
A lead shot of $1mm$ diameter falls through a long column of glycerin. The variation of the velocity ($v$) with distance covered ($s$) is correctly represented by
A.
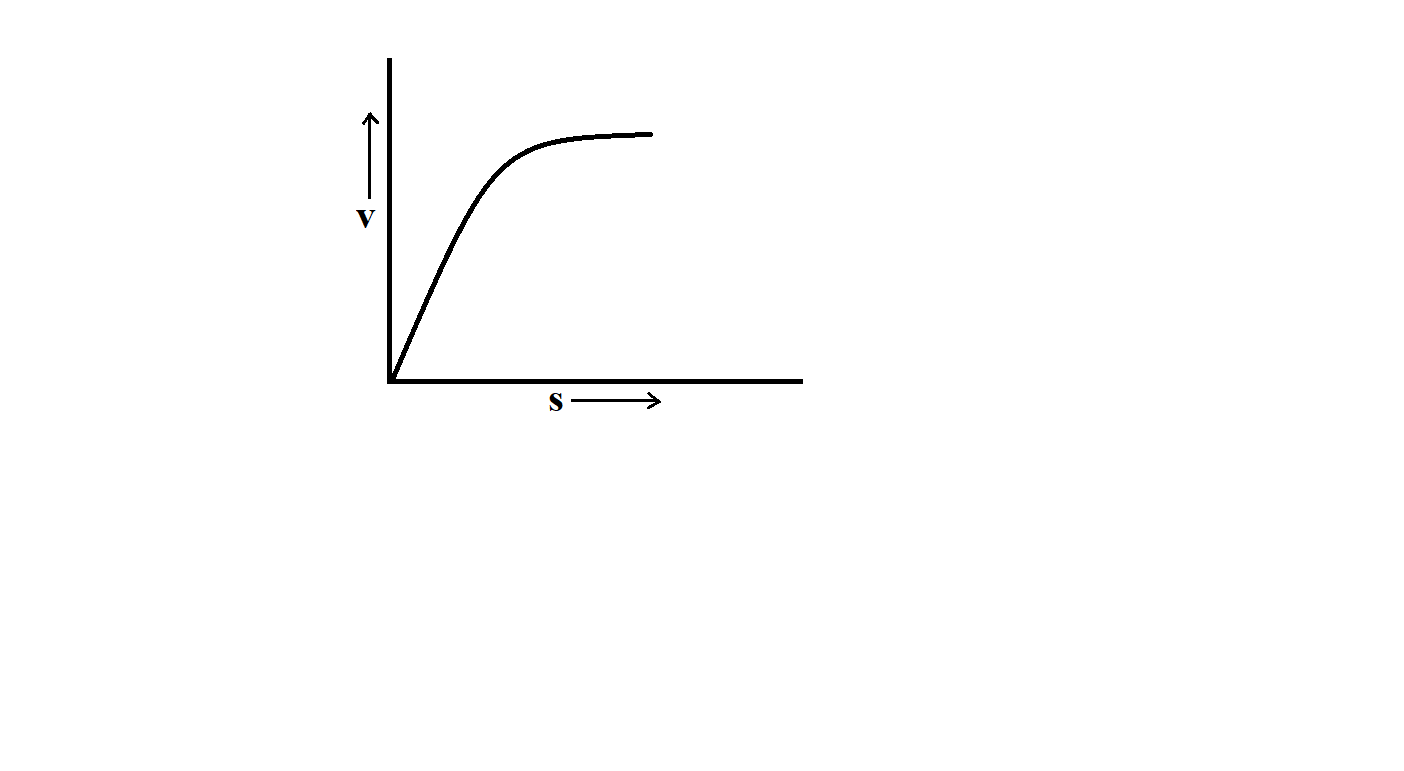
B.
C.
D.
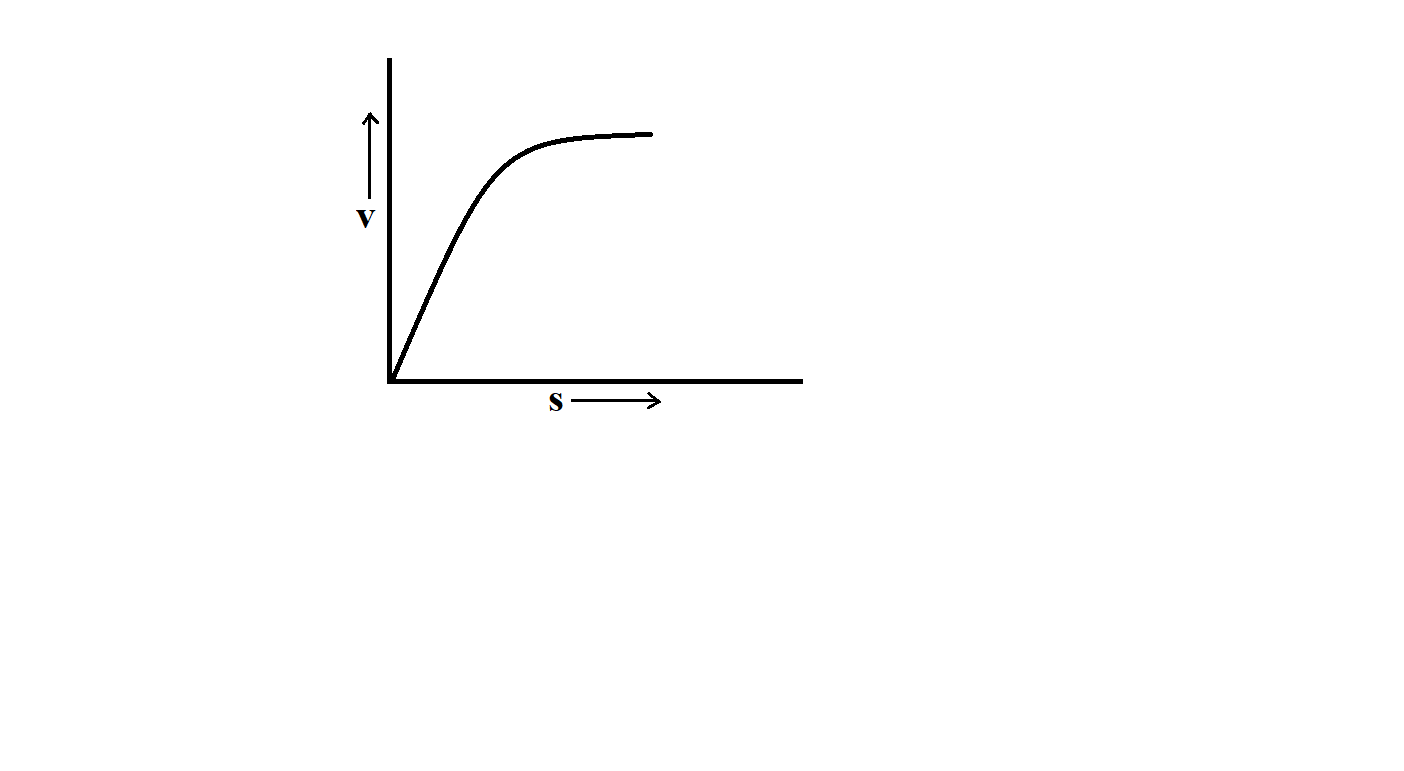


Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: When an object moves through a viscous fluid, buoyant force and viscous force acts on the body in opposite directions. When viscous force becomes equal to the buoyant force, the object acquires a constant speed in the fluid.
Formula used:
$F=6\pi \eta rv$
The viscous drag force on a sphere of radius$r$moving with a velocity $v$ in a fluid of viscosity $\eta $ is given by Stokes’ law.
$F=6\pi \eta rv$
Complete step by step answer:
The viscosity of a fluid is the measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. Viscous force acting on an object in a fluid is proportional to the rate at which the fluid velocity is changing in space. The proportionality constant is the viscosity.
The viscous drag force on a sphere of radius $r$ moving with a velocity $v$ in a fluid of viscosity $\eta $ is given by Stokes’ law.
$F=6\pi \eta rv$
The viscous force acting on a body is directly proportional to the following parameters:
the radius of the spherical body
coefficient of viscosity
the velocity of the object
Terminal velocity: The constant speed which a freely falling body acquires eventually when the resistance of the medium, say fluid, through which it is falling prevents further acceleration. It is the maximum velocity acquired by the object as it falls through a fluid.
Expression for terminal velocity,
$v=\dfrac{2{{r}^{2}}\left( \rho -{{\rho }_{o}} \right)}{9\eta }$
Where,
$v$ is the terminal velocity of object
${{\rho }_{o}}$ is the density of fluid
$\rho $ is the density of the object
In the beginning due to gravitational pull, the lead shot will be accelerated and hence will move, with increasing velocity for some time. When the viscous force balances the gravitational force, then the shot will continue moving with a constant velocity. While in the beginning, the velocity of shot is not fully linear with the effective distance covered by the shot.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: While calculating the terminal velocity, gravitational force is not taken into consideration since we only have to consider the variable forces only, that is buoyant force and the viscous force.
