
A: Length of focal chord of a parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=8x\] making an angle of ${{60}^{\circ }}$ with x-axis is $\dfrac{32}{3}$ .
R: Length of focal chord of parabola ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ making an angle $\alpha $ with x-axis is $4a\cos e{{c}^{2}}\left( \alpha \right)$ .
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Take the coordinate of focal chord A and B as $\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$ parametric form. Find the length of focal chord AB. Take slope as equal to t and thus substitute and prove $4a{{\cos }^{2}}\alpha $. Put $\alpha ={{60}^{\circ }}$ and get the value of a, to get the value of $\dfrac{32}{3}$.
Complete step by step answer:
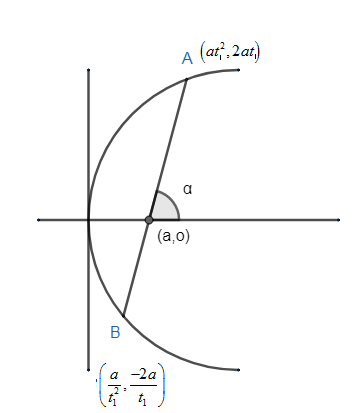
We have been given the equation of parabola as \[{{y}^{2}}=8x\] .
The length of the focal chord, ${{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=-1$ i.e. ${{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{1}}}$ ,
Hence, if A and B are the coordinate of the point on the parabola then. We can take their coordinate as,
$A\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)$ .
But we found out that ${{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{1}}}$ .
$\therefore $ coordinate of B changes to, \[B\equiv \left( a{{\left( \dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}^{2}},2a\left( \dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{1}}} \right) \right)\equiv \left( \dfrac{a}{t_{1}^{2}},\dfrac{-2a}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)\].
Let’s assume ${{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{2}}}=t$.
Thus, we can write the coordinate as \[A\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] and $B\left( \dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}},\dfrac{-2a}{t} \right)$ .
So, here $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( \dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}},\dfrac{-2a}{t} \right)$, $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$.
The focus of the parabola is given as $\left( a.0 \right)$ .
Now, let us find the length of AB by using the distance formula,
i.e. distance $AB=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( a{{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2at+\dfrac{2a}{t} \right)}^{2}}}$
\[\begin{align}
& =\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( {{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2a \right)}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}+4{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that ${{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)$. Similarly, ${{\left( {{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \left| \overline{AB} \right|=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}\left\{ {{\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}+4 \right\}}$ [taking ${{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}$common both the terms].
$=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}\left( {{t}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{2}}}+2 \right)}=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{4}}}$ [we know ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab={{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}$]
Hence it become, $AB=a{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}$ ……………… (1)
Now, m = slope of line AB $=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}=\dfrac{2at+\dfrac{2a}{t}}{a{{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}}}=\dfrac{2a\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}{a\left( {{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}=\dfrac{2\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}=\dfrac{2}{t-\dfrac{1}{t}}$ .
So,
$\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{2}{t-\dfrac{1}{t}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \alpha =m=\dfrac{2}{t-\dfrac{1}{t}} \\
& \Rightarrow t-\dfrac{1}{t}=\dfrac{2}{\tan \alpha }=2\cot \alpha \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }$ , by basic trigonometric identity.
Similarly
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}+4 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 2\cot \alpha \right)}^{2}}+4=4{{\cot }^{2}}\alpha +4=4\left( {{\cot }^{2}}\alpha -1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
We know that ${{\cot }^{2}}\alpha -1=\cos e{{c}^{2}}\alpha $ .
$\therefore {{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}=4\left[ {{\cot }^{2}}\alpha -1 \right]=4\cos e{{c}^{2}}\alpha $
We got the length of focal chord $AB=a{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}=4a\cos e{{c}^{2}}\alpha $
The equation of parabola given is \[{{y}^{2}}=8x\]. Now let us compare it with the general equation of the parabola is ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ .
Hence, we get latus rectum $4a=8\Rightarrow a=2$ and $\alpha ={{60}^{\circ }}$
Thus, length focal chord $=4a\cos e{{c}^{2}}\alpha =4\times 2\cos e{{c}^{2}}{{60}^{\circ }}=8\cos e{{c}^{2}}{{60}^{\circ }}$
From trigonometric table we know that $\sin {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\therefore \cos ec{{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\therefore $ Length of focal chord $8\cos e{{c}^{2}}{{60}^{\circ }}=8\times {{\left( \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{8\times 4}{3}=\dfrac{32}{3}$ .
Hence, it’s proved that both statement 1 and statement 2 are correct and R is the perfect reason for A.
