{mile/hr}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{1\,{\text{hr}}}}{{3600\,{\text{s}}}}} \right)\left( {0.857} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_S} = 0.019\,{\text{miles/s}}\]
Using Doppler’s formula for apparent frequency when both source and observer is moving, we have,
\[{f_{app}} = f\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v - {v_S}}}} \right)\]
Here, f is the original frequency, v is the speed of sound and \[{v_S}\] is the speed of source.
Substituting 400 Hz for f, 0.200 miles/s for v and 0.019 miles/s for \[{v_S}\] in the above equation, we get,
\[{f_{app}} = \left( {400} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{0.200}}{{0.200 - 0.019}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {f_{app}} = \left( {400} \right)\left( {1.105} \right)\]
\[ \therefore {f_{app}} = 442\,{\text{Hz}}\]
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note:Make sure that the unit of speed of sound and speed of the observer is the same. In the solution, we have converted the unit from mile/hr to mile/s since the speed of sound is in miles/s. When the source and observer are moving towards each other, the sign of the velocity of source should be negative in the denominator so as the apparent frequency increases.
Formula used:
Apparent frequency, \[{f_{app}} = f\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v - {v_S}}}} \right)\]
Here, f is the original frequency, v is the speed of sound and \[{v_S}\] is the speed of source.
Complete step by step answer:
As we can see this is the case of both observer and source are moving towards each other but the direction is perpendicular to each other. We have to determine the speed of the source along the line of sight of the observer.

Let’s determine the distance AC using Pythagoras theorem as follows,
\[AC = \sqrt {{{\left( {AB} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {BC} \right)}^2}} \]
Substituting 1 mile for AB and 0.60 mile for BC in the above equation, we get,
\[AC = \sqrt {{{\left( 1 \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0.6} \right)}^2}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow AC = 1.166\,{\text{mile}}\]
Let’s determine the angle \[\theta \] as follows,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
Substituting 1 mile for AB and 1.166 mile for AC in the above equation, we get,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{1}{{1.166}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = 0.857\]
We have the speed of the source along the line of sight is,
\[{v_S} = {v_L}\cos \theta \]
Substituting 80 miles/hr for \[{v_L}\] and 0.857 for \[\cos \theta \] in the above equation, we get,
\[{v_S} = \left( {80\,{\text{mile/hr}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{1\,{\text{hr}}}}{{3600\,{\text{s}}}}} \right)\left( {0.857} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_S} = \left( {80\,{\text{mile/hr}}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{1\,{\text{hr}}}}{{3600\,{\text{s}}}}} \right)\left( {0.857} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_S} = 0.019\,{\text{miles/s}}\]
Using Doppler’s formula for apparent frequency when both source and observer is moving, we have,
\[{f_{app}} = f\left( {\dfrac{v}{{v - {v_S}}}} \right)\]
Here, f is the original frequency, v is the speed of sound and \[{v_S}\] is the speed of source.
Substituting 400 Hz for f, 0.200 miles/s for v and 0.019 miles/s for \[{v_S}\] in the above equation, we get,
\[{f_{app}} = \left( {400} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{0.200}}{{0.200 - 0.019}}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {f_{app}} = \left( {400} \right)\left( {1.105} \right)\]
\[ \therefore {f_{app}} = 442\,{\text{Hz}}\]
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note:Make sure that the unit of speed of sound and speed of the observer is the same. In the solution, we have converted the unit from mile/hr to mile/s since the speed of sound is in miles/s. When the source and observer are moving towards each other, the sign of the velocity of source should be negative in the denominator so as the apparent frequency increases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




