
2-Bromobutane is optically active but 1-Bromobutane is optically inactive. Why?
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: A molecule is said to be optically active if it is chiral. A molecule is chiral if it has four different substituents attached to the valencies of the carbon. A compound is optically active only if it is chiral. We may determine the chirality by knowing the structures of the compounds given.
Complete answer:
It was found by Baptiste in 1813 that the plane polarised light when passed through single crystals of quartz or aqueous solutions of lactic acid, rotated the plane polarised light either to the right or to the left. When it was rotated towards right, it was called dextrorotatory, while towards left it is known as laevo rotatory. All the substances that rotate the plane polarised light are said to be optically active.
Optically active molecules are always chiral. The chirality of a molecule results from its structure. It is the property of the molecules that arise from the way they interact with the light. We are given two molecules 2-Bromobutane and 1-Bromobutane. The structure of the molecules can be given as:
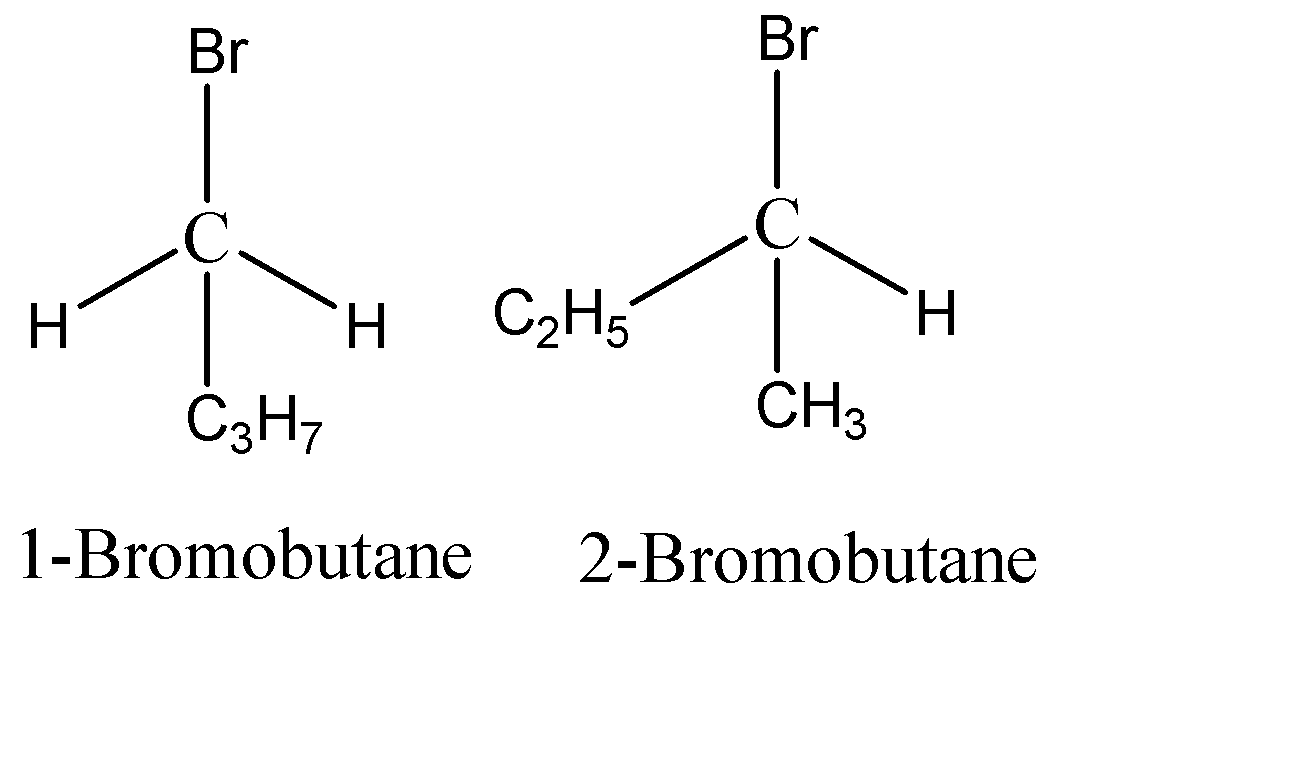
As we can see in 2-Bromobutane will have for different substituents- $ H,Br,{C_2}{H_5},C{H_3} $ , whereas 1-bromobutane has 2 same substituents (H) attached to the carbon. Since 2-bromobutane has all different substituents attached to the carbon, this carbon is known as the Chiral Carbon and the compound is optically active. Since in 1-bromobutane, 2 same Hydrogen atoms are attached, it cannot be a chiral centre.
