
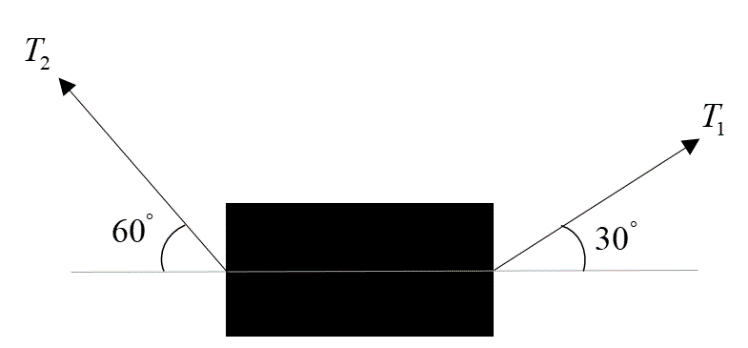
A body of mass 5kg is suspended using string making an angle $30^{\circ}$ and $60^{\circ}$ with the horizontal then:
$\text{A}. \ T_{1}=25\ N$
$\text{B}. \ T_{2}=25\ N$
$\text{C}. \ T_{1}=25\sqrt 3\ N$
$\text{D}. \ T_{2}=25\sqrt 3\ N$

Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: This type of question can be easily solved by drawing the free body diagram of the block and applying the equilibrium equations in x and y directions. Since we are not given the information about motion, we will assume the block to be at rest. Hence the net force in x and y direction is zero.
Formula used: $\sum F_{x} = 0, \sum F_{y} = 0$
Complete step by step answer:
First of all drawing the free body diagram of the block, by resolving the forces into x and y components:
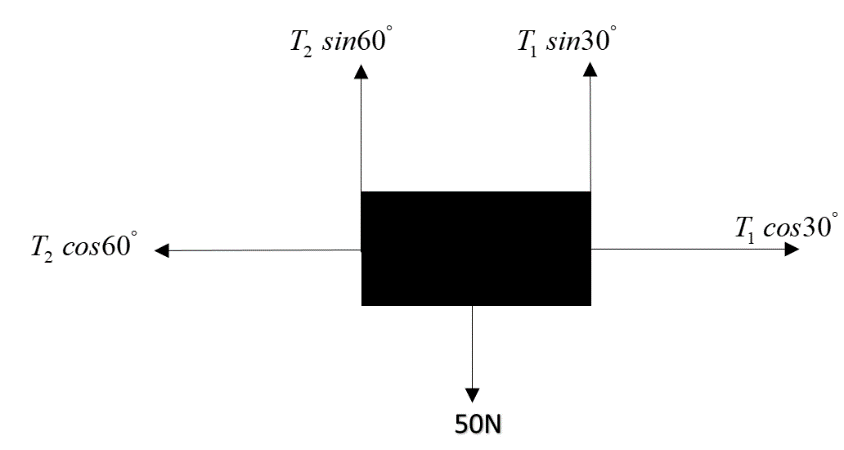
Now, writing equation for x direction:
$T_2cos60^{\circ} = T_1cos30^{\circ}$
Or $\dfrac{T_2}{2} = \dfrac{T_1\times \sqrt3}{2}$
Hence $T_2=T_1 \sqrt 3$
And writing the equation of force in y direction:
$T_2 sin60^{\circ}+T_1sin30^{\circ}=Weight=50N$
Or $T_2 \dfrac{\sqrt 3}{2} + \dfrac{T_1}{2} =50$
Or $T_2 \sqrt 3 +T_1=100$
But $T_2=T_1 \sqrt 3$
Hence $T_1(3)+T_1=100$
Or $4T_1=100$
$T_1=25N$
And hence $T_2=T_1 \sqrt 3$
So, $T_2=25\sqrt 3 N$
So, the correct answer is “Option A and D”.
Note: Here it is important to note that the given block was freely suspended. That’s why we took its acceleration zero (both in x and y directions). That also means that the net force is also zero as$F_{net}=m\times a$. When a block is suspended in air using some technique, if it is at rest, without motion, then we can say that the block is under transitional and rotational equilibrium i.e. the sum of forces along any given direction is zero and also the sum of moments about any given point is zero. This concept can be easily applied to solve any level of questions.
Formula used: $\sum F_{x} = 0, \sum F_{y} = 0$
Complete step by step answer:
First of all drawing the free body diagram of the block, by resolving the forces into x and y components:

Now, writing equation for x direction:
$T_2cos60^{\circ} = T_1cos30^{\circ}$
Or $\dfrac{T_2}{2} = \dfrac{T_1\times \sqrt3}{2}$
Hence $T_2=T_1 \sqrt 3$
And writing the equation of force in y direction:
$T_2 sin60^{\circ}+T_1sin30^{\circ}=Weight=50N$
Or $T_2 \dfrac{\sqrt 3}{2} + \dfrac{T_1}{2} =50$
Or $T_2 \sqrt 3 +T_1=100$
But $T_2=T_1 \sqrt 3$
Hence $T_1(3)+T_1=100$
Or $4T_1=100$
$T_1=25N$
And hence $T_2=T_1 \sqrt 3$
So, $T_2=25\sqrt 3 N$
So, the correct answer is “Option A and D”.
Note: Here it is important to note that the given block was freely suspended. That’s why we took its acceleration zero (both in x and y directions). That also means that the net force is also zero as$F_{net}=m\times a$. When a block is suspended in air using some technique, if it is at rest, without motion, then we can say that the block is under transitional and rotational equilibrium i.e. the sum of forces along any given direction is zero and also the sum of moments about any given point is zero. This concept can be easily applied to solve any level of questions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




