
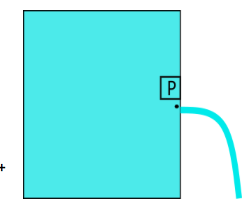
A leakage begins in the water tank at position P as shown in the figure. The initial gauge pressure at P was $5 \times {10^5}N/{m^2}$ .if the density of water is $1000kg/{m^3}$ the initial velocity with which water gushes out is:
A) $3.2m/\sec $
B) $32m/\sec $
C) $28m/\sec $
D) $2.8m/\sec $

Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint:
To solve this question we use Bernoulli’s theorem which is ${P_1} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_1}^2 + \rho g{h_1} = {P_2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_2}^2 + \rho g{h_2}$
And we know the gauge pressure is pressure above that of the atmospheric pressure at that point can be represented as $P - {P_{atm}} = \rho gh$ .
Where $P \Rightarrow $ is the total pressure at that point or at that level
Step by step solution:
First we mark another point Q at the same level of P let as assume the point P and Q are $h$ height below the free surface of the water tank.
As shown in figure.
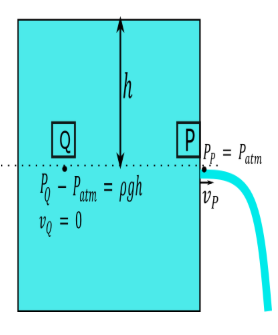
From figure we can write the gauge pressure at point Q is ${P_Q} - {P_{atm}} = \rho gh$
Where $\rho \Rightarrow $ density of water
${P_Q} \Rightarrow $ Total pressure at point Q
$h \Rightarrow $ Height from free surface
So from this we can Wright the pressure at point Q is
$ \Rightarrow {P_Q} = {P_{atm}} + \rho gh$ ......... (1)
Pressure at point P is equal to the atmospheric pressure
${P_P} = {P_{atm}}$ ......... (2)
Velocity at point Q is approximately equal to zero
${v_Q} = 0$....... (3)
Let us assume the velocity at point P is with which water comes out is ${v_P}$
Step 2
Now we apply Bernoulli’s theorem for horizontal points P and Q.
$ \Rightarrow {P_P} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_P}^2 + \rho g{h_P} = {P_Q} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_Q}^2 + \rho g{h_Q}$
Because point P and Q are at same horizontal level ${h_P} = {h_Q}$ so Bernoulli theorem reduced to
$ \Rightarrow {P_P} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_P}^2 = {P_Q} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_Q}^2$
Put all values in this equation from (1) (2) and (3)
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{atm}} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_P}^2 = \left( {{P_{atm}} + \rho gh} \right) + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {\left( 0 \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_P}^2 = \rho gh\]
Now ${P_Q} - {P_{atm}} = \rho gh = 5 \times {10^5}N/{m^2}$ given in question
Put $\rho gh = 5 \times {10^5}$ and density of water $\rho = 1000kg/{m^3}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1000 \times {v_P}^2 = 5 \times {10^5}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_P}^2 = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^5} \times 2}}{{1000}}\]
Further solving
\[ \Rightarrow {v_P} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^5} \times 2}}{{1000}}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_P} = \sqrt {1000} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_P} = 31.62m/\sec \]
Hence the velocity to exit the water tank at point P is approximately $32m/\sec $
therefore Option B is correct
Note:
We can solve this question by another short method which is given below
We know gauge pressure $P = \rho gh$ from this we can find height of hole from free surface
$
\Rightarrow 5 \times {10^5} = 1000 \times 10 \times h \\
\Rightarrow h = 50m \\
$
And now apply Torricelli’s theorem formula velocity of Efflux $v = \sqrt {2gh} $
$
\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {2 \times 10 \times 50} \\
\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {1000} \\
\therefore v = 31.62m/\sec \\
$
To solve this question we use Bernoulli’s theorem which is ${P_1} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_1}^2 + \rho g{h_1} = {P_2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_2}^2 + \rho g{h_2}$
And we know the gauge pressure is pressure above that of the atmospheric pressure at that point can be represented as $P - {P_{atm}} = \rho gh$ .
Where $P \Rightarrow $ is the total pressure at that point or at that level
Step by step solution:
First we mark another point Q at the same level of P let as assume the point P and Q are $h$ height below the free surface of the water tank.
As shown in figure.

From figure we can write the gauge pressure at point Q is ${P_Q} - {P_{atm}} = \rho gh$
Where $\rho \Rightarrow $ density of water
${P_Q} \Rightarrow $ Total pressure at point Q
$h \Rightarrow $ Height from free surface
So from this we can Wright the pressure at point Q is
$ \Rightarrow {P_Q} = {P_{atm}} + \rho gh$ ......... (1)
Pressure at point P is equal to the atmospheric pressure
${P_P} = {P_{atm}}$ ......... (2)
Velocity at point Q is approximately equal to zero
${v_Q} = 0$....... (3)
Let us assume the velocity at point P is with which water comes out is ${v_P}$
Step 2
Now we apply Bernoulli’s theorem for horizontal points P and Q.
$ \Rightarrow {P_P} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_P}^2 + \rho g{h_P} = {P_Q} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_Q}^2 + \rho g{h_Q}$
Because point P and Q are at same horizontal level ${h_P} = {h_Q}$ so Bernoulli theorem reduced to
$ \Rightarrow {P_P} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_P}^2 = {P_Q} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_Q}^2$
Put all values in this equation from (1) (2) and (3)
\[ \Rightarrow {P_{atm}} + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_P}^2 = \left( {{P_{atm}} + \rho gh} \right) + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {\left( 0 \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v_P}^2 = \rho gh\]
Now ${P_Q} - {P_{atm}} = \rho gh = 5 \times {10^5}N/{m^2}$ given in question
Put $\rho gh = 5 \times {10^5}$ and density of water $\rho = 1000kg/{m^3}$
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} \times 1000 \times {v_P}^2 = 5 \times {10^5}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_P}^2 = \dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^5} \times 2}}{{1000}}\]
Further solving
\[ \Rightarrow {v_P} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{5 \times {{10}^5} \times 2}}{{1000}}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_P} = \sqrt {1000} \]
\[ \Rightarrow {v_P} = 31.62m/\sec \]
Hence the velocity to exit the water tank at point P is approximately $32m/\sec $
therefore Option B is correct
Note:
We can solve this question by another short method which is given below
We know gauge pressure $P = \rho gh$ from this we can find height of hole from free surface
$
\Rightarrow 5 \times {10^5} = 1000 \times 10 \times h \\
\Rightarrow h = 50m \\
$
And now apply Torricelli’s theorem formula velocity of Efflux $v = \sqrt {2gh} $
$
\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {2 \times 10 \times 50} \\
\Rightarrow v = \sqrt {1000} \\
\therefore v = 31.62m/\sec \\
$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