Note:
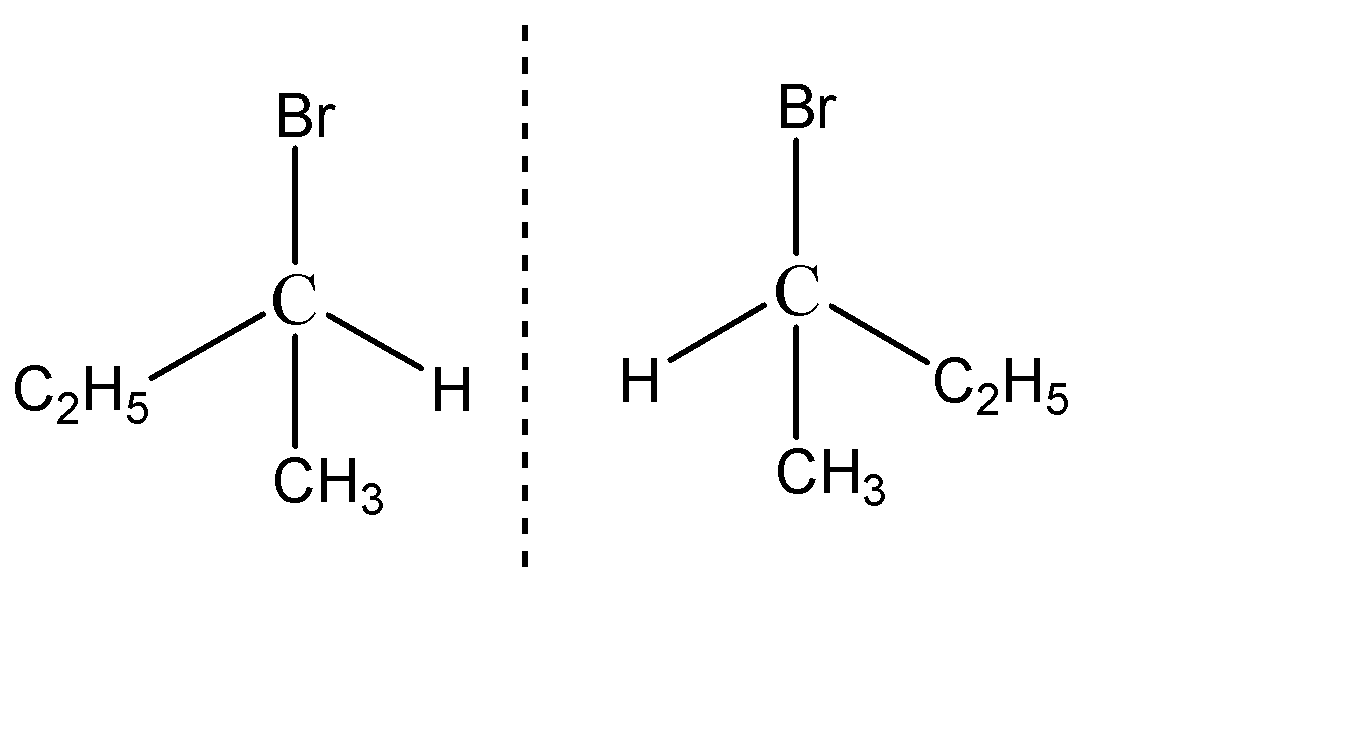
Chiral molecules, forming mirror images, which are non-superimposable on each other, are known as enantiomers. 2-Bromobutane forms a mirror image, which on stacking up on the original 2-bromobutane doesn’t superimpose on each other, and thus are known as enantiomers.
Complete answer:
It was found by Baptiste in 1813 that the plane polarised light when passed through single crystals of quartz or aqueous solutions of lactic acid, rotated the plane polarised light either to the right or to the left. When it was rotated towards right, it was called dextrorotatory, while towards left it is known as laevo rotatory. All the substances that rotate the plane polarised light are said to be optically active.
Optically active molecules are always chiral. The chirality of a molecule results from its structure. It is the property of the molecules that arise from the way they interact with the light. We are given two molecules 2-Bromobutane and 1-Bromobutane. The structure of the molecules can be given as:

As we can see in 2-Bromobutane will have for different substituents- $ H,Br,{C_2}{H_5},C{H_3} $ , whereas 1-bromobutane has 2 same substituents (H) attached to the carbon. Since 2-bromobutane has all different substituents attached to the carbon, this carbon is known as the Chiral Carbon and the compound is optically active. Since in 1-bromobutane, 2 same Hydrogen atoms are attached, it cannot be a chiral centre.
Note:
Chiral molecules, forming mirror images, which are non-superimposable on each other, are known as enantiomers. 2-Bromobutane forms a mirror image, which on stacking up on the original 2-bromobutane doesn’t superimpose on each other, and thus are known as enantiomers.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




