
A can be

A. $C\text{onc}\text{. }{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{S}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$
B. Alcoholic KOH
C. $E{{t}_{3}}N$
D. $t-BuOK$

Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: You should know that; cyclohexene will dimerize when it is treated with a strong concentrated acid. Try to figure out which one of the options is a strong acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that,
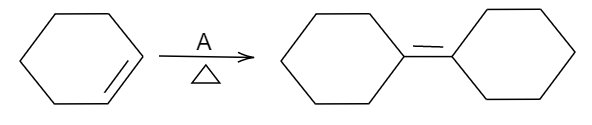
In the above reaction, the given reactant is a cyclohexene and the product formed is a dimer of that compound given.
So, we should know that a cyclohexene dimerizes when treated with strong concentrated acid. In the given options, concentrated sulphuric acid ($Conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$) is a strong acid. Being a strong acid, it will try to protonate an alkene molecule such that a carbocation intermediate will be obtained. This then will attack another molecule of alkene which is a nucleophile that will result in another carbocation intermediate and since migration of hydrogen atom from an adjacent tertiary carbon will result into a more stable carbocation intermediate. Then, finally deprotonation will occur from that adjacent carbon atom resulting in an alkene. The final step includes deprotonation which will result in a dimerized product.
In short, we can say that the hexene takes hydrogen ions from sulphuric acid which forms an intermediate carbocation. This carbocation gains pi electrons from another hexene and at the final step hydrogen is removed from the adjacent carbon atom to a carbocation and at last a dimer is formed.
Hence the answer id option A.
Note: It is important to note that two molecules of cyclohexene are only used so that to control the attack of carbocation on other alkene groups. $E{{t}_{3}}N$ is referred to as the triethylamine and $t-BuOK$ is potassium tert-butoxide.
Complete step by step answer:
Given that,

In the above reaction, the given reactant is a cyclohexene and the product formed is a dimer of that compound given.
So, we should know that a cyclohexene dimerizes when treated with strong concentrated acid. In the given options, concentrated sulphuric acid ($Conc.{{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$) is a strong acid. Being a strong acid, it will try to protonate an alkene molecule such that a carbocation intermediate will be obtained. This then will attack another molecule of alkene which is a nucleophile that will result in another carbocation intermediate and since migration of hydrogen atom from an adjacent tertiary carbon will result into a more stable carbocation intermediate. Then, finally deprotonation will occur from that adjacent carbon atom resulting in an alkene. The final step includes deprotonation which will result in a dimerized product.
In short, we can say that the hexene takes hydrogen ions from sulphuric acid which forms an intermediate carbocation. This carbocation gains pi electrons from another hexene and at the final step hydrogen is removed from the adjacent carbon atom to a carbocation and at last a dimer is formed.
Hence the answer id option A.
Note: It is important to note that two molecules of cyclohexene are only used so that to control the attack of carbocation on other alkene groups. $E{{t}_{3}}N$ is referred to as the triethylamine and $t-BuOK$ is potassium tert-butoxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




