




How to Identify and Calculate Area of Composite Figures
Simple Ways to Teach Composite Figure to Kids
As kids start progressing in their classes, they are introduced to various new concepts in every subject. They are introduced to vast literature, history, political sciences and science. Science, especially mathematical operations, are very interesting and can be used to explain the cause and functioning of almost all natural phenomena. One such concept introduced in mathematics is the introduction of composite figures. By understanding what is a composite figure, kids will be able to know the measurement and geometry of the things around them. Needless to say, learning new things and doing experiments is fun. This article is aimed to help kids, parents and teachers to create a precise understanding of the composite figures. The article mentions the definition and examples of composite figures for a better understanding of the concept.
What is a Composite Figure?
The composite figure can be defined as a shape that constitutes more than two-dimensional shapes. When deconstructed, a composite shape is made up of a number of other shapes. A more technical definition of the term is based on the constituent shapes that make up the composite figure. The composite figure is a two-dimensional figure constructed up of basic two-dimensional shapes such as triangles, rectangles, circles, semi-circles, and so on. The examples of the composite figures are mentioned below for a better understanding.
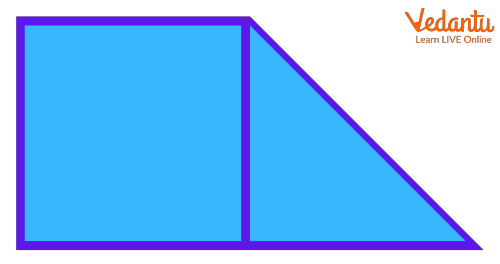
The above image is made up of a triangle and square

Image illustrating a parallelogram made up of two triangles
How to Calculate the Area of the Composite Figures or Shapes?
As we have learnt about the definition of composite figures, let us look into the areas of the composite figure. As we know that simple geometric forms make up a composite figure, the area can be calculated by dividing the composite figure into basic, non overlapping figures to get its area. In simpler terms, the overall area can be calculated by adding the areas of the individual area of the geometric shapes. This method of calculation of area in mathematics is known as the additive method of area calculation. Now as we have learnt about the additive method let us look into the units that are used to represent the area. m2, cm2, in2 or ft2 are some of the common units used to represent the area. Mentioned below is an image that can be used to explain the additive method.
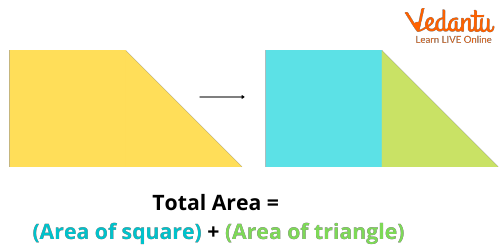
Image illustrating the area of the composite figure
Formulas to Calculate the Area of Different Shapes
Along with learning the additive method, we must also know the formulas for the calculation of the area of the various shapes that can make up a composite figure. The table mentioned below provides a formula to calculate the area of triangle, square, rectangle and so on.
Solved Examples
Example 1- Calculate the area of a composite figure that is made up of a square and a triangle. The triangle has a base of 6 cm while the height of the triangle is 7 cm. The side of the square is 5 cm.
Solution- Since we know that to calculate the area of a composite figure we must add the area of the individual shape. The figure is made up of triangles and squares, so let us calculate the area of a triangle and square.
Area of the square- (length)2
Area of the square- 52 = 25
Area of triangle = (1/2) × base × height.
