




An Introduction to Employee Stock Option Scheme and ESOP Advantages
ESOP stands for Employee Stock Ownership Plan. Under this scheme, employers offer their employees a share of the company at low or no additional cost that they can encash after a specified period at a specified price. ESOPs can have significant time value even if they have zero or little intrinsic value.
The Companies Act provides certain rules and regulations that employers need to follow while granting employee stock ownership plans to their employees.

ESOP
ESOP Meaning
An employee stock ownership plan is an employee benefit plan which offers employees and executives an ownership interest in the business. ESOPs, give the company, selling shareholders, and participants various tax benefits. This is used as a corporate finance strategy by employers to collaborate the interests of their employees with those of their shareholders.
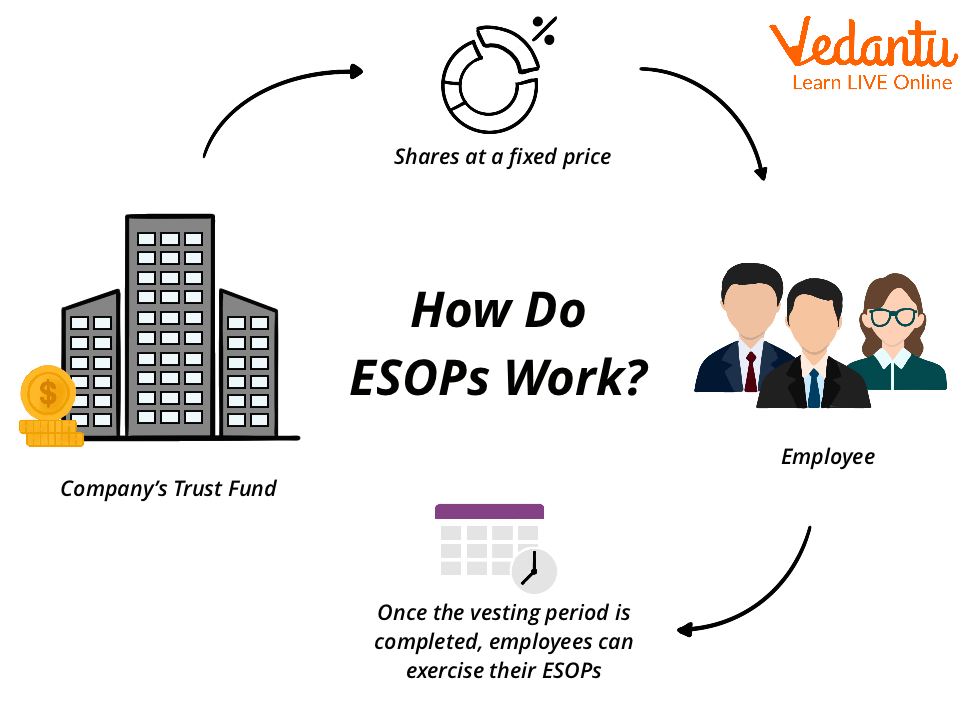
How does ESOP Work?
The first step is to set up an ESOP trust, a legal entity that holds shares on behalf of the employees.
Next, the company contributes money to the trust. The trust can borrow money from banks or sellers, known as leveraged ESOP.
Then, using the money, the trust buys some or all of the company's shares from the owners. In this case, the price of the share is determined by the independent appraiser.
After that, the trust begins allocating shares to employees' retirement accounts. In the case of leveraged ESOP, it allocates the shares as it pays back the loan.
When employees leave the organisation, these ESOPs provide them with a significant retirement plan.
How ESOP Works
ESOP Benefits
The following are the ESOP advantages for both employees and employers.
For Employers:
Boosts employee job satisfaction and financial position by providing many lucrative incentives.
This is an excellent option for startups or companies operating on a low budget.
It helps reshuffle ownership.
It also helps the company to grow and expand.
For Employees:
It provides an opportunity to share directly in the company’s success.
The employees may feel motivated to be fully productive as they own shares in the company.
It provides a tangible representation of how much their contributions are worth to the employer.
Employee Stock Option
ESO refers to a type of equity compensation granted by companies to their employees. The company gives derivatives options on the stock rather than giving shares directly. These options give the employee the right to buy the company’s stock at a specified price for a finite period.
When a share’s price rises above the call option exercise price, call options are exercised, and the holder obtains the company’s share at a discount. The holder may sell the share in the open market for better returns.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, ESOPs are considered the best tool for businesses looking to attract new employees and those who want their businesses to grow and succeed. These ESOP programs are adopted by companies that don’t change staff frequently, resulting in a bigger payout and financial compensation to employees. However, they are not always straightforward and fail to provide benefits if the participant does not understand the required rules and regulations, as not all ESOPs are the same.
FAQs on Employee Stock Ownership Plans (ESOPs)
1. What are two types of ESOPs?
The two types of ESOPs are:
Incentive stock options: These options are also known as qualified or statutory options offered to key employees and top management. In many cases, they also receive preferential tax treatment as gains on such options are treated as long-term capital gains.
Non-qualified stock options: These types of options are granted to all types of employees, as well as to consultants and board members. These options are also known as non-statutory stock options, as profits on these options are considered ordinary income.
2. What are some other forms of employee ownership plans?
The other forms of employee ownership plans include:
Direct stock purchase plan: This allows employees to purchase respective shares of the companies with their personal after-tax money.
Restricted stock: This gives employees the right to receive shares as a gift or a purchased item after meeting particular targets.
Stock options allow: employees to buy shares at a specified price for a specified time.
Phantom stock: This provides cash bonuses to employees after a good performance.
Stock appreciation rights: This gives employees the right to raise the value of an assigned number of shares.
3. What are some problems related to ESOPs for employers?
ESOPs have complex rules and regulations. The company may require some internal personnel for the smooth conduct of the scheme. Once the ESOPs are established, the company needs proper administration. Company owners and managers should consider the ongoing costs. Companies which require additional capital for carrying the business operations should avoid ESOPs. If a company requires the funds for additional working capital or capital expenditures, the ESOP transactions will compete with this requirement. It will create a crisis for the management.