Note: The angle inclination of a line is the angle formed by the intersection of the line and the x-axis, using a horizontal “run” of 1 and m for slope, The angle of inclination $\alpha ={{\tan }^{-1}}m$ or $m=\tan \alpha $. Thus, the reason why we took $\tan \alpha =slope$.
Complete step by step answer:

We have been given the equation of parabola as \[{{y}^{2}}=8x\] .
The length of the focal chord, ${{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=-1$ i.e. ${{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{1}}}$ ,
Hence, if A and B are the coordinate of the point on the parabola then. We can take their coordinate as,
$A\left( at_{1}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)$ and $B\left( at_{2}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)$ .
But we found out that ${{t}_{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{1}}}$ .
$\therefore $ coordinate of B changes to, \[B\equiv \left( a{{\left( \dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)}^{2}},2a\left( \dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{1}}} \right) \right)\equiv \left( \dfrac{a}{t_{1}^{2}},\dfrac{-2a}{{{t}_{1}}} \right)\].
Let’s assume ${{t}_{1}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{t}_{2}}}=t$.
Thus, we can write the coordinate as \[A\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] and $B\left( \dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}},\dfrac{-2a}{t} \right)$ .
So, here $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( \dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}},\dfrac{-2a}{t} \right)$, $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)$.
The focus of the parabola is given as $\left( a.0 \right)$ .
Now, let us find the length of AB by using the distance formula,
i.e. distance $AB=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( a{{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2at+\dfrac{2a}{t} \right)}^{2}}}$
\[\begin{align}
& =\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( {{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 2a \right)}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}+4{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that ${{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)$. Similarly, ${{\left( {{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow \left| \overline{AB} \right|=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}\left\{ {{\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}+4 \right\}}$ [taking ${{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}$common both the terms].
$=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}\left( {{t}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{2}}}+2 \right)}=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{4}}}$ [we know ${{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab={{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}$]
Hence it become, $AB=a{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}$ ……………… (1)
Now, m = slope of line AB $=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}=\dfrac{2at+\dfrac{2a}{t}}{a{{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{a}{{{t}^{2}}}}=\dfrac{2a\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}{a\left( {{t}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{2}}} \right)}=\dfrac{2\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}=\dfrac{2}{t-\dfrac{1}{t}}$ .
So,
$\begin{align}
& m=\dfrac{2}{t-\dfrac{1}{t}} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \alpha =m=\dfrac{2}{t-\dfrac{1}{t}} \\
& \Rightarrow t-\dfrac{1}{t}=\dfrac{2}{\tan \alpha }=2\cot \alpha \\
\end{align}$
We know that $\cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }$ , by basic trigonometric identity.
Similarly
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( t-\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}+4 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 2\cot \alpha \right)}^{2}}+4=4{{\cot }^{2}}\alpha +4=4\left( {{\cot }^{2}}\alpha -1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
We know that ${{\cot }^{2}}\alpha -1=\cos e{{c}^{2}}\alpha $ .
$\therefore {{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}=4\left[ {{\cot }^{2}}\alpha -1 \right]=4\cos e{{c}^{2}}\alpha $
We got the length of focal chord $AB=a{{\left( t+\dfrac{1}{t} \right)}^{2}}=4a\cos e{{c}^{2}}\alpha $
The equation of parabola given is \[{{y}^{2}}=8x\]. Now let us compare it with the general equation of the parabola is ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ .
Hence, we get latus rectum $4a=8\Rightarrow a=2$ and $\alpha ={{60}^{\circ }}$
Thus, length focal chord $=4a\cos e{{c}^{2}}\alpha =4\times 2\cos e{{c}^{2}}{{60}^{\circ }}=8\cos e{{c}^{2}}{{60}^{\circ }}$
From trigonometric table we know that $\sin {{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
$\therefore \cos ec{{60}^{\circ }}=\dfrac{1}{\sin {{60}^{\circ }}}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}}$
$\therefore $ Length of focal chord $8\cos e{{c}^{2}}{{60}^{\circ }}=8\times {{\left( \dfrac{2}{\sqrt{3}} \right)}^{2}}=\dfrac{8\times 4}{3}=\dfrac{32}{3}$ .
Hence, it’s proved that both statement 1 and statement 2 are correct and R is the perfect reason for A.
Note: The angle inclination of a line is the angle formed by the intersection of the line and the x-axis, using a horizontal “run” of 1 and m for slope, The angle of inclination $\alpha ={{\tan }^{-1}}m$ or $m=\tan \alpha $. Thus, the reason why we took $\tan \alpha =slope$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




