




How to Use the Area Model for Multiplication Problems
Multiplication is a fundamental arithmetic operation that students learn at a young age. If they have a keen understanding of multiplication, they can start applying this concept to real-world problems. The area model multiplication worksheets consist of various questions that help students to visualise multiplication. With the help of the given solved examples, students will understand the area model of multiplication more clearly. Some practice problems are given that need to be solved by the students on their own, to develop a better understanding of the topic.
What is the Multiplication with Area Model?
In mathematics, an area model is defined as a rectangular diagram or model which is used in multiplication and division problems, where the factors or the quotient and divisor specify the length and width of the rectangle. One can break one large area of the rectangle into several smaller boxes, using number bonds, to make the calculation easier. Then add the number to get the area of the whole, which is the product.
By using the area model we can multiply 2 two-digits numbers by following the given steps:
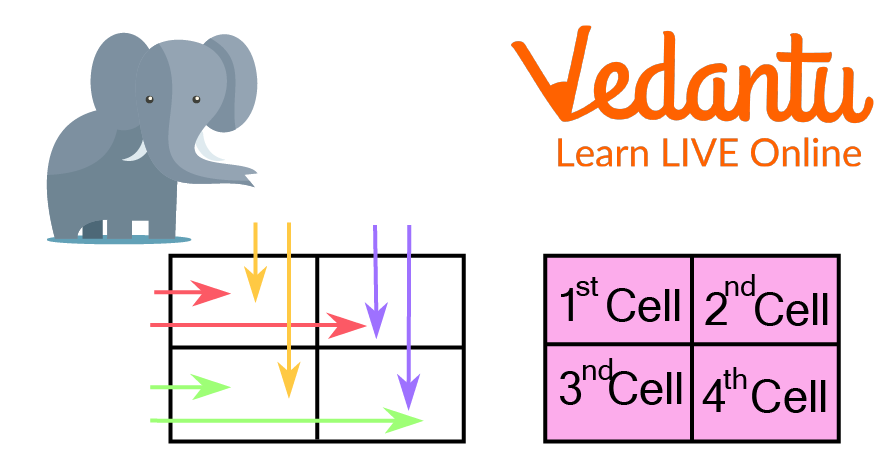
Multiplication with Area Model
Here, as an example, the area model has been used to multiply 27 and 35.
Write the multiplicands in expanded form as tens and ones. For example, 27 is 20 and 7, and 35 is 30 and 5.
Draw a 2 × 2 grid, which is a box with 2 rows and 2 columns.
Write the terms of 1 of the multiplicands on the highest of the grid (box). One of the highest of every cell.
On the left of the grid write the terms of the other multiplicand. One on the side of every cell.
Write the product of the number on the tens in the first cell. Then write the product of the tens and ones in the second and third cells. Write the product of the ones in the fourth cell.
Lastly, to get the final product, add all the partial products.
Thus, The multiplication of 27 and 35 is 945.

Area Model Multiplication
Multiplying with Area Model a 1-Digit Number
One can use area models in multiplying large numbers. Display the problem as the area of a rectangle, and then break that rectangle into smaller parts to solve it easily. This method is also known as the box multiplication method. Now, try it with 628 × 5. Let the problem be shown as the area of a rectangle:
Next, let the rectangle split into smaller pieces for easier multiplication. We will use the expanded form of 628 to keep the maths simple:
628 = 600 + 20 + 8
Now, multiply to find the area of each smaller rectangle. Lastly, to find the area of the original rectangle adds those products.
3000 + 100 + 40 = 3140
So, the product 628 × 5 is equal to 3140.
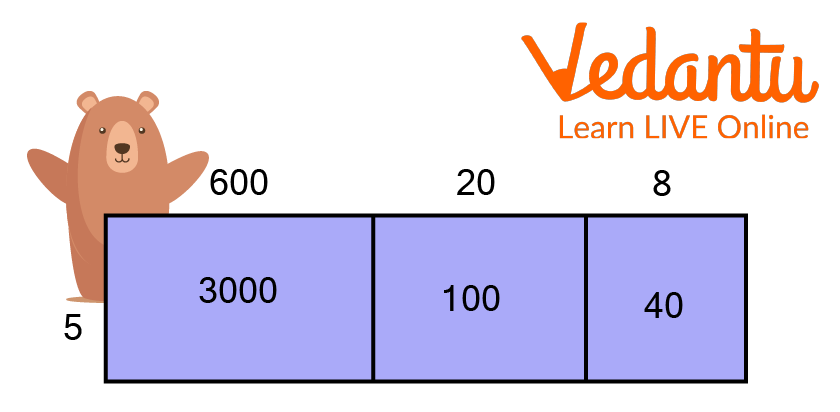
Multiplying with The Area Model
Multiplying with Area Model a 2-Digit Number
One can use area models for larger problems, too. Let's use 36×52 as an example. Firstly, write each factor in expanded form, i.e.
