
A foot of normal from the point $\left( {4,3} \right)$ to a circle is $\left( {2,1} \right)$ and the diameter of the circle has the equation $2x - y = 2$. Then, the equation of circle is
A. ${x^2} + {y^2} = 1$
B. ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x + 1 = 0$
C. ${x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 1 = 0$
D. ${x^2} + {y^2} = 5$
Answer
602.4k+ views
Hint: Firstly, find the equation of the normal with the given points. They had already given the equation of diameter. The intersection of diameter and the normal will be the center of the circle. So, we can find out the equation of the circle with radius as a variable. After that if we substitute the foot of normal in the circle equation as it will be on the circle, we can get the radius also.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us note down the given data,
A foot of normal from the point $\left( {4,3} \right)$ to a circle is $\left( {2,1} \right)$
Diameter of the circle has an equation $2x - y = 2$.
Let us draw a diagram to visualize it clearly,
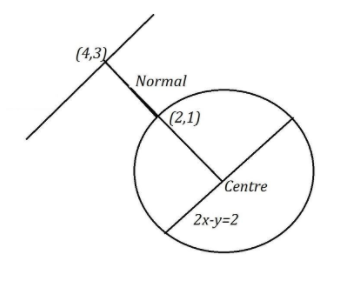
Now we can notice that the points $\left( {4,3} \right)$ and $\left( {2,1} \right)$ lie on the normal, we can find out the equation of the normal.
So, the equation of the normal can be found through the above formula.
Slope of the normal $ = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$
Substitute the values we get,
Slope of the normal $ = \dfrac{{1 - 3}}{{2 - 4}}$
$ = 1$
The equation of a line which passes through two points $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ with slope $m$ is \[\left( {y - {y_1}} \right) = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)\].
So, the equation of the normal is $\left( {y - {y_1}} \right) = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)$
When we substitute the values, we get as follows:
The equation of normal,
$
\Rightarrow y - 1 = 1\left( {x - 2} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y - 1 = x - 2 \\
\Rightarrow x - y - 1 = 0 \\
$
Now, to get the centre, we need to solve the normal equation and the diameter equation.
In the normal equation,
$
\Rightarrow x - y - 1 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x = 1 + y \\
$
Put this in the diameter equation.
Diameter of the circle is $2x - y = 2$
$
\Rightarrow 2\left( {1 + y} \right) - y = 2 \\
\Rightarrow 2 + y = 2 \\
\Rightarrow y = 0 \\
$
Put this value in the normal equation or diameter equation to get the centre coordinators. Here we are going to use the normal equation. You can use any equation. Both give the same answer.
$
\Rightarrow x = 1 + y \\
\Rightarrow x = 1 + 0 \\
\Rightarrow x = 1 \\
$
So, the coordinates of the centre of the circle are $\left( {1,0} \right)$.
Now the equation of the circle with centre $\left( {a,b} \right)$ and radius $r$ is \[{\left( {x - a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - b} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
So, the circle equation will be as follows:
\[
\Rightarrow {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 0} \right)^2} = {r^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {y^2} = {r^2} \\
\]
We know that the point $\left( {2,1} \right)$ is on the circle. So, substitute this point in the equation to get the value of radius.
\[
\Rightarrow {\left( {2 - 1} \right)^2} + {1^2} = {r^2} \\
\Rightarrow 1 + 1 = {r^2} \\
\Rightarrow {r^2} = 2 \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt 2 \\
\]
Substitute this value in the equation of circle, we will get \[{\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {y^2} = 2\]
Expand the equation using the formula ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$.
Where $a = x$ and $b = 1$.
Then we will get,
\[
{\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {y^2} = 2 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 1 - 2x + {y^2} = 2 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 1 = 0 \\
\]
So, the equation of the circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 1 = 0\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: These kinds of geometric problems are very interesting and would be very easy to solve when we clearly get the concepts. We must know all the properties related to the structures in the geometry. The present question that we solved can be done in a little bit different way by finding the radius using distance formula because we have a center and one point on the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us note down the given data,
A foot of normal from the point $\left( {4,3} \right)$ to a circle is $\left( {2,1} \right)$
Diameter of the circle has an equation $2x - y = 2$.
Let us draw a diagram to visualize it clearly,

Now we can notice that the points $\left( {4,3} \right)$ and $\left( {2,1} \right)$ lie on the normal, we can find out the equation of the normal.
So, the equation of the normal can be found through the above formula.
Slope of the normal $ = \dfrac{{{y_2} - {y_1}}}{{{x_2} - {x_1}}}$
Substitute the values we get,
Slope of the normal $ = \dfrac{{1 - 3}}{{2 - 4}}$
$ = 1$
The equation of a line which passes through two points $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ with slope $m$ is \[\left( {y - {y_1}} \right) = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)\].
So, the equation of the normal is $\left( {y - {y_1}} \right) = m\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)$
When we substitute the values, we get as follows:
The equation of normal,
$
\Rightarrow y - 1 = 1\left( {x - 2} \right) \\
\Rightarrow y - 1 = x - 2 \\
\Rightarrow x - y - 1 = 0 \\
$
Now, to get the centre, we need to solve the normal equation and the diameter equation.
In the normal equation,
$
\Rightarrow x - y - 1 = 0 \\
\Rightarrow x = 1 + y \\
$
Put this in the diameter equation.
Diameter of the circle is $2x - y = 2$
$
\Rightarrow 2\left( {1 + y} \right) - y = 2 \\
\Rightarrow 2 + y = 2 \\
\Rightarrow y = 0 \\
$
Put this value in the normal equation or diameter equation to get the centre coordinators. Here we are going to use the normal equation. You can use any equation. Both give the same answer.
$
\Rightarrow x = 1 + y \\
\Rightarrow x = 1 + 0 \\
\Rightarrow x = 1 \\
$
So, the coordinates of the centre of the circle are $\left( {1,0} \right)$.
Now the equation of the circle with centre $\left( {a,b} \right)$ and radius $r$ is \[{\left( {x - a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - b} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
So, the circle equation will be as follows:
\[
\Rightarrow {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - 0} \right)^2} = {r^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {y^2} = {r^2} \\
\]
We know that the point $\left( {2,1} \right)$ is on the circle. So, substitute this point in the equation to get the value of radius.
\[
\Rightarrow {\left( {2 - 1} \right)^2} + {1^2} = {r^2} \\
\Rightarrow 1 + 1 = {r^2} \\
\Rightarrow {r^2} = 2 \\
\Rightarrow r = \sqrt 2 \\
\]
Substitute this value in the equation of circle, we will get \[{\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {y^2} = 2\]
Expand the equation using the formula ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab$.
Where $a = x$ and $b = 1$.
Then we will get,
\[
{\left( {x - 1} \right)^2} + {y^2} = 2 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + 1 - 2x + {y^2} = 2 \\
\Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 1 = 0 \\
\]
So, the equation of the circle is \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 2x - 1 = 0\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: These kinds of geometric problems are very interesting and would be very easy to solve when we clearly get the concepts. We must know all the properties related to the structures in the geometry. The present question that we solved can be done in a little bit different way by finding the radius using distance formula because we have a center and one point on the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Why was the Vernacular Press Act passed by British class 11 social science CBSE

How did silk routes link the world Explain with three class 11 social science CBSE

Graph between Concentration and Time for a first order class 11 chemistry CBSE

The compound used in treatment of lead poisoning is class 11 chemistry CBSE




