




An Overview of Class 11 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers Basic Laboratory Techniques Questions Experiment
The chemistry laboratory is the first place you should familiarise yourself with before learning scientific procedures and experimental skills. Some basic laboratory procedures frequently required during chemistry laboratory experiments include heating, filtration, crystallisation, decantation, volume measurements, and weighing solids and liquids. The process of crystallisation is one of the methods for purifying impure compounds, particularly if the original crude material obtained by the reaction is extremely impure.
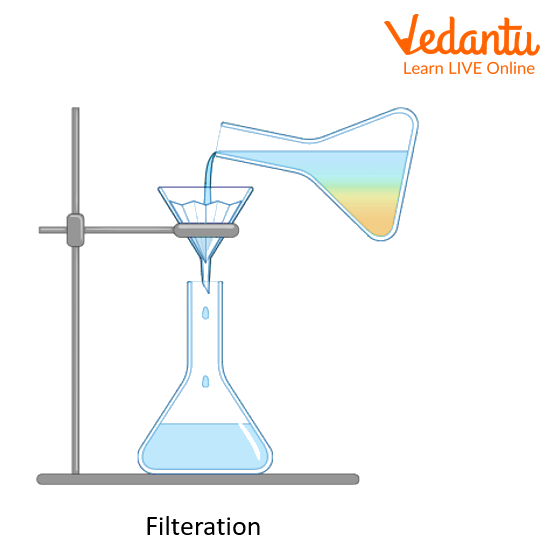
Filtration involves passing a liquid through a porous material to separate solids from liquids. This article covers both filtration and crystallisation along with chemistry lab viva questions with answers.
Table of Content
Aim
Theory
Apparatus required
Procedure
Observation
Result
Precautions
Aim
To purify the sample of a compound (copper sulphate, potash alum, or benzoic acid) by crystallisation.
Theory
As the first step in the process of crystallization, the crude material is dissolved readily when hot, but to a limited extent when cold, using a single or a mixture of solvents. A saturated solution is then obtained by dissolving the crude substance in a minimum amount of boiling solvent. Filtration removes insoluble impurities from hot solutions. Once the solution reaches its crystallisation point, it is cooled slowly, and the impurities are left behind.
Apparatus Required
Beaker (250 ml)
Glass funnel
Tripod stand
Porcelain dish
Glass rod
Sand bath
Copper sulphate, potash alum, and benzoic acid
Procedure
A saturated solution of potash alum/copper sulphate is prepared in a beaker with 30-50 ml of distilled water by stirring in small amounts of the impure solid sample.
When the solid has not dissolved further, stop adding it.
Hot water is used to prepare saturated solutions of benzoic acid.
Transfer the filtrate from the saturated solution into a porcelain dish.
In a sand bath, heat it until almost three fourth of the solvent has evaporated.
Blow air from your mouth as you take a glass rod out of the solution.
Stop heating the rod if a solid film forms.
Keep the porcelain dish undisturbed while cooling, covered with a watch glass.
After crystallisation, decant the mother liquor (the liquid left over after crystallization).
Remove adhering mother liquor from the crystals of potash alum and copper sulphate obtained by washing them in ethanol containing a small amount of water, followed by washing them in alcohol to remove moisture.
Wash benzoic acid crystals with cold water.
The crystals should be dried between the folds of filter paper and stored at a safe and dry location after they have been dried.
Repeat the following steps to get the maximum quantity of pure substance.
Observation
The shape of copper sulphate, potash alum, and benzoic acid are observed and noted down.
Result
The crystals of copper sulfate, benzoic acid, and potash alum are blue, greenish-white, and white, respectively.
Precautions
The solution should not be evaporated completely while being concentrated.
The solution should not be disturbed when it is getting cooled.
Aim
To separate a solid from a liquid by filtration.
Theory
Filters may have different pore sizes. When a filter paper has large pores, liquid can pass through it more easily, resulting in a faster filtering process. It is also possible for solid particles of smaller sizes to pass through the filter. A filtering method and filtering material must be chosen according to the particle size of the material that needs to be retained on the filter paper.
Apparatus Required
Funnel
Beaker
Funnel stand
Glass rod
Filter paper
Procedure
Once the circular filter paper has been folded in half, tear off a small piece from its corner and fold it once more.
Make a cone by folding the filter paper in half, three folds on one side and one on the other, so that the torn corner is on the outside.
Make sure the filter paper cone fits within one cm of the funnel's rim when fitting it into the funnel.
Apply the solvent, usually water, to the paper and adjust it so that it fits tightly onto the glass funnel's inner surface, with no air gaps.
Pour more water into the funnel until the stem is filled.
The filter paper in the funnel stem can support a column of water if fitted appropriately.
A mild suction is created by the weight of this column of water, which speeds up the filtration process.