36 = 30 + 6
52 = 50 + 2
Then, draw your model.
To find the area of each smaller rectangle, multiply the above expansion

On Multiplying The Above Expansion
Lastly, add those products to find the total area.
1500 + 300 + 60 + 12 = 1872
So, the required product of 36 × 52 is 1872.
Solved Examples
Q1. Multiply Using Area Model
(1). 6 x 24
Ans: Multiplication with area model of the term, 6 x 24 is given by:
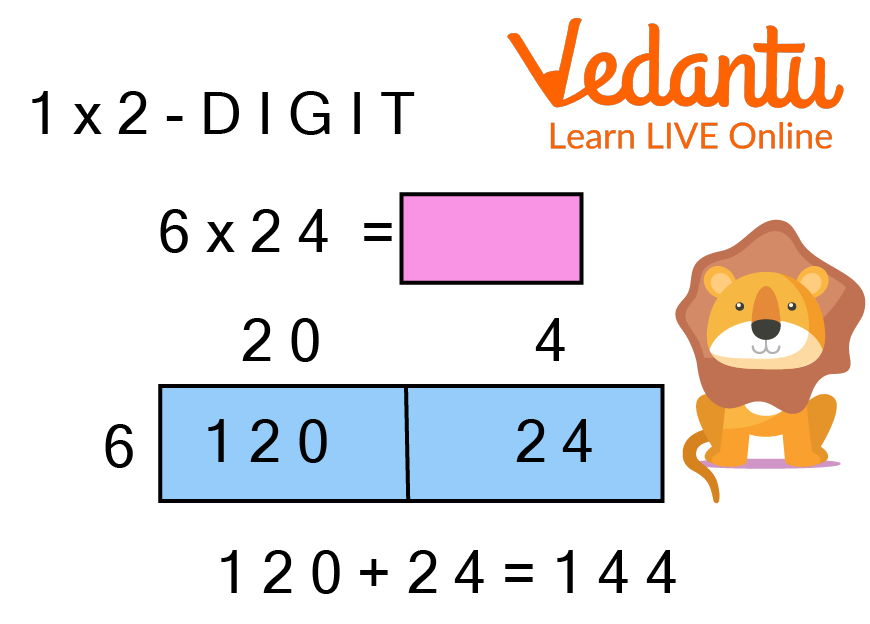
Multiplication of 6 and 24
Thus, the multiplication of 6 x 24 using the area model is 144.
(2). 4 x 125
Ans: Multiplication with area model of the term, 4 x 125 is given by:
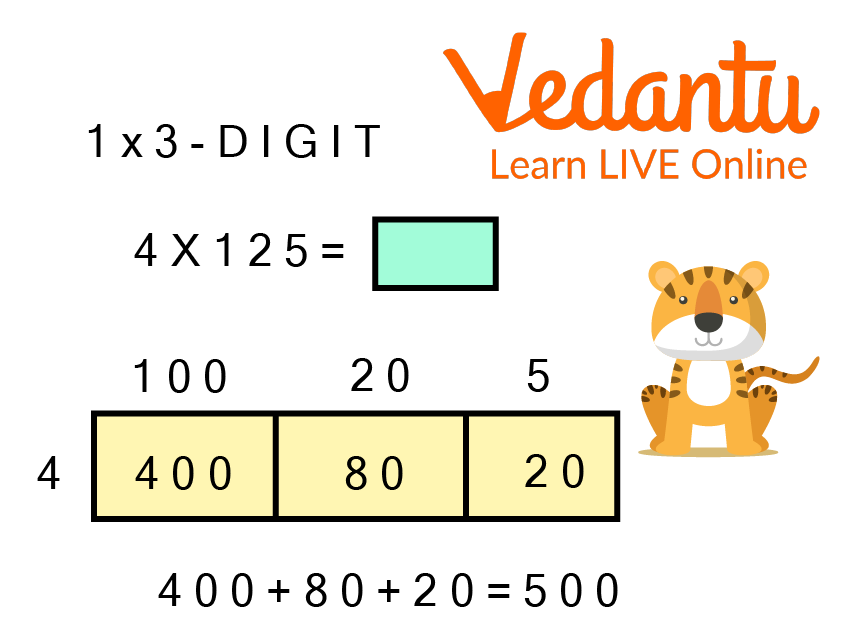
Multiplication of 4 and 125
Thus, the multiplication of 4 x 125 using the area model is 500.