Area of triangle = [(1/2) × 6 × 7] = 21
Area of composite shape= area of triangle + area of square
Area of composite shape= 21 + 25
Area of composite shape= 46 cm2
Example 2- Find the area of the figure given below
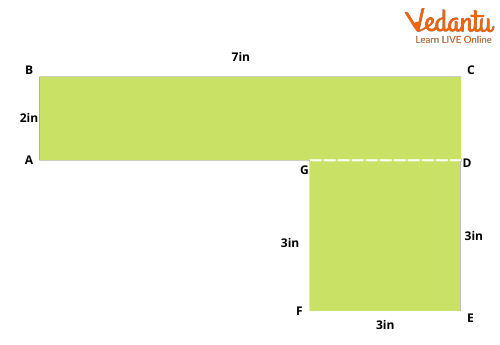
Solution- Area of composite shape = Area of rectangle + area of the square
area of the rectangle ABCD = length × breadth
area of the rectangle ABCD = 7 × 2 = 14
Area of square = (length)2
Area of square = 32 = 9
Area of composite shape = 14+9 = 23 in2
In conclusion of the article, we have learnt about the definition of the composite figure and calculation of the area of the triangle. We hope that this discussion will help kids to better understand the concept of composite figures.
FAQs on Composite Figures: Meaning, Properties & Examples
1. What is a composite figure in Maths? Provide some examples.
A composite figure, also known as a composite or compound shape, is a two-dimensional figure made by combining two or more basic geometric shapes. The main property of a composite figure is that its total area and perimeter can be determined by working with the individual shapes it is composed of. Common examples include:
- An L-shaped room, which can be seen as two joined rectangles.
- The shape of an ice cream cone, which combines a triangle and a semi-circle.
- An arched window, which is a rectangle topped with a semi-circle.
2. How do you find the area of a composite figure?
To find the area of a composite figure, you follow a standard three-step method. There is no single formula for all composite shapes, so this process is key:
- Decompose: First, break down the complex figure into simple, non-overlapping shapes like squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles.
- Calculate: Next, find the area of each of these individual basic shapes using their respective standard formulas (e.g., Area = length × width for a rectangle).
- Combine: Finally, add the areas of all the individual shapes together to get the total area of the composite figure.
3. How is the perimeter of a composite figure calculated?
The perimeter of a composite figure is the total length of its outer boundary. To calculate it correctly, you must sum the lengths of all the external sides only. A common mistake is to add the perimeters of the individual shapes; this is incorrect because it would include the internal lines where the shapes are joined. You must only measure and add the lengths that form the external border of the entire figure.
4. Why is it important to break down a composite figure into basic shapes before calculating its area?
Breaking down a composite figure is a crucial strategy because there is no single, universal formula for an irregularly shaped figure like a 'T' shape or an 'L' shape. By decomposing it into standard shapes such as rectangles and triangles, we can use their simple and reliable area formulas. This method transforms a complex problem into a series of smaller, manageable calculations, ensuring an accurate and straightforward way to determine the total area.
5. What is the main difference between calculating the area and the perimeter of a composite figure?
The primary difference between calculating area and perimeter lies in what is being measured and how internal lines are treated:
- Area measures the total surface space inside the figure. To find it, you decompose the figure and add the areas of its component parts.
- Perimeter measures the length of the outer boundary only. It is found by adding the lengths of all external sides, completely ignoring any internal lines where the basic shapes connect.
6. Can a composite figure's area be found by subtracting one shape from another?
Yes, this is a common and important technique, especially for figures with holes or cut-outs. The method involves calculating the area of the larger, outer shape and then subtracting the area of the smaller, inner shape that has been removed. A perfect real-world example is finding the area of a grassy lawn (a large rectangle) that has a circular swimming pool in its centre. You would calculate the area of the rectangle and then subtract the area of the circle to find the remaining area of the lawn.
7. What are some common real-life examples of composite figures?
Composite figures appear frequently in the world around us. Recognising them helps in practical situations like construction, design, and planning. Some common examples are:
- The floor plan of a house or an L-shaped kitchen.
- An athletic running track, which is a rectangle with a semi-circle at each end.
- A keyhole, which is a combination of a rectangle and a circle.
- A wrench, often composed of hexagonal and rectangular parts.
- Architectural designs like arched doorways, which combine a rectangle and a part of a circle.

















