
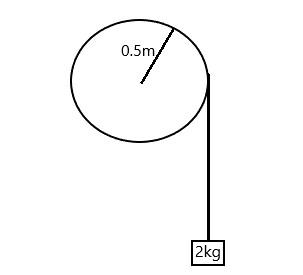
A block of mass 2 kg, hangs from the rim of a wheel of radius \[0.5\] m. On releasing from rest, the block falls through 5m height in 2s. the moment of inertia of the wheel is (take \[g = 10m/{s^2}\])
(A) \[1kg{m^2}\]
(B) \[3.2kg{m^2}\]
(C) \[2.5kg{m^2}\]
(D) \[1.5kg{m^2}\]

Answer
553.2k+ views
Hint: The acceleration of the block is the same as the linear acceleration of the rim. The tension in the string is the driver of the rim.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\] where \[s\] is the distance covered by an accelerating body, \[u\] is the initial velocity, \[a\] is the acceleration of the body, and \[t\] is the time elapsed.
\[Fr = I\alpha \] where \[F\] is the force acting on a body, \[r\] is the distance of \[F\] from an axis of rotation, \[I\] is the moment of inertia of the body and \[\alpha \] is the angular acceleration. The quantity, \[Fr\] is the torque on a body.
\[\alpha = \dfrac{a}{r}\] where \[a\] is the linear acceleration, and \[r\] is the radius of a body.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Generally, moment of inertial and the force acting on a body are related through
\[Fr = I\alpha \] where \[F\] is the force acting on a body, \[r\] is the distance of \[F\] from an axis of rotation, \[I\] is the moment of inertia of the body and \[\alpha \] is the angular acceleration.
Hence, to find the moment of inertia, we need to know the force of the rim and the angular acceleration.
Angular acceleration is \[\alpha = \dfrac{a}{r}\] where \[a\] is the linear acceleration, and \[r\] is radius.
The acceleration can be gotten from
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\] where \[s\] is the distance covered by an accelerating body, \[u\] is the initial velocity, \[a\] is the acceleration of the body, and \[t\] is the time elapsed.
Hence,
\[5 = \dfrac{1}{2}a{\left( 2 \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{5}{2}m/s\]
Then
\[\alpha = \dfrac{{\dfrac{5}{2}}}{{0.5}} = 5rad/{s^2}\]
The force driving the rim is the tension, hence to calculate tension on string, we perform newton's law analysis on block
\[mg - T = ma\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left( {10} \right) - T = 2\left( {\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)\]
Hence,
\[T = 15N\]
Then,
\[Tr = I\alpha \]
\[ \Rightarrow 15(0.5) = I\left( 5 \right)\]
Then by dividing both side by 5, we have
\[I = \dfrac{{15\left( {0.5} \right)}}{5} = 2.5kg{m^2}\]
Hence, the correct option is C
Note: For clarity, the tension is the force which drives the rim because the string is the object directly in contact with the rim. The tension is as a result of the block hanging down, however it’s not the weight that drives it but the transmitted force along the string (which is the tension).
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\] where \[s\] is the distance covered by an accelerating body, \[u\] is the initial velocity, \[a\] is the acceleration of the body, and \[t\] is the time elapsed.
\[Fr = I\alpha \] where \[F\] is the force acting on a body, \[r\] is the distance of \[F\] from an axis of rotation, \[I\] is the moment of inertia of the body and \[\alpha \] is the angular acceleration. The quantity, \[Fr\] is the torque on a body.
\[\alpha = \dfrac{a}{r}\] where \[a\] is the linear acceleration, and \[r\] is the radius of a body.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
Generally, moment of inertial and the force acting on a body are related through
\[Fr = I\alpha \] where \[F\] is the force acting on a body, \[r\] is the distance of \[F\] from an axis of rotation, \[I\] is the moment of inertia of the body and \[\alpha \] is the angular acceleration.
Hence, to find the moment of inertia, we need to know the force of the rim and the angular acceleration.
Angular acceleration is \[\alpha = \dfrac{a}{r}\] where \[a\] is the linear acceleration, and \[r\] is radius.
The acceleration can be gotten from
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\] where \[s\] is the distance covered by an accelerating body, \[u\] is the initial velocity, \[a\] is the acceleration of the body, and \[t\] is the time elapsed.
Hence,
\[5 = \dfrac{1}{2}a{\left( 2 \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{5}{2}m/s\]
Then
\[\alpha = \dfrac{{\dfrac{5}{2}}}{{0.5}} = 5rad/{s^2}\]
The force driving the rim is the tension, hence to calculate tension on string, we perform newton's law analysis on block
\[mg - T = ma\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2\left( {10} \right) - T = 2\left( {\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)\]
Hence,
\[T = 15N\]
Then,
\[Tr = I\alpha \]
\[ \Rightarrow 15(0.5) = I\left( 5 \right)\]
Then by dividing both side by 5, we have
\[I = \dfrac{{15\left( {0.5} \right)}}{5} = 2.5kg{m^2}\]
Hence, the correct option is C
Note: For clarity, the tension is the force which drives the rim because the string is the object directly in contact with the rim. The tension is as a result of the block hanging down, however it’s not the weight that drives it but the transmitted force along the string (which is the tension).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