Practice Questions
Q1. 94 x 12
Ans: 1128.
Q2. 70 x 13
Ans: 910.
Q3. 69 x 36
Ans: 2484.
Summary
In this article, we have learned about the Area Model Multiplication. In area model multiplication, a rectangular diagram or model is used for solving multiplication and division problems. In this article, we have learned to multiply a 1-digit number & a 2-digit number using an area model. Lastly, we have also learned about some fun facts related to multiplying with the area model. Some solved examples based on the area model are being discussed for the clarity of concepts. Practice problems are also assigned, along with their answers.
FAQs on Area Model Multiplication Explained with Examples
1. What is the area model for multiplication?
The area model is a visual method used to solve multiplication problems, especially with multi-digit numbers. It uses a rectangle, or a 'box', to represent the problem. The numbers being multiplied are broken down into their place values (e.g., 45 becomes 40 + 5) and used as the dimensions of the rectangle. This method helps in understanding how each part of the numbers contributes to the final product.
2. How do you use the area model to multiply two numbers?
To use the area model for multiplication, you can follow these simple steps:
Expand the Numbers: Break down each number into its expanded form based on place value. For example, 53 becomes 50 + 3, and 24 becomes 20 + 4.
Draw the Grid: Draw a rectangle and divide it into smaller boxes based on the number of expanded terms. For 53 x 24, you would need a 2x2 grid.
Multiply the Parts: Multiply the numbers along the length and width of each smaller box to find its 'partial product'.
Add the Products: Add all the partial products from the boxes together to get the final answer.
3. Can you provide an example of multiplying a 3-digit number by a 2-digit number using the area model?
Certainly. Let's multiply 142 x 25 using the area model.
1. First, expand the numbers: 142 becomes 100 + 40 + 2, and 25 becomes 20 + 5.
2. Draw a 3x2 grid. Write 100, 40, and 2 across the top and 20 and 5 down the side.
3. Multiply to fill each box:
- 100 x 20 = 2000
- 40 x 20 = 800
- 2 x 20 = 40
- 100 x 5 = 500
- 40 x 5 = 200
- 2 x 5 = 10
4. Finally, add all the partial products: 2000 + 800 + 40 + 500 + 200 + 10 = 3550.
4. Why is this method called the 'area model'?
This method is called the 'area model' because it is based on the geometric principle of finding the area of a rectangle (Area = Length × Width). In this method, the two numbers being multiplied are treated as the length and width of a larger rectangle. By breaking these numbers into expanded form, we are essentially dividing the large rectangle into smaller ones. The final answer is the sum of the areas of all these smaller rectangles, which equals the total area.
5. What is the main advantage of using the area model over the traditional long multiplication method?
The main advantage of the area model is its visual clarity. It helps students see exactly what they are multiplying by breaking down large numbers into simpler parts (like tens and ones). This makes it easier to keep track of place values and reduces the chances of errors that can occur in the standard algorithm. It builds a stronger conceptual understanding of multiplication rather than just following a set of rules.
6. How does the area model for multiplication relate to the distributive property?
The area model is a visual representation of the distributive property of multiplication. The distributive property states that a(b + c) = ab + ac. When we multiply 25 x 14, we expand it to (20 + 5) x (10 + 4). Using the distributive property, we multiply every term in the first bracket by every term in the second: (20x10) + (20x4) + (5x10) + (5x4). Each of these calculations corresponds to one of the boxes in the area model, showing how the method is mathematically structured.
7. What is a common mistake students might make when using the area model?
A very common mistake is an error in place value expansion. For example, a student might incorrectly expand a number like 142 as 1 + 4 + 2 instead of the correct 100 + 40 + 2. Another frequent error occurs during the final step when adding all the partial products, where a calculation mistake can lead to an incorrect final answer even if the model was set up correctly.
8. Can the area model be used for multiplying numbers with decimals?
Yes, the area model is a versatile tool that can also be used to multiply decimals. The process remains the same. You expand the decimal numbers into their parts. For example, to multiply 3.5 x 2.1, you would expand them as (3 + 0.5) and (2 + 0.1). You would then create a 2x2 grid and find the partial products (3x2, 3x0.1, 0.5x2, and 0.5x0.1) and add them together for the final answer.























