




An Overview of Class 11 Chemistry To Determine The Ph Of Various Samples Of Naoh Solution Experiment
In our daily life, we use many compounds like water, baking soda, lemon juice, etc. Do they all lie in the same category? They all fall into different categories. Water is neutral, lemon juice is acidic and baking soda is alkaline.
There are three types of chemicals used in laboratories: basic, acidic and neutral. Their characteristics are determined by the ions they release. A chemical that releases H+ ions in its aqueous solutions is said to be acidic, while a chemical that releases OH– ions in its aqueous solutions is said to be basic. The acidity or alkalinity of a solution can be measured using pH which is the hydrogen ion concentration in the solution.
Table of Content
Aim
Theory
Apparatus Required
Procedure
Observation
Result
Precautions
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Aim
To determine the pH of different samples of NaOH solution using: (i) pH paper method and (ii) universal indicator solution method.
Theory
The alkalinity and acidity of a solution are determined by pH, which is a measurement of hydrogen ion concentration. In general, if a solution has a pH value of less than 7, it is an acidic solution, if it has a pH value greater than 7, it is a basic solution, and if it has a pH value equal to 7, it is a neutral solution.
Apparatus Required
Test tubes
Measuring cylinder
Dropper
pH paper
Universal indicator solution
Different concentrations of NaOH solution (0.1 M, 0.01 M, 0.001 M, 0.0001 M and 0.00001 M)
Procedure
i) pH paper Method
Add 2-3 drops of NaOH solution on pH paper with the help of a glass rod.
Observe the change of colour on the pH paper.
Take a look at the 'pH indicator chart' and compare the shade of colour formed with different colours.
Based on this information, record the pH of sodium hydroxide samples approximately in a table.
ii) Universal Indicator Solution
Take five clean and dry test tubes.
With the help of a measuring cylinder, pour 5ml of each solution into different test tubes.
Add 2-3 drops of ‘universal indicator solution’ to each test tube with the help of a dropper.
Observe the colour of each test tube and compare it with the different colour shades given in the "pH indicator chart".
Record the pH of the solution in the table after comparing the colour in each tube.
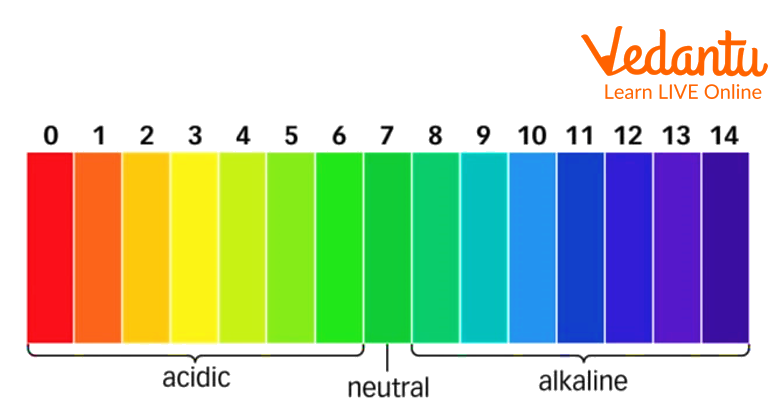
pH scale
Observation
To find out the pH of the sample, first we need to find out H3O+ ion concentration,
\[[O{H^ - }][{H_3}{O^ - }] = 1 \times {10^{ - 14}}\]
\[Or\,[{H_3}{O^ + }] = \dfrac{{1 \times {{10}^{ - 14}}}}{{[O{H^ - }]}}\]
\[pH = - \log [{H_3}{O^ + }]\]
Result
After finding the pH of the following samples, from the above experiment, we can conclude that the pH of the solution decreases with a decrease in concentration.
Precautions
Prepare the samples freshly before the experiment.
Wash droppers and glass rods before putting them into different samples.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What is the pH scale?
Ans: pH scale is a scale that determines whether a solution is neutral, basic or acidic by measuring its pH value.
2. Can you explain the difference between acids and bases?
Ans:
3. How do you measure pH?
Ans: pH of a solution can be determined by various methods. pH can be determined by the pH paper method, pH metre or by using a universal indicator solution.
4. What is a universal indicator solution?
Ans: Universal indicators are pH indicators made from solutions of several compounds that exhibit smooth colour changes over a wide range of pH values.
Viva Questions
1. When NaOH is added to water, what happens to its pH?
Ans: pH of water increases if NaOH is added.
2. What is the pH of 0.01 M NaOH?
Ans: pH of 0.01 M NaOH is 12.
3. What is an indicator solution?
Ans: An indicator is a weak acid or weak base that changes colour with a change in hydrogen ion concentration or pH.
4. What is the colour of the pH paper at neutral pH?
Ans: pH paper colour is green at neutral pH.
5. Which method gives accurate results to find pH?
Ans: pH metre gives accurate results to find pH.
6. Which ions are released by acids in a solution?
Ans: Hydrogen ions are released by acids in a solution.
7. What is the disadvantage of pH paper?
Ans: Accuracy is not adequate in the case of pH paper as compared to pH metre.
8. What are the main components of a universal indicator solution?
Ans: Thymol blue, methyl red, phenolphthalein, and bromothymol blue are the main components of a universal indicator solution.
9. What is the colour of pH paper if the solution has a pH of 14?
Ans: The colour of the pH paper is blue if the solution has a pH of 14.
10. What is the range of acidic pH?
Ans: Acidic pH ranges from 0 to 7.
