
A body of mass M is kept on a rough horizontal surface (friction coefficient\[\mu \]). A person is trying to pull the body by applying a horizontal force but the body is not moving. The force by the horizontal surface on the surface of the body is F, where
\[A.\,F=Mg\]
\[B.\,F=\mu MgF\]
\[C.\,Mg\le f\le Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}}\]
\[D.\,Mg\ge f\ge Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}}\]
Answer
573k+ views
Hint: The question is based on the concept of the force acting on the body. So we will make use of the free body diagram to solve this type of question. We will solve the given problem using the formulae of the forces acting on the body, such as the normal force and the frictional force.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& N=mg \\
& {{f}_{s}}=\mu N \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step solution:
The free body diagram of the mass M kept on a rough horizontal surface is given as follows.
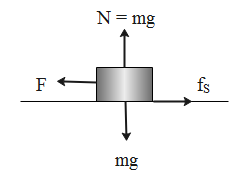
The normal force acting on the body is given as follows.
\[N=ma\]
Where m is the mass of the body and a is the acceleration of the body.
The frictional force acting on the body is given as follows.
\[{{f}_{s}}=\mu N\]
Where \[\mu \] is the coefficient of friction and N is the normal force acting on the body.
From the free body diagram of the mass M kept on a rough horizontal surface, it’s clear that the horizontal forces acting on the body is the resultant of the force and the frictional force.
\[\begin{align}
& f=\sqrt{{{(Mg)}^{2}}+{{(\mu Mg)}^{2}}} \\
& f=Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
This force will be lying between that of the normal force and the frictional force. Thus, this can be expressed in the mathematical form as follows.
\[Mg\le f\le Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}}\]
\[\therefore \] The force by the horizontal surface on the surface of the body is F, where \[Mg\le f\le Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}}\].
As, the force, \[Mg\le f\le Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Using a free body diagram makes it easy to solve this type of question by understanding the forces acting on the body and the directions of the force. The units of the parameters should be taken care of.
Formula used:
\[\begin{align}
& N=mg \\
& {{f}_{s}}=\mu N \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step solution:
The free body diagram of the mass M kept on a rough horizontal surface is given as follows.

The normal force acting on the body is given as follows.
\[N=ma\]
Where m is the mass of the body and a is the acceleration of the body.
The frictional force acting on the body is given as follows.
\[{{f}_{s}}=\mu N\]
Where \[\mu \] is the coefficient of friction and N is the normal force acting on the body.
From the free body diagram of the mass M kept on a rough horizontal surface, it’s clear that the horizontal forces acting on the body is the resultant of the force and the frictional force.
\[\begin{align}
& f=\sqrt{{{(Mg)}^{2}}+{{(\mu Mg)}^{2}}} \\
& f=Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
This force will be lying between that of the normal force and the frictional force. Thus, this can be expressed in the mathematical form as follows.
\[Mg\le f\le Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}}\]
\[\therefore \] The force by the horizontal surface on the surface of the body is F, where \[Mg\le f\le Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}}\].
As, the force, \[Mg\le f\le Mg\sqrt{1+{{\mu }^{2}}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Using a free body diagram makes it easy to solve this type of question by understanding the forces acting on the body and the directions of the force. The units of the parameters should be taken care of.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