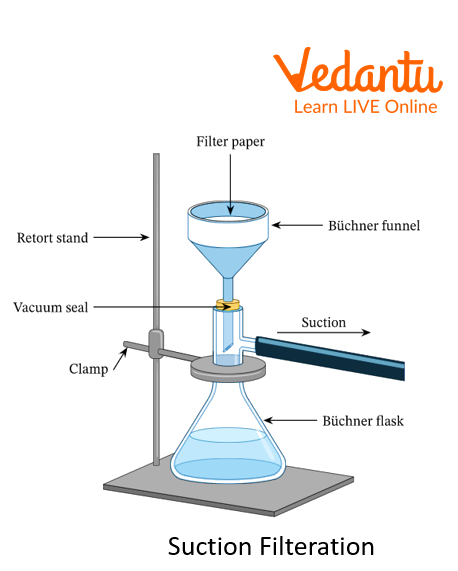
Suction Filtration: The above method of filtration can be sped up by using suction, which can be applied by using a vacuum pump or aspirator.
Filtration
Suction Filtration
Observation
Residues are observed on the filter paper.
Result
Filtration results in the separation of solid materials from liquid through a porous material.
Precautions
To avoid splashing, the stem of the funnel should contact the side of the beaker in which the filtrate is collected.
A portion of the filtered liquid may pass through the funnel into the beaker beneath the funnel to collect the filtrate if the liquid level rises above the cone.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What is the purpose of preparing a saturated solution before crystallising?
Ans: As a saturated hot solution cools, the solute becomes insoluble in the solvent and crystallises into pure compounds. So, a saturated solution is prepared before crystallisation.
2. What is the advantage of suction filtration over normal filtration?
Ans: The filtration process can be done at high speed by using the suction filtration method, which can be applied by using a vacuum pump or aspirator.
3. What are the processes of crystallization?
Ans: Crystallization starts with nucleation, the appearance of crystals from either supercooled liquids or supersaturated solvents. Secondly, crystal growth occurs, which is the process of increasing particle size and resulting in crystals.
4. What is seeding in crystallisation?
Ans: To facilitate crystallization, a small amount of the solid (which is being purified) is sometimes added to the solution during cooling, which is called seeding. As a result of the addition of a tiny crystal, new crystals grow around it.
Viva Questions
1. What is mother liquor?
Ans: Mother liquor is the liquid left behind after a substance crystallises.
2. What is a saturated solution?
Ans: A solution that has dissolved all the solutes it can dissolve is a saturated solution.
3. Which funnel is used in suction filtration?
Ans: Buchner funnel is used in suction filtration.
4. What is the role of glass rod during filtration?
Ans: Glass rod directs the flow of liquid into the funnel and prevents small amounts of liquid from running down the outside of the beaker when the transfer process is interrupted.
5. What is a sand bath?
Ans: The sand bath is a vessel of hot sand in a laboratory that partially immerses vessels that need to be heated.
6. Define filtration.
Ans: Filtration involves passing a solution through a filter paper to separate insoluble substances.
7. What is the colour of the benzoic acid crystals?
Ans: Benzoic acid crystals are an opaque white colour.
8. Why the hot saturated solution doesn't cool down suddenly?
Ans: During the cooling process of a saturated solution, crystals expand in size. To minimise the chances of small or disfigured crystals, rapid cooling should be avoided.
9. What is crystallisation?
Ans: Crystallization refers to the arrangement of the atoms/molecules of a substance in a well-defined three-dimensional lattice, which minimises the system's overall energy.
10. What is a funnel?
Ans: A funnel is a pipe or tube with a wide top and narrow bottom used to pour liquid or powder through a narrow opening and to hold filter papers.
Practical-Based Questions
1. Which of the following factor affects filtration?
Density
Viscosity
Temperature
All the above
Ans: D) All the above
2. For initial crystallisation, minute quantities of the substance are added to the solution during cooling. This is called
