




What Is Long Division? Definition, Steps, and Solved Examples
Long division is a method in Mathematics for dividing big numbers into steps or parts, breaking the division questions into smaller stages. It is the most commonly used approach for dividing problems and makes it easier for kids to learn about the division better. Examine the following long division to find the divisor, dividend, quotient, and remainder. Before executing it, we must be aware of the crucial aspects of long division.
Long Division with Single-Digit Divisor
Long division is done like simple division. When the divisor is a single digit, it is easy to divide the dividend. You can learn and practice the steps that need to be followed while long division is given.
Step One: Check the first unit of the dividend whether it is divisible by the divisor or not.
Step Two: If the first unit is less than the divisor, take the second digit into account.
Step Three: Then, find the suitable multiple and subtract the numbers. After subtraction brings down the next digit and then again repeat the above steps till you get the remainder as 0 or a number that further cannot be divided.
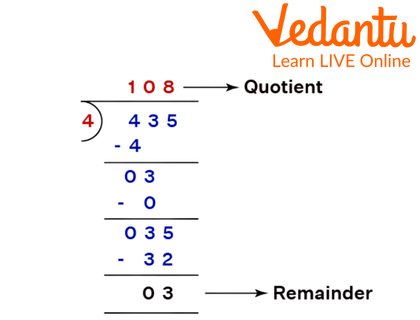
Example of Long Division With Single Digit Divisor
Long Division with Two-Digit Divisor
The long division with a two-digit divisor can be done using the same steps that are mentioned above. In this, the only change is that in the dividend we take the first two digits of the number to subtract it from the multiple of the divisor. And the rest of the steps are the same.
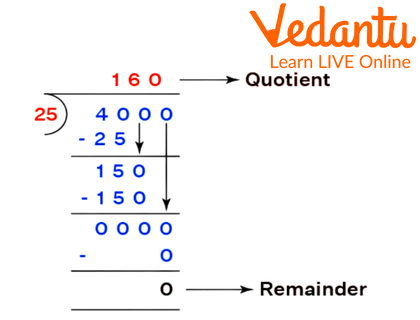
Example of Long Division of Two- Digit Divisor
Long Division with Remainders
The long division ends when there is a remainder left that cannot be further divided by the divisor or the value of the number is less than the divisor itself. Like in the above-mentioned 435 divided by 4 sample questions, after taking down the last digit 5 to be subtracted we are left with 3. As 3 is less than the divisor 4 so we will now conclude the long division as there are no more digits present in the dividend, which can be used to reduce it. So, we are left with 3 as the remainder.
Long Division without Remainders
Long division without remainders means that the remainder is 0 or the last number to be subtracted by the multiple of the divisor was the same giving us the remainder 0. In an example of a division of 126 by 2, we will get 63 as the quotient. As the last digit 6 is completely divisible by 2 we get the remainder as 0 making it a long division without remainder.
Conclusion
The long division is similar to the standard division. The division consists of dividend, divisor, quotient, and the remainder where the divisor can be single-digit, double-digit, or triple-digit. The remainder can be zero or a number that is less than the divisor. If the dividend does not get divided fully or does not have a remainder as 0, then the division can continue further by using a decimal point. The divisor can be single-digit, two-digit, or three-digit.
Long Division Worksheets
1. Divide 432 by 15.
27
28
29
30
Ans: 28
Explanation: In this, we will take the first two digits of the dividend as our divisor is two digits. A multiple of 15 which is less than or equal to 43 is found and then it is subtracted. The remainder along with the next digit of the dividend is then evaluated and subtracted again.
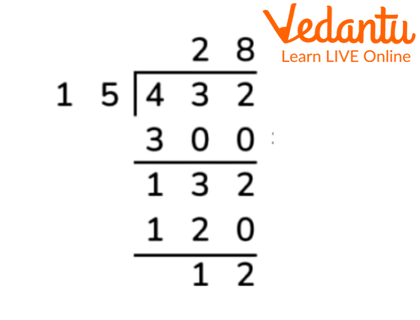
Solution of the division of 432 by 15
2. Divide 1850 by 12 using long division.
144
154
164
174
Ans: 154
Explanation: Step one: As 18 is a little greater than the divisor itself so we will subtract it by 12. We get 6 as the remainder.
Step Two: Bring down 5 and the new number becomes 65 which can be subtracted from 60 which is a multiple of 12.
Step Three: Now bring down 0 and subtract it with the multiple of 12. There is a remainder left as 2. We get our answer as 154 the quotient.
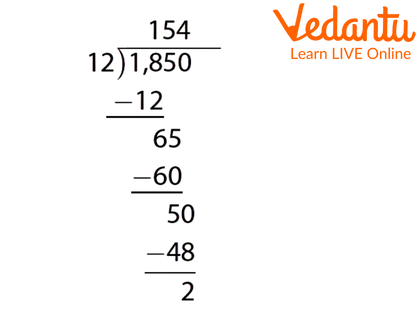
Solution of Division of 1850 by 12
3. What is the value of the remainder when the division ends without any remainder left?
1
0
not defined
none of the above
Ans: 0
FAQs on Long Division for Class 3 – Simple Guide & Practice
1. What is long division for Class 3 students?
Long division for Class 3 students is a method used to divide large numbers step by step. It helps them break down complex division problems into smaller, manageable steps, making it easier to find the quotient and remainder using basic division skills.
2. What are the steps of long division for Class 3?
The steps of long division for Class 3 include:
- Divide
- Multiply
- Subtract
- Bring down the next digit
- Repeat until all digits are used
3. Why is learning long division important in Class 3?
Learning long division in Class 3 is important because it teaches children how to handle large numbers, improves logical thinking, and prepares them for advanced math topics like factors and multiples, building a strong foundation in mathematics.
4. What is a divisor and dividend in long division?
Dividend is the number being divided, and divisor is the number you divide by. For example, in $42 \div 6 = 7$, $42$ is the dividend, $6$ is the divisor, and $7$ is the quotient.
5. How do you check your answer after doing long division?
After long division, you verify your answer using this formula:
- Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder
6. What is a remainder in long division for Class 3?
A remainder in long division is the amount left over after dividing one number by another when the division is not exact. For example, in $17 \div 5 = 3$ with remainder $2$, $2$ is the remainder.
7. Can long division be used for 2-digit numbers in Class 3?
Yes, long division is commonly used in Class 3 to divide two-digit numbers by single-digit numbers. This technique helps students solve division problems step by step, even when the numbers are big or the results include a remainder.
8. What mistakes should Class 3 students avoid in long division?
Class 3 students should avoid:
- Forgetting to write the remainder
- Skipping steps
- Making errors in subtraction
- Bringing down the wrong digit
9. How is the long division symbol written?
The long division symbol looks like a right parenthesis with a horizontal line on top. The divisor goes outside the symbol, while the dividend is placed inside, helping students organize the numbers during each division step.
10. What is the difference between long division and short division?
Long division breaks down the problem into several clear steps, which is good for large numbers. Short division is quicker but skips intermediate steps, making it more suitable for small numbers or those who already know division well.
11. How does long division help in solving word problems in Class 3?
Long division helps solve word problems in Class 3 by allowing students to break down complex problems into simple steps. This ensures clarity, helps find accurate answers, and reinforces understanding of division applied in real-life situations such as sharing items equally.