Formula used:
$F=6\pi \eta rv$
The viscous drag force on a sphere of radius$r$moving with a velocity $v$ in a fluid of viscosity $\eta $ is given by Stokes’ law.
$F=6\pi \eta rv$
Complete step by step answer:
The viscosity of a fluid is the measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. Viscous force acting on an object in a fluid is proportional to the rate at which the fluid velocity is changing in space. The proportionality constant is the viscosity.
The viscous drag force on a sphere of radius $r$ moving with a velocity $v$ in a fluid of viscosity $\eta $ is given by Stokes’ law.
$F=6\pi \eta rv$
The viscous force acting on a body is directly proportional to the following parameters:
the radius of the spherical body
coefficient of viscosity
the velocity of the object
Terminal velocity: The constant speed which a freely falling body acquires eventually when the resistance of the medium, say fluid, through which it is falling prevents further acceleration. It is the maximum velocity acquired by the object as it falls through a fluid.
Expression for terminal velocity,
$v=\dfrac{2{{r}^{2}}\left( \rho -{{\rho }_{o}} \right)}{9\eta }$
Where,
$v$ is the terminal velocity of object
${{\rho }_{o}}$ is the density of fluid
$\rho $ is the density of the object
In the beginning due to gravitational pull, the lead shot will be accelerated and hence will move, with increasing velocity for some time. When the viscous force balances the gravitational force, then the shot will continue moving with a constant velocity. While in the beginning, the velocity of shot is not fully linear with the effective distance covered by the shot.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: While calculating the terminal velocity, gravitational force is not taken into consideration since we only have to consider the variable forces only, that is buoyant force and the viscous force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




