
A horizontal plane with the coefficient of friction \[k\] supports two bodies: a bar and an electric motor with a battery on a block. A thread attached to the bar is wound on the shaft of the electric motor. The distance between the bar and the electric motor is equal to \[l\]. When the motor is switched on, the bar whose mass is twice as great as that of the other body, starts moving with constant acceleration \[w\]. The bodies will collide after time \[\tau = \sqrt {\dfrac{{xl}}{{3w + kg}}} \]. Find \[x\].
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint:Use the expression for Newton’s second law of motion. Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the bar and the system of the motor-battery-block (body) in the horizontal and vertical direction and determine the acceleration of the body. Also use a kinematic equation for displacement of the bar and the body and calculate the time required for the collision of the bar and the body.
Formulae used:
The expression for Newton’s second law of motion is
\[{F_{net}} = ma\] …… (1)
Here, \[{F_{net}}\] is net force on the block, \[m\] is mass of the object and \[a\] is acceleration of the object.
The kinematic equation for displacement \[s\] of an object is
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\] …… (2)
Here, \[u\] is initial velocity of the object, \[t\] is time and \[a\] is acceleration of the object.
The frictional force \[{F_f}\] acting on an object is
\[{F_f} = \mu N\] …… (3)
Here, \[\mu \] is the coefficient of friction and \[N\] is the normal force acting on the object.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that a bar and an electric motor with a battery on a block are placed on a horizontal table and the coefficient of friction of the horizontal table is.The distance between the bar and the electric motor is \[l\].The bar is connected to the motor with a thread with which the bar is pulled towards the motor when the electric motor is switched on.
The acceleration of the bar when it moves towards the motor is \[w\].The mass of the bar is twice the mass of the system of the motor-battery-block.Let \[m\] be the mass of the bar and \[2m\] be the mass of the motor-battery-block system.Let us draw the free body diagram of the given system.
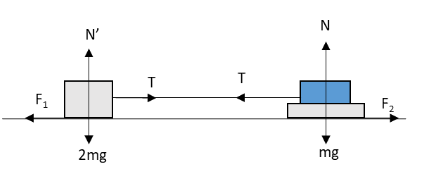
In the above figure, \[T\] is the tension in the thread, \[2mg\] and \[mg\] are the weights of the bar and the body, \[N'\] and \[N\] are the normal forces acting on the bar and the body, \[{F_1}\] and \[{F_2}\] are the frictional forces acting on the bar and the body respectively.Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the bar in the vertical direction.
\[N' = 2mg\]
Using equation (1), the frictional force on the bar is
\[{F_1} = kN'\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_1} = k\left( {2mg} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_1} = 2kmg\]
Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the bar in the horizontal direction.
\[T - {F_1} = 2mw\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - 2kmg = 2mw\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = 2mw + 2kmg\] …… (4)
Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the body in the vertical direction.
\[N = mg\]
Using equation (1), the frictional force on the body is
\[{F_2} = kN\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_2} = k\left( {mg} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_2} = kmg\]
Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the body in the horizontal direction.
\[{F_2} - T = - mw'\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - {F_2} = mw'\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - kmg = mw'\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = mw' + kmg\] …… (5)
Here, is \[w'\] the acceleration of the body.
Equating equations (4) and (5).
\[2mw + 2kmg = mw' + kmg\]
\[ \Rightarrow w' = 2w + kg\]
Initially, the bar and the body is at rest. Hence, the initial velocity of the bar and the body is zero.So, equation (2) for the displacement of the bar and body is
\[l = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {w + w'} \right){\tau ^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2l = \left( {w + w'} \right){\tau ^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \tau = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{w + w'}}} \]
Here, \[\tau \] is the time required for the bar and body to collide each other.
Substitute \[2w + kg\] for \[w'\] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \tau = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{w + \left( {2w + kg} \right)}}} \]
\[ \therefore \tau = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{3w + kg}}} \]
From the above equation, the value of \[x\] is 2.
Note: The students should be careful while applying Newton’ second law of motion to the bar and the body. The students should use the sign of the forces carefully. If the signs of these forces are not taken correctly then the final expression for time required for the collision of the bar and body will be incorrect and we will obtain the incorrect answer.
Formulae used:
The expression for Newton’s second law of motion is
\[{F_{net}} = ma\] …… (1)
Here, \[{F_{net}}\] is net force on the block, \[m\] is mass of the object and \[a\] is acceleration of the object.
The kinematic equation for displacement \[s\] of an object is
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\] …… (2)
Here, \[u\] is initial velocity of the object, \[t\] is time and \[a\] is acceleration of the object.
The frictional force \[{F_f}\] acting on an object is
\[{F_f} = \mu N\] …… (3)
Here, \[\mu \] is the coefficient of friction and \[N\] is the normal force acting on the object.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that a bar and an electric motor with a battery on a block are placed on a horizontal table and the coefficient of friction of the horizontal table is.The distance between the bar and the electric motor is \[l\].The bar is connected to the motor with a thread with which the bar is pulled towards the motor when the electric motor is switched on.
The acceleration of the bar when it moves towards the motor is \[w\].The mass of the bar is twice the mass of the system of the motor-battery-block.Let \[m\] be the mass of the bar and \[2m\] be the mass of the motor-battery-block system.Let us draw the free body diagram of the given system.

In the above figure, \[T\] is the tension in the thread, \[2mg\] and \[mg\] are the weights of the bar and the body, \[N'\] and \[N\] are the normal forces acting on the bar and the body, \[{F_1}\] and \[{F_2}\] are the frictional forces acting on the bar and the body respectively.Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the bar in the vertical direction.
\[N' = 2mg\]
Using equation (1), the frictional force on the bar is
\[{F_1} = kN'\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_1} = k\left( {2mg} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_1} = 2kmg\]
Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the bar in the horizontal direction.
\[T - {F_1} = 2mw\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - 2kmg = 2mw\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = 2mw + 2kmg\] …… (4)
Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the body in the vertical direction.
\[N = mg\]
Using equation (1), the frictional force on the body is
\[{F_2} = kN\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_2} = k\left( {mg} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {F_2} = kmg\]
Apply Newton’s second law of motion to the body in the horizontal direction.
\[{F_2} - T = - mw'\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - {F_2} = mw'\]
\[ \Rightarrow T - kmg = mw'\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = mw' + kmg\] …… (5)
Here, is \[w'\] the acceleration of the body.
Equating equations (4) and (5).
\[2mw + 2kmg = mw' + kmg\]
\[ \Rightarrow w' = 2w + kg\]
Initially, the bar and the body is at rest. Hence, the initial velocity of the bar and the body is zero.So, equation (2) for the displacement of the bar and body is
\[l = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {w + w'} \right){\tau ^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2l = \left( {w + w'} \right){\tau ^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \tau = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{w + w'}}} \]
Here, \[\tau \] is the time required for the bar and body to collide each other.
Substitute \[2w + kg\] for \[w'\] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \tau = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{w + \left( {2w + kg} \right)}}} \]
\[ \therefore \tau = \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{3w + kg}}} \]
From the above equation, the value of \[x\] is 2.
Note: The students should be careful while applying Newton’ second law of motion to the bar and the body. The students should use the sign of the forces carefully. If the signs of these forces are not taken correctly then the final expression for time required for the collision of the bar and body will be incorrect and we will obtain the incorrect answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