Seeding
Seedling
Filtration
Separation
Ans: A) Seeding
3. Which of the following can be used as a porous material during filtration?
Sintered glass
Paper
Asbestos
All the above
Ans: D) All the above
4. Insoluble particles are separated from liquids by which of the following processes??
Evaporation
Filtration
Crystallization
None of the above
Ans: B) Filtration
5. A filtering method and filtering material must be chosen according to the __.
Particle size
Color
Density
pH
Ans: A) Particle size
6. Copper sulphate crystals are ___ in colour?
Green
White
Blue
Orange
Ans: C) Blue
7. Benzoic acid crystals are washed with ___?
Alcohol
Cold water
Hot water
Methanol
Ans: B) Cold water
8. Which of the following is used for the evaporation of excess solvents to make a concentrated solution?
China dish
Measuring cylinder
Beaker
Burette
Ans: A) China dish
9. The porcelain dish is covered with a ___?
Filter paper
Asbestos sheet
Watch glass
Sintered glass
Ans: C) Watch glass
10. What is the remaining liquid after crystallization?
Saturated solution
Unsaturated solution
Mother liquor
None of the above
Ans: C) Mother liquor
Conclusion
The process of crystallisation is one of the methods for purifying impure compounds, particularly if the original crude material obtained by the reaction is extremely impure. Filtration involves passing a liquid through a porous material to separate solids from liquids. When a filter paper has large pores, liquid can pass through it more easily, resulting in a faster filtering process. Benzoic acid crystals are monoclinic, copper sulfate crystals and potash alum crystals are triclinic in geometry.
FAQs on Class 11 Chemistry Viva Questions With Answers Basic Laboratory Techniques Questions Experiment
1. What are the key factors that affect the formation of crystals during the crystallisation process?
Several factors influence the success of crystallisation, which is an important technique for Class 11 practicals. Key factors include:
- Solubility: The compound must be significantly more soluble in the solvent at high temperatures than at low temperatures.
- Rate of Cooling: Slow and gradual cooling generally produces larger and purer crystals. Rapid cooling often leads to the formation of small, impure crystals.
- Concentration: A supersaturated solution is required for crystallisation to begin, but an overly concentrated solution may cause the substance to precipitate out as an amorphous solid instead of forming crystals.
- Purity of the Solution: The presence of impurities can hinder crystal growth or be incorporated into the crystal lattice, reducing the purity of the final product.
2. Why are boiling chips or small porcelain pieces added to the distillation flask before heating the liquid?
This is a frequently asked viva question for Class 11 Chemistry. Boiling chips or porcelain pieces are added to ensure smooth and even boiling of the liquid. Without them, the liquid can become superheated and boil violently in sudden bursts, a phenomenon known as 'bumping'. This can cause the apparatus to shake, potentially breaking the setup, and can also result in the impure liquid splashing into the condenser, contaminating the distillate.
3. When is fractional distillation preferred over simple distillation for separating a mixture of liquids?
Fractional distillation is an essential technique in the CBSE Class 11 syllabus. It is preferred over simple distillation when the boiling points of the two miscible liquids in a mixture are very close to each other (typically with a difference of less than 25 K or 25°C). A simple distillation cannot effectively separate such liquids because the vapours would be rich in both components. The fractionating column in fractional distillation provides a large surface area for repeated cycles of vaporisation and condensation, allowing for a much more efficient separation.
4. Explain the principle of distillation under reduced pressure. Why is it used for purifying compounds like glycerol?
Distillation under reduced pressure works on the principle that a liquid boils at a temperature lower than its normal boiling point if the external pressure is reduced. This technique is crucial for purifying substances that are heat-sensitive and decompose at or below their normal boiling points. Glycerol, for example, has a high boiling point (290°C) and decomposes before reaching it. By reducing the pressure, its boiling point is lowered significantly, allowing it to be distilled and purified without decomposition.
5. What is the Retention Factor (Rf value) in paper chromatography, and what is its significance?
The Retention Factor, or Rf value, is a key parameter in chromatography. It is defined as the ratio of the distance travelled by the solute (the component) to the distance travelled by the solvent front on the chromatogram. The formula is:
Rf = (Distance travelled by the solute) / (Distance travelled by the solvent front)
Its significance lies in the fact that for a given substance, solvent, and stationary phase, the Rf value is a constant. It helps in the identification of an unknown substance by comparing its Rf value with that of a known substance under identical experimental conditions.
6. In paper chromatography, why is it critical to place the initial spot of the mixture above the solvent level in the chamber?
This is a crucial procedural step and an important conceptual question for the 2025-26 practical exams. The initial spot of the mixture must be applied above the solvent level to ensure that the separation actually occurs. If the spot is submerged in the solvent, the mixture will dissolve directly into the solvent pool at the bottom of the chamber instead of being carried up the paper by capillary action. As a result, the components of the mixture will not separate and move up the stationary phase, and the chromatogram will not develop.
7. For a Class 11 exam, compare crystallisation and evaporation as methods for obtaining a solid from a solution. Which one is considered superior and why?
Both crystallisation and evaporation can separate a soluble solid from a solvent, but they differ in their purpose and outcome:
- Evaporation: In this method, the solvent is completely evaporated to leave the solid behind. It is faster but can lead to the decomposition of heat-sensitive solids and may trap impurities within the residue. It does not yield well-defined crystals.
- Crystallisation: This technique involves creating a hot, saturated solution and then allowing it to cool slowly, causing the pure solid to form crystals. Soluble impurities remain in the mother liquor.
