Practical Based Questions
1. Which is not a component of the universal indicator solution?
A) Thymol blue
B) Methyl red
C) Phenolphthalein
D) safranin
Ans: D) safranin
2. What is the range of pH of the basic solution?
A) 0 to 7
B) 0 to 5
C) 7 to 14
D) 7
Ans: C) 7 to 14
3. Since the pH of NaOH solution is more than 7, it is ____.
A) acidic
B) Basic
C) Neutral
D) None of the above
Ans: B) Basic
4. Can you tell me what the pH of 0.01M NaOH is?
A) 12
B) 11
C) 10
D) 14
Ans: A) 12
5. What is the colour of the pH paper at pH zero?
A) Orange
B) Blue
C) Green
D) Red
Ans: D) Red
6. What happens to the pH of an acidic solution on dilution?
A) pH increases
B) pH decreases
C) pH does not change
D) None of the above
Ans: A) pH increases
7. Which among the following is more efficient?
A) pH paper
B) Universal indicator solution
C) pH metre
D) All the above
Ans: C) pH metre
8. What is the value of neutral pH?
A) 7
B) 9
C) 3
D) 4
Ans: A) 7
9. pH of 0.1M NaOH solution is ____.
A) 11
B) 12
C) 13
D) 14
Ans: C) 13
10. The negative logarithm of OH- ion concentration is known as ___.
A) pH
B) pOH
C) Both A and B
D) None of the above
Ans: B) pOH
Conclusion
There are three types of chemicals used in laboratories: basic, acidic and neutral. Their characteristics are determined by the ions they release. Add 2-3 drops of NaOH solution on pH paper with the help of a glass rod. Observe the change of colour on the pH paper. Take a look at the 'pH indicator chart' and compare the shade of colour formed with different colours. After finding the pH of the following samples, we can conclude that the pH of the solution decreases with a decrease in concentration.
FAQs on Class 11 Chemistry To Determine The Ph Of Various Samples Of Naoh Solution Experiment
1. What are the important steps to determine the pH of different samples of NaOH solution using pH paper for the Class 11 Chemistry exam (2025-26)?
To determine the pH of a given sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution, follow these important steps:
Take a clean, dry test tube and add the given NaOH sample.
Use a clean dropper to place a drop of the solution onto a strip of pH paper.
Observe the colour change on the pH paper immediately.
Compare the developed colour with the shades on the standard pH colour chart to find the corresponding pH value.
Record the observation. Repeat the process for samples with different concentrations, ensuring you use fresh apparatus each time.
2. What colour change is expected on a pH paper when testing a dilute sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution, and what does this indicate about its pH value?
When a drop of dilute NaOH solution is placed on pH paper, the paper will turn a shade of blue or violet. This colour change indicates that the solution is alkaline (basic). By comparing the specific shade to a standard pH chart, the pH value is typically found to be in the range of 11 to 13, confirming it is a strong base.
3. For a Class 11 exam, a student states that the pH scale only runs from 0 to 14. Is it possible for a strong base like NaOH to have a pH value greater than 14? Explain why.
Yes, it is conceptually possible for a solution to have a pH greater than 14. The 0-14 scale is a common convention that applies to standard aqueous solutions at 25°C. However, for a highly concentrated strong base, such as 10 M NaOH, the hydroxide ion concentration [OH⁻] is 10 M. The pOH = -log[OH⁻] = -log(10) = -1. Since pH + pOH = 14, the pH would be calculated as pH = 14 - (-1) = 15. This is considered a high-order thinking skills (HOTS) concept.
4. How would the pH value of a 0.1 M NaOH solution compare to a 0.001 M NaOH solution? Explain the expected observation and the underlying principle.
The 0.1 M NaOH solution will have a higher pH than the 0.001 M NaOH solution. The underlying principle is that NaOH is a strong base that dissociates completely.
For 0.1 M NaOH, [OH⁻] = 0.1 M, pOH = 1, and pH = 13.
For 0.001 M NaOH, [OH⁻] = 0.001 M, pOH = 3, and pH = 11.
A higher concentration of a strong base leads to a higher concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻), which results in a lower pOH and consequently, a higher pH value, indicating stronger alkalinity.
5. From an exam perspective, what are two important real-world applications of measuring pH that you should know for Class 11 Chemistry?
Two important applications relevant for exams are:
Agriculture: Farmers test soil pH to determine its acidity or alkalinity. Different crops have specific pH requirements for optimal growth, and the soil is treated with chemicals like lime (basic) or gypsum (acidic) to adjust the pH accordingly.
Human Physiology: The pH of human blood is strictly maintained at around 7.35-7.45. Any significant deviation from this range, a condition known as acidosis or alkalosis, can impair metabolic processes and indicates serious health problems.
6. Why is it an important precaution to use a clean, dry dropper for each different sample of NaOH when measuring its pH? What error could occur otherwise?
Using a clean, dry dropper for each sample is crucial to prevent cross-contamination, which can lead to significant errors in measurement. If a dropper used for a more concentrated NaOH solution is used for a dilute one without cleaning, it will transfer excess NaOH, causing the measured pH of the dilute solution to be inaccurately high. This is a critical procedural point in practical examinations.
7. For determining the specific pH of an NaOH solution, why is a universal indicator or pH paper a more important tool than simple red litmus paper?
While red litmus paper can confirm that NaOH is a base (it will turn blue), it acts only as a qualitative indicator and cannot determine the strength of the base. A universal indicator or pH paper is more useful because it contains a mixture of indicators that produce a spectrum of colours corresponding to different pH values. This allows for a quantitative estimation of the pH (e.g., pH 11, 12, or 13), providing crucial information about the concentration and strength of the NaOH solution.
























